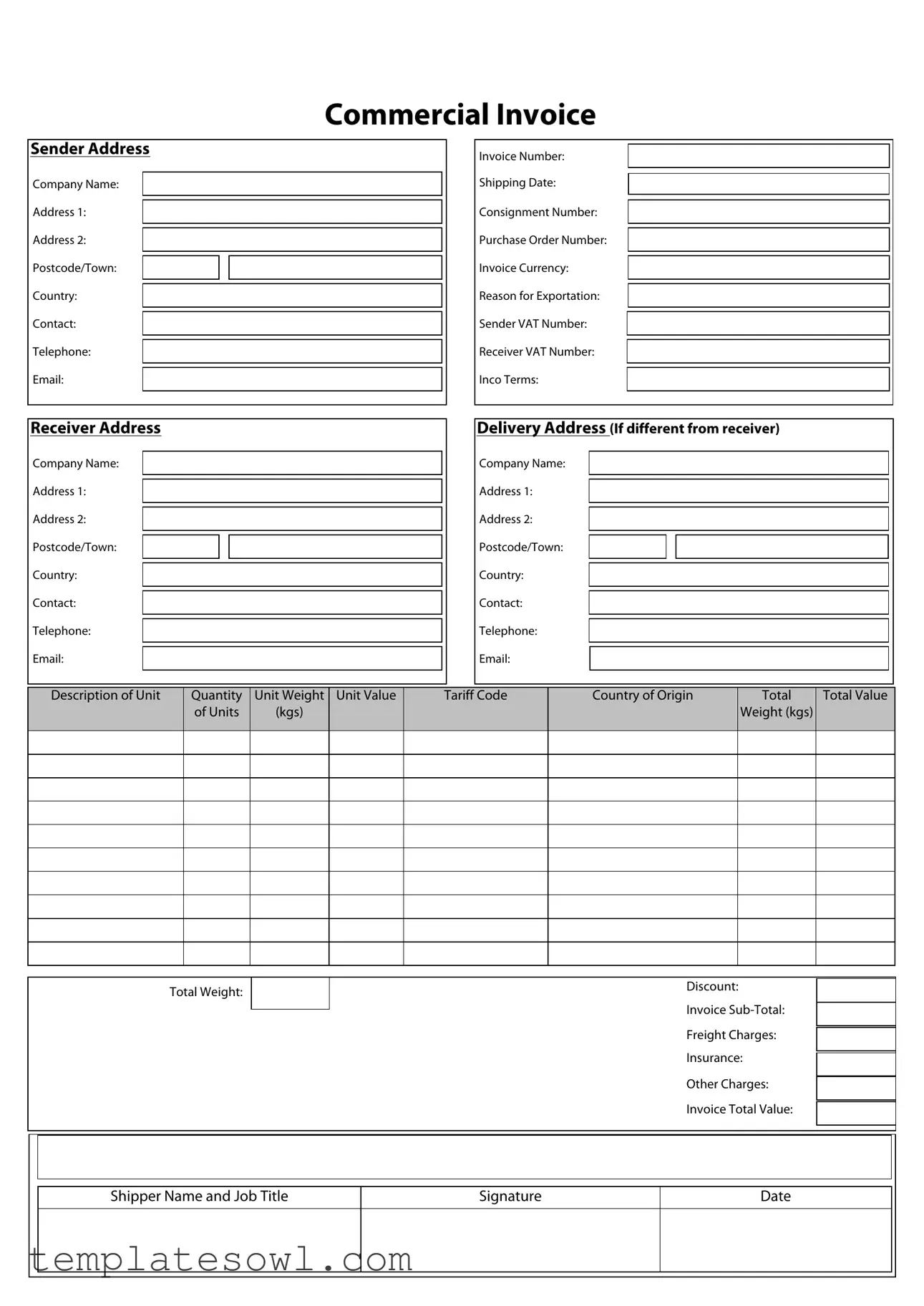
Fill Out Your Commercial Invoice Form
The Commercial Invoice form serves as a crucial document in international trade, outlining the transaction details between the sender and receiver of goods. This form typically includes important information regarding both parties, such as their names, addresses, and contact details, ensuring effective communication and logistics. Key identifiers like the invoice number, shipping date, and purchase order number help track the transaction throughout the shipping process. Additionally, the form contains financial specifics, such as unit prices, total value, and any applicable discounts or charges, providing transparency in the financial exchange. The sender's and receiver's VAT numbers are also needed for tax purposes, while Inco terms clarify the responsibilities of each party in terms of shipping and delivery. It is important to accurately describe each unit, indicating quantity, weight, and origin, as this information can influence customs processes. Lastly, both a signature and date are required to validate the document, which can expedite the clearance process through customs. Understanding the structure and components of a Commercial Invoice can help streamline international shipping and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Commercial Invoice Example
Commercial Invoice
Sender Address
Company Name:
Address 1:
Address 2:
Postcode/Town:
Country:
Contact:
Telephone:
Email:
Invoice Number:
Shipping Date:
Consignment Number:
Purchase Order Number:
Invoice Currency:
Reason for Exportation:
Sender VAT Number:
Receiver VAT Number:
Inco Terms:
Receiver Address
Company Name:
Address 1:
Address 2:
Postcode/Town:
Country:
Contact:
Telephone:
Email:
Delivery Address (If different from receiver)
Company Name:
Address 1:
Address 2:
Postcode/Town:
Country:
Contact:
Telephone:
Email:
Description of Unit
Quantity
of Units
Unit Weight Unit Value (kgs)
Tariff Code
Country of Origin
Total
Weight (kgs)
Total Value
Total Weight:
Discount:
Invoice
Freight Charges:
Insurance:
Other Charges:
Invoice Total Value:
Shipper Name and Job Title
Signature
Date
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Fact Details |
|---|---|
| Sender Information | The Commercial Invoice requires the sender's details, including company name and address, to ensure proper identification of the entity issuing the invoice. |
| Receiver Information | Complete information about the receiver is essential. This includes the receiver's name, address, and contact information to facilitate smooth delivery. |
| Invoice Number | An invoice number must be assigned to track shipments and payments effectively. This is linked to accounting and export documentation. |
| Shipping Date | The date of shipping must be clearly stated. This is crucial for determining delivery timelines and in customs declarations. |
| Export Purpose | Filing the reason for exportation is necessary for customs compliance. Common reasons include sales, returns, or samples. |
| Governing Laws | The completion and use of the Commercial Invoice must adhere to federal export laws in the United States, particularly those outlined by the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) and the Customs and Border Protection (CBP). |
Guidelines on Utilizing Commercial Invoice
Completing a Commercial Invoice form requires care and attention to detail. This document is crucial for international shipping and must be filled out accurately to prevent delays. Follow these steps to ensure you provide all necessary information clearly and correctly.
- Sender Address: Fill in your company name, address details (including postcode, town, and country), contact person, telephone number, and email address.
- Invoice Details: Enter the invoice number, shipping date, consignment number, and purchase order number.
- Currency: Specify the invoice currency you are using.
- Exportation Reason: State the reason for exportation.
- VAT Numbers: Include your VAT number and the receiver's VAT number if applicable.
- Inco Terms: Indicate the Incoterms that govern the transaction.
- Receiver Address: Provide the receiver's company name, address, contact details, and telephone number, similar to the sender section.
- Delivery Address: If different from the receiver, enter the delivery address details as well.
- Description of Goods: For each item, include a clear description, quantity, unit weight, unit value, tariff code, and country of origin.
- Total Weight and Value: Calculate and fill in total weight and total value fields for all items listed.
- Discount and Charges: Include any discounts, invoice subtotal, freight charges, insurance, and other charges as applicable.
- Invoice Total Value: Calculate and enter the final total value of the invoice.
- Shipper Details: Finally, sign the invoice, enter your name, job title, and date of signing.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is a Commercial Invoice used for?
A Commercial Invoice serves as an important document for international shipping. It outlines the details of the transaction between the sender and receiver. This form includes information such as the sender's and receiver's addresses, items being shipped, and the total value of the shipment. Customs authorities require this document to determine the appropriate duties and taxes, ensuring smooth customs clearance for the shipment.
What information is needed when filling out a Commercial Invoice?
When completing a Commercial Invoice, accurate information is crucial. Required details include the sender's and receiver's addresses, contact information, and VAT numbers. Additionally, you must list each item being shipped by describing it, providing the quantity, unit weight, unit value, and tariff code. Other financial details include the total weight, invoice sub-total, freight charges, and insurance, as well as the invoice's total value. Each piece of information aids in facilitating the shipment through customs.
How does the Invoice Currency influence international shipping?
The Invoice Currency specified on the Commercial Invoice indicates the monetary currency used for the transaction. This matters for both the sender and receiver, as it influences how costs are calculated and paid during the shipment process. The currency can also affect how customs duties and taxes are assessed by customs authorities. It is essential to align this currency with the expectations of involved parties to avoid any confusion or complications.
What should be done if there is an error on the Commercial Invoice?
If an error is discovered on the Commercial Invoice after submission, prompt action is necessary. Contact the shipping service and inform them of the mistake. You'll likely need to provide a corrected invoice and possibly additional documentation to clarify the changes. Addressing errors swiftly helps mitigate potential delays in shipping and customs processes, ensuring that the shipment continues smoothly.
Common mistakes
Filling out a Commercial Invoice form accurately is crucial for international shipping. One common mistake occurs when individuals neglect to include all necessary details for the sender's address. This section requires complete information, such as the company name, address, and contact information. Missing even a single component, like the telephone number, can lead to delays or returned shipments.
Another frequent oversight is in the invoice number section. Each Commercial Invoice should have a unique invoice number. This helps in tracking the shipment and managing records efficiently. Failing to include this number, or using a duplicate, can create confusion and impact logistics.
People often miscalculate the total weight and total value on the invoice. Thoroughly checking these numbers is essential. Any discrepancies can result in fines or customs issues. It's important to ensure that the individual weights and values of each unit add up correctly to reflect accurate totals.
The reason for exportation is another crucial detail that is often overlooked. Buyers and sellers must provide a clear and accurate reason. Leaving this section blank or providing vague information can lead to customs complications, delaying the shipping process.
Moreover, neglecting to provide accurate Inco terms can also pose a problem. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding costs and risks during transport. Incorrect Inco terms can lead to misunderstandings and potentially costly disputes over shipping responsibilities.
Lastly, individuals sometimes forget to include all relevant charges, such as freight charges and insurance fees. These elements should be clearly listed in the invoice. Incomplete information can result in an incorrect invoice total, complicating payment processes and potentially leading to rejected shipments.
Documents used along the form
In international trade, the Commercial Invoice serves as a crucial document, detailing the transaction between a seller and a buyer. However, several other forms and documents may accompany it to ensure compliance with regulations and facilitate the shipping process. Below are some of the most commonly used documents alongside the Commercial Invoice.
- Bill of Lading: This document acts as a receipt for the goods being shipped. It includes details of the shipment, such as the destination, shipper, and consignee. Additionally, the Bill of Lading serves as a contract between the carrier and the shipper, outlining the obligations of both parties.
- Packing List: The Packing List complements the Commercial Invoice by providing a detailed inventory of the items included in the shipment. It typically includes descriptions of each product, their quantities, and dimensions. This list assists in customs clearance and inventory management.
- Certificate of Origin: This document certifies the country in which the goods were produced. It is often required by customs authorities to determine the origin of the goods, which can affect tariff rates. The Certificate of Origin may need to be signed by a chamber of commerce or a government authority.
- Export License: Depending on the type of goods being exported, an Export License might be necessary. This document is issued by a government agency and grants permission to export specific items. It is vital for ensuring that the goods comply with national export regulations.
Utilizing these documents alongside the Commercial Invoice is essential for smooth international transactions. Providing accurate and complete documentation helps facilitate customs clearance, minimizes delays, and ensures compliance with legal requirements. Importers and exporters should remain vigilant about these requirements to avoid potential issues.
Similar forms
The Commercial Invoice form plays a critical role in international trade, offering vital information about goods being shipped. Several other documents serve similar purposes, each fulfilling specific needs in the shipping and customs processes. Here’s a breakdown of eight documents that share similarities with the Commercial Invoice:
- Pro Forma Invoice: This document provides an estimate before the sale transaction occurs. It outlines the details of the goods, like the description and quantities, similar to the Commercial Invoice but is often used for customs purposes rather than for final accounting.
- Packing List: While the Packing List details what is actually packed in a shipment, it can complement a Commercial Invoice by ensuring the items listed on the invoice match the physical goods being shipped.
- Bill of Lading: This document serves as a receipt for the shipping goods and also acts as a contract between the shipper and carrier. Like the Commercial Invoice, it includes details about the sender and receiver, though its primary function is related to transportation.
- Customs Declaration: Required for international shipments, this document provides customs authorities with detailed information about the nature and value of the goods, similar in purpose to the Commercial Invoice in facilitating customs clearance.
- Export License: This is a government-issued document that controls the export of certain goods. While it differs in scope, it shares the purpose of ensuring compliance, just as the Commercial Invoice supports regulatory fairness.
- Certificate of Origin: This document certifies the country where the goods were manufactured and may be necessary for customs. It parallels the Commercial Invoice in that both help authorities assess tariffs and trade agreements.
- Insurance Certificate: This document proves that the goods are insured during transit. It complements the Commercial Invoice by providing additional assurances in case of damage or loss, contributing to a smoother transaction process.
- Delivery Order: Issued by a carrier, this document authorizes the release of goods to the consignee. Similar to the Commercial Invoice, it contains details such as consignee information, helping facilitate the final stages of the shipment process.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out a Commercial Invoice form is crucial for clear communication during shipping. Here are some essential do's and don'ts to help you complete the form effectively.
- Do double-check the sender and receiver addresses for accuracy.
- Do ensure that all relevant invoice numbers and dates are included.
- Do clearly describe each unit with enough detail for customs purposes.
- Do list the currency in which the invoice is issued.
- Do include your VAT numbers if applicable.
- Don't leave any mandatory fields blank.
- Don't use vague descriptions for the items being shipped.
- Don't forget to include the total weight and value of the shipment.
- Don't overstate or understate item values or weights.
- Don't ignore the Inco Terms, as they clarify shipment responsibilities.
Following these guidelines will help ensure your Commercial Invoice is clear and complete, facilitating smoother processing and delivery of your items.
Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about the Commercial Invoice form can lead to unnecessary complications in international shipping. Here are ten common misconceptions and the clarifications for each:
- All shipments require a Commercial Invoice. In many cases, shipments valued below a certain threshold may not require a Commercial Invoice, depending on the destination country’s regulations.
- It is the same as a pro forma invoice. A Commercial Invoice is a definitive document for customs, while a pro forma invoice is more of a preliminary estimate that does not serve the same legal purpose.
- The sender's VAT number is optional. It is crucial for verification and processing. Including it can avoid delays during customs clearance.
- All items in the shipment must be individually listed. Only the items that are considered significant or are subject to duties need to be detailed; minor items can often be grouped.
- Commercial Invoices do not need to include shipping charges. Including all costs, such as freight and insurance, provides a clear total value that customs requires for processing.
- There is no need to specify the reason for exportation. This information helps customs officials understand the shipment’s purpose and can impact duty assessments.
- The invoice does not impact delivery times. Delays in processing a Commercial Invoice can lead to significant delays in delivery, so accuracy is essential.
- Using your own format is acceptable. While many companies create their own templates, it is important to ensure that all required information is clearly presented and complies with customs regulations.
- Once submitted, the information cannot be changed. If errors are discovered, it is possible to correct and resubmit, but prompt action is necessary to prevent further issues.
- Only businesses need to complete a Commercial Invoice. Individuals importing or exporting goods for personal use may also be required to complete this form, depending on the circumstances.
Understanding these misconceptions can pave the way for smoother international transactions and ensure compliance with customs requirements.
Key takeaways
When filling out a Commercial Invoice form, understanding the key components can help streamline the process and ensure compliance. Here are some important takeaways:
- Complete Sender and Receiver Information: Always provide detailed contact information for both the sender and receiver. This includes company names, addresses, and contact methods like telephone and email.
- Accurate Description of Goods: Clearly describe each item being shipped. Include the unit quantity, unit weight, unit value, and other specifics like the tariff code and country of origin.
- Invoicing Details: Be diligent in entering the invoice number, shipping date, purchase order number, and total values. This information is crucial for tracking and accounting purposes.
- Additional Charges: Don’t forget to include any freight charges, insurance costs, or other charges that may apply. These figures contribute to the invoice total and impact shipping logistics.
Utilizing these guidelines will enhance clarity and efficiency in the commercial invoice process.
Browse Other Templates
Remodeling Contract Example - Specifies that the homeowner agrees to indemnify the builder for any third-party claims regarding provided materials.
Alpha Kappa Alpha - Successful candidates are those who meet all outlined criteria.