Fill Out Your Cms 802 Form
The CMS 802 form plays a vital role in ensuring quality care for residents in healthcare facilities. It serves as a comprehensive matrix that allows providers to document critical information concerning newly admitted residents within the last 30 days, as well as all other residents currently residing in the facility. By carefully filling out the resident's name, room number, and relevant categories, facilities can efficiently assess the healthcare needs of their population. The matrix addresses key aspects such as the presence of Alzheimer’s disease or dementia, the administration of various medications, and the management of conditions like pressure ulcers and dehydration. It also includes important data on physical restraints, falls, and other health issues that may affect the well-being of residents. Verification of all entries by knowledgeable staff is mandated to ensure the accuracy of the information recorded. Properly documenting these details allows for an effective evaluation of residents' conditions, paving the way for improved care plans and timely interventions.
Cms 802 Example

DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES |
|
CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES |
OMB Exempt |
MATRIX INSTRUCTIONS FOR PROVIDERS
The Matrix is used to identify pertinent care categories for: 1) newly admitted residents in the last 30 days who are still residing in the facility, and 2) all other residents. The facility completes the resident name, resident room number and columns
All information entered into the form should be verified by a staff member knowledgeable about the resident population. Information must be reflective of all residents as of the day of survey.
Unless stated otherwise, for each resident mark an X for all columns that are pertinent.
1.Residents Admitted within the Past 30 days: Resident(s) who were admitted to the facility within the past 30 days and currently residing in the facility.
2.Alzheimer’s/Dementia: Resident(s) who have a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease or dementia of any type.
3.MD, ID or RC & No PASARR Level II: Resident(s) who have a serious mental disorder, intellectual disability or a related condition but does not have a PASARR level II evaluation and determination.
4.Medications: Resident(s) receiving any of the
following medications: (I) = Insulin, (AC) = Anticoagulant (e.g. Direct thrombin inhibitors and low weight molecular weight heparin [e.g., Pradaxa, Xarelto, Coumadin, Fragmin]. Do not include Aspirin or Plavix), (ABX) = Antibiotic, (D) = Diuretic,
(O) = Opioid, (H) = Hypnotic, (AA) = Antianxiety, (AP) = Antipsychotic, (AD) Antidepressant, (RESP) = Respiratory (e.g., inhaler, nebulizer).
NOTE: Record meds according to a drug’s pharmacological classification, not how it is used.
5.Pressure Ulcer(s) (any stage): Resident(s) who have a pressure ulcer at any stage, including suspected deep tissue injury (mark the highest stage: I, II, III, IV, U for unstageable, S for sDTI) and whether the pressure ulcer is facility acquired (FA).
6.Worsened Pressure Ulcer(s) at any stage: Resident(s) with a pressure ulcer at any stage that have worsened.
7.Excessive Weight Loss without Prescribed Weight Loss program: Resident(s) with an unintended (not on a prescribed weight loss program) weight loss > 5% within the past 30 days or >10% within the past 180 days. Exclude residents receiving hospice services.
8.Tube Feeding: Resident(s) who receive enteral (E) or parenteral (P) feedings.
9.Dehydration: Resident(s) identified with actual hydration concerns takes in less than the recommended 1,500 ml of fluids daily (water or liquids in beverages and water in foods with high fluid content, such as gelatin and soups).
10.Physical Restraints: Resident(s) who have a physical restraint in use. A restraint is defined as the use of any manual method, physical or mechanicaldevice, material or equipment attached or adjacent to the resident’s body that the individual cannot remove easily which restricts freedom of movement or normal access to one’s body (e.g., bed rail, trunk restraint, limb restraint, chair prevents rising, mitts on hands, confined to room, etc.). Do not code wander guards as a restraint.
11.Fall(s) (F) or Fall(s) with Injury (FI) or Major Injury (FMI): Resident(s) who have fallen in the facility in the past 90 days or since admission and have incurred an injury or not. A major injury includes bone fractures, joint dislocation, closed head injury with altered consciousness, subdural hematoma.
12.Indwelling Urinary Catheter: Resident(s) with an indwelling catheter (including suprapubic catheter and nephrostomy tube).
13.Dialysis: Resident(s) who are receiving (H) hemodialysis or (P) peritoneal dialysis either within the facility (F) or offsite (O).
14.Hospice: Resident(s) who have elected or are currently receiving hospice services.
15.End of Life/Comfort Care/Palliative Care: Resident(s) who are receiving end of life or palliative care (not including Hospice).
16.Tracheostomy: Resident(s) who have a tracheostomy.
17.Ventilator: Resident(s) who are receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
18.
19.Intravenous therapy: Resident(s) who are receiving intravenous therapy through a central line, peripherally inserted central catheter, or other intravenous catheter.
20.Infections: Resident(s) who has a communicable disease or infection (e.g.,
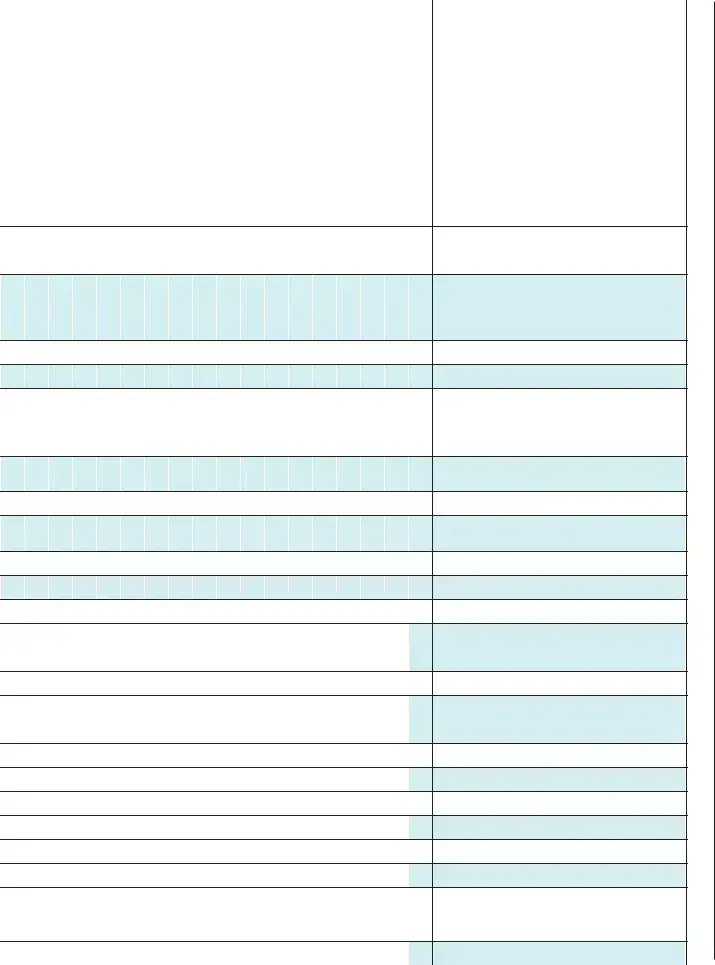
Resident |
|
11/2020 |
Name |
) |
|
|
Resident Room Number |
|
1 |
Date of Admission if Admitted within the |
|
Past 30 Days |
||
|

















 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
Alzheimer’s / Dementia
MD, ID or RC & No PASARR Level II
Medications: Insulin (I), Anticoagulant (AC), Antibiotic (ABX), Diuretic (D), Opioid (O), Hypnotic (H), Antianxiety (AA), Antipsychotic (AP), Antidepressant (AD), Respiratory (RESP)
Pressure Ulcer(s) (highest stage I, II, III, IV, U, S), Facility Acquired (FA)
Worsened Pressure Ulcer(s) (any stage)
Excessive Weight Loss
Without Prescribed Weight Loss Program
Tube Feeding: Enteral (E) or Parenteral (P)
Dehydration
Physical Restraints
Fall (F), Fall with Injury (FI), or
Fall w/Major Injury (FMI)
Indwelling Catheter
Dialysis: Peritoneal (P), Hemo (H), in facility (F) or offsite (O)
Hospice
End of Life Care / Comfort Care / Palliative Care
Tracheostomy
Ventilator
Intravenous therapy
Infections (M, WI, P, TB, VH, C, UTI, SEP, SCA, GI, COVID, O - describe)
MATRIX FOR PROVIDERS
CENTERS FOR |
DEPARTMENT |
MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES |
OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES |
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of the Form | The CMS-802 form is used to track and identify pertinent care categories for residents in a healthcare facility. |
| Resident Categories | It addresses newly admitted residents in the last 30 days and includes all other residents at the facility. |
| Verification Requirement | All information entered must be verified by a staff member knowledgeable about the resident population. |
| Pressure Ulcer Documentation | The form specifies how to record pressure ulcers, including stages and whether they are facility-acquired. |
| Weight Loss Criteria | It identifies residents with excessive weight loss not on a prescribed weight loss program, measuring losses greater than 5% in the past 30 days. |
| Medication Classification | Medications are recorded according to their pharmacological classifications, including insulin and anticoagulants. |
| Required Data Fields | Key fields include resident's name, room number, date of admission (if applicable), and various health conditions. |
| Fall Incident Tracking | Residents who have fallen and suffered injuries must be documented, along with details of the injuries. |
| State-Specific Laws | Each state may have additional governing laws requiring specific documentation related to resident care and safety. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Cms 802
Completing the CMS 802 form is an important task that requires careful attention to detail. This form collects critical information about resident care categories, and it must accurately reflect the status of all residents as of the survey date. Following these steps will help ensure the form is filled out correctly and thoroughly.
- Begin by locating the CMS 802 form. Ensure you have the most recent version, dated 11/2020.
- At the top of the form, write the name of the resident in the designated area.
- Next to the resident’s name, enter the resident’s room number.
- If the resident was admitted within the past 30 days, record the date of admission.
- For each resident, carefully review the categories from 1 to 20 on the form.
- Using a pen, mark an "X" in the appropriate columns corresponding to the resident's care categories. Make sure to only check those that are pertinent to the current status of the resident.
- Consult with a knowledgeable staff member, if necessary, to verify the accuracy of the information provided.
- Once all columns have been filled out, double-check the form for completeness and accuracy.
- Ensure that all entries accurately reflect the status of the resident population on the day of the survey.
- Finally, submit the completed form to the designated authority as required.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the CMS 802 form used for?
The CMS 802 form is utilized by healthcare facilities to document and identify important care categories for residents. This includes newly admitted residents who have been in the facility for the past 30 days, as well as all other residents. The information captured on the form helps ensure that each resident's care needs are properly recognized and addressed during surveys.
Who is responsible for completing the CMS 802 form?
Staff members who are knowledgeable about the resident population are responsible for completing the CMS 802 form. It is essential that the information entered reflects an accurate and current understanding of residents' health and care needs as of the survey date.
What types of information are documented on the CMS 802 form?
The CMS 802 form includes various categories, such as whether residents have specific diagnoses (e.g., Alzheimer’s, dementia), are on particular medications, or have conditions like pressure ulcers or excessive weight loss. Each resident’s name and room number are also documented, alongside pertinent categories categorized by checkboxes marked with an "X."
How are medications recorded on the CMS 802 form?
Medications are recorded based on their pharmacological classifications rather than how they are administered. Categories include insulin, anticoagulants, antibiotics, opioids, and others. This requires careful verification to ensure accurate documentation of each resident's medication regimen.
What should be done if a resident has a pressure ulcer?
If a resident has a pressure ulcer, the CMS 802 form must document the highest stage of the ulcer (I, II, III, IV, U for unstageable, or S for suspected deep tissue injury). Additionally, the form identifies whether the ulcer was acquired in the facility.
Are there any exemptions for residents under hospice care when filling out the CMS 802 form?
Yes, residents receiving hospice services are excluded from certain data entries, particularly those related to unintentional weight loss. Facilities should focus on the care aspects relevant to hospice care when completing the form for these residents.
Common mistakes
Filling out the CMS 802 form can be straightforward, but there are common mistakes that people make. One common error occurs when the resident's name and room number are not recorded accurately. It's crucial to ensure this basic information is correct as it serves as the foundation of the form. If the details are incorrect, it can lead to confusion and potential issues in care and reporting.
Another frequent mistake is not marking the correct indicators in columns 1 to 20. Each column corresponds to specific conditions or care categories, and it is vital to assess each resident thoroughly before marking an 'X'. Failure to do this can result in incomplete data, which may affect the quality of care provided to the resident.
Overlooking the medication categories is also a significant issue. Many individuals may mistakenly categorize medications based on how they are used rather than adhering to their pharmacological classification. This error can compromise the accuracy of medication records, which are essential for ensuring residents receive appropriate care and treatment.
Inconsistency in documenting pressure ulcers can lead to further problems. Care providers might either underreport or overreport the stages of pressure ulcers present. It is essential to accurately reflect the highest stage of any pressure ulcer present. This ensures that residents receive the necessary care and interventions based on their actual needs.
Additionally, people often forget to review the entire form with a knowledgeable staff member before submission. Verification is a key step that should not be skipped. Having an experienced person check the details can catch any errors that might have been missed during the initial completion of the form.
Finally, neglecting to update the CMS 802 form can lead to outdated and misleading information. The form must reflect the current status of all residents at the time of the survey. Failing to maintain updated records can impede effective care planning and quality assurance efforts.
Documents used along the form
The CMS-802 form is a crucial document used by healthcare providers to capture essential information about residents within a care facility. Along with this form, several other documents often facilitate effective resident assessment and care planning. Each of these documents serves a specific purpose, ensuring that the needs and medical histories of residents are addressed comprehensively.
- CMS 671 (Long-Term Care Facility Resident Assessment): This form helps gather detailed information about a resident’s physical and mental health, preferences, and daily activities to develop personalized care plans.
- CMS 1500 (Health Insurance Claim Form): Used for billing purposes, this form provides information about services provided to residents, ensuring healthcare providers get reimbursed appropriately.
- CMS 683 (Comprehensive Care Plan): This document outlines the strategies and approaches for addressing the specific needs and goals of each resident, formulated based on assessments from various sources.
- Resident Agreement: This agreement details the terms of admission, outlining the rights and responsibilities of both the resident and the facility regarding care, services, and charges.
- Incident Report Form: Used to document any incidents affecting a resident’s care, including falls or medication errors. It helps ensure safety and informs necessary changes in care protocols.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): This document tracks the medications administered to residents, ensuring that they receive the correct dosages at the right times.
- Assessment Tool for Patient Safety Protocols: This tool assesses adherence to safety measures within the facility, helping to identify gaps and areas for improvement in resident safety.
- Transfer Record: This document is essential for residents moving from one care level to another, ensuring continuity of care by communicating critical health information.
- Advance Directives: These are legal documents that enable residents to outline their preferences for medical treatment, ensuring that their wishes are respected in critical situations.
- Family Communication Log: This log maintains records of communication with family members about resident care, ensuring transparency and involvement of loved ones in care decisions.
These documents work together with the CMS-802 form to create a comprehensive care plan for residents. Each form plays a vital role in promoting the wellbeing, safety, and dignity of individuals in long-term care facilities.
Similar forms
CMS-674 - Minimum Data Set (MDS): Like the CMS 802 form, the MDS collects detailed information about the health status and needs of residents in skilled nursing facilities. It covers a broad range of care categories and is essential for care planning and reimbursement.
CMS-1500 - Health Insurance Claim Form: This form is essential for healthcare providers to bill Medicare and Medicaid. Similar to CMS 802, it requires accurate information about patients and the services provided, ensuring proper reimbursement.
CMS-8571 - Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) Quality Reporting Program: This form is used by ASCs to report on quality measures. Its purpose aligns with CMS 802 in evaluating patient outcomes and quality of care in a healthcare setting.
CMS-416 - Medicaid Annual Report: This form tracks the performance of state Medicaid programs, similar to how the CMS 802 assesses residents' needs. Both facilitate compliance with federal regulations and quality standards.
CMS-1450 - UB-04 Claim Form: Healthcare facilities use this form to bill Medicare for inpatient and outpatient services. The collection of resident data in CMS 802 mirrors the information gathering required in UB-04 for accurate billing.
CMS-1930 - Nursing Facility Worksheet: This is a tool for skilled nursing facilities to assess quality measures. Much like the CMS 802, it focuses on relevant parameters of resident care and helps with compliance during surveys.
CMS-2728 - End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Medical Evidence Report: This form collects information about patients beginning dialysis treatment. The thorough documentation process is comparable to the data collection in the CMS 802.
CMS-671 - Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Quality Reporting Program: This form reports quality care data, much like the CMS 802's role in evaluating resident care quality and compliance for nursing facilities.
CMS-855 - Medicare Enrollment Application: This application is used by healthcare providers to enroll in Medicare. It requires meticulous information collection, akin to the specifics gathered through the CMS 802 form.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing the CMS 802 form, attention to detail is crucial. Here’s a guideline of what you should and shouldn’t do:
- Do verify all information with a knowledgeable staff member.
- Don’t leave any columns blank unless specified for surveyor use.
- Do mark an "X" for all relevant columns for each resident.
- Don’t include medications that are not specified in the provided categories.
- Do record residents’ names and room numbers accurately.
- Don’t forget to note if a pressure ulcer is facility acquired.
- Do complete the form reflecting the status as of the day of the survey.
- Don’t confuse any resident’s actual hydration status when assessing dehydration.
- Do ensure the data consists of all residents, including those admitted in the last 30 days.
Misconceptions
1. The CMS 802 form is only for new residents. This is incorrect. While it does include information for residents admitted within the last 30 days, it also collects data on all other residents in the facility.
2. Only medical staff can complete the CMS 802 form. Not true. Any staff member who is knowledgeable about the resident population can verify and complete the information on the form.
3. The CMS 802 form is not important for resident care. This misconception overlooks the form's role in identifying care needs. It is crucial for assessing the health status of residents and ensuring they receive appropriate care.
4. The form only tracks pressure ulcers. This is misleading. The CMS 802 form tracks a variety of health conditions, including dementia, medication usage, falls, and hydration issues, among others.
5. The CMS 802 form is only used during official surveys. While it is part of the survey process, the information gathered can and should be used regularly to monitor and improve the quality of care provided to residents.
Key takeaways
Filling out the CMS 802 form accurately is crucial for proper resident care assessment. Here are some key takeaways to ensure effective use of the form:
- Verify Information: Before entering any data, ensure that a knowledgeable staff member reviews all resident information. Accuracy is essential for correct categorization.
- Mark Pertinent Categories: Use an "X" to indicate all relevant categories for each resident. This marks residents accurately in essential care areas, which aids in timely interventions.
- Review Classification of Medications: Record medications according to their pharmacological classifications instead of their usage. Be precise; this helps in assessing medication management efficiently.
- Understand Care Categories: Familiarize yourself with the various care categories that the form addresses. This keeps you prepared to identify all necessary conditions affecting the residents.
Browse Other Templates
Couples' Registry Form,Wedding Essentials Registry,Nuptial Wish List,Bridal Registry Sheet,Happily Ever After Registry,Love's Gift List,Ceremony Registry Form,Evermore Registry,Union Registry Document,Wedding Gift Selection Form - Pigeon Toe is dedicated to making your wedding dreams a reality.
Universal Claim Form Pharmacy - Accurate completion of this form supports consistent revenue for healthcare providers.
How to Make an Ig Complaint Army - The form documents requests for action and supports the procedure of military accountability.
