Fill Out Your Da 1307 Form
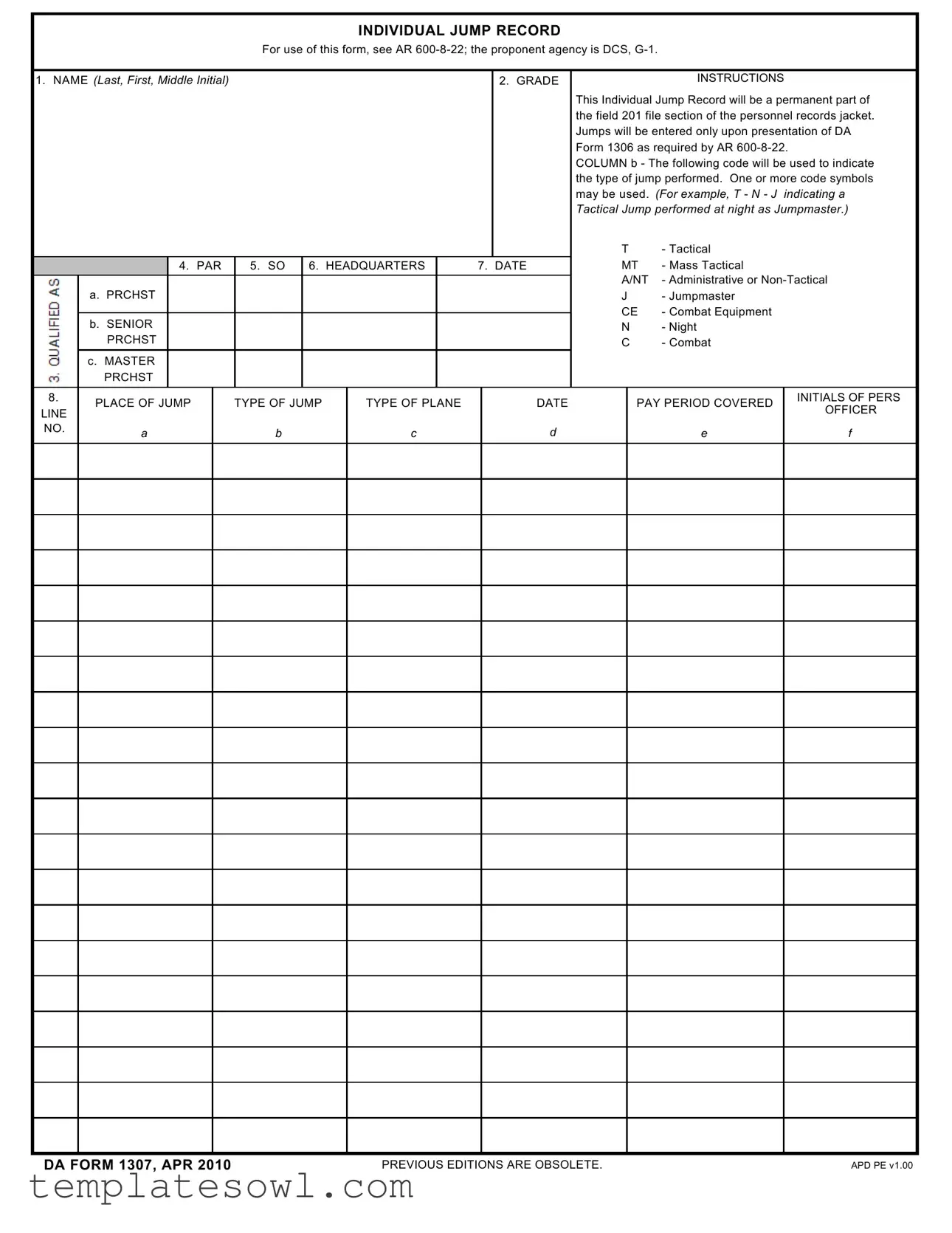
The DA 1307 form, known as the Individual Jump Record, plays a vital role in the documentation of parachuting activities for military personnel. As mandated by Army Regulation 600-8-22, this form serves as a permanent addition to an individual's field 201 file within the personnel records system. The form captures essential data, including the service member's name, grade, and critical jump details, which can include the type of jump performed and the aircraft used. For accurate recording, jumps are documented only when a DA Form 1306 is presented as required. Specific codes indicate the nature of each jump, allowing for a detailed understanding of the activity; these codes range from Tactical (T) to Night (N) jumps, and can even specify whether the individual acted as a Jumpmaster (J), illustrating the multifaceted roles that personnel may take on during jumps. Furthermore, the DA 1307 continuously underscores the importance of precise record-keeping in maintaining military readiness and supporting personnel evaluations. This article will delve deeper into the various components of the Da 1307, explore its significance within military operations, and discuss best practices for its completion and use.
Da 1307 Example

INDIVIDUAL JUMP RECORD
For use of this form, see AR
|
1. NAME (Last, First, Middle Initial) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. GRADE |
|
|
INSTRUCTIONS |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This Individual Jump Record will be a permanent part of |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the field 201 file section of the personnel records jacket. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jumps will be entered only upon presentation of DA |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form 1306 as required by AR |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COLUMN b - The following code will be used to indicate |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the type of jump performed. One or more code symbols |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
may be used. (For example, T - N - J |
indicating a |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tactical Jump performed at night as Jumpmaster.) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T |
- Tactical |
|
|
|
|
|
4. PAR |
5. SO |
6. HEADQUARTERS |
|
7. DATE |
MT |
- Mass Tactical |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A/NT |
- Administrative or |
||
|
|
a. PRCHST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J |
- Jumpmaster |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CE |
- Combat Equipment |
|
|
|
|
b. SENIOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
- Night |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
PRCHST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
- Combat |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
c. MASTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PRCHST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
PLACE OF JUMP |
|
TYPE OF JUMP |
TYPE OF PLANE |
|
|
DATE |
|
PAY PERIOD COVERED |
INITIALS OF PERS |
||||
|
LINE |
|
|
|
|
OFFICER |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NO. |
a |
|
b |
|
c |
|
|
d |
|
|
e |
f |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DA FORM 1307, APR 2010 |
PREVIOUS EDITIONS ARE OBSOLETE. |
APD PE v1.00 |
8. LINE NO.
PLACE OF JUMP
a
TYPE OF JUMP
b
TYPE OF PLANE
c
DATE
d
PAY PERIOD COVERED
e
INITIALS OF PERS
OFFICER
f
REVERSE OF DA FORM 1307, APR 2010 |
APD PE v1.00 |
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The DA 1307 form is designed to document individual jump records for military personnel. |
| Regulation | This form is governed by Army Regulation (AR) 600-8-22, which outlines personnel management procedures. |
| Permanent Record | The Individual Jump Record is a permanent part of a soldier's field 201 file and personnel records jacket. |
| Flying Codes | Specific code symbols indicate the type of jump performed (e.g., T for Tactical, N for Night). |
| Jump Types | Types of jumps include Tactical, Mass Tactical, Administrative or Non-Tactical, and more. |
| Record Requirements | Jumps can only be recorded upon presentation of the DA Form 1306, as specified in AR 600-8-22. |
| Line Officer Initials | Initials of the Personnel Line Officer are required to validate the jump entries. |
| Date Updates | The form must be updated regularly to reflect current jump data, including the date and pay period covered. |
| Version | As of April 2010, the DA 1307 is the current version; previous editions are no longer valid for use. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Da 1307
After obtaining your DA Form 1307, it's essential to fill it out completely and accurately. This form is part of your permanent personnel records and helps maintain an official record of your jump activities. Make sure you have all necessary information on hand before starting. Follow these steps to fill out the form correctly.
- Name: Enter your last name, first name, and middle initial in the designated space.
- Grade: Write your military grade in the appropriate box.
- Jump Types: Use the code symbols to indicate the type of jump performed. You can select multiple codes if necessary. Refer to the provided key for acceptable codes like T for Tactical, J for Jumpmaster, etc.
- Jump Details: Fill out the following sections regarding the jump:
- PAR: Indicate the parachute type.
- SO: Provide the specific jump type, follow the instructions provided.
- Headquarters: Write the name of your headquarters.
- Date: Enter the date of the jump.
- Place of Jump: Specify where the jump took place.
- Type of Plane: Mention the aircraft used for the jump.
- Date: Reiterate the jump date in the next section.
- Pay Period Covered: Indicate the pay period associated with the jump.
- Initials of Personnel Officer: Have the personnel officer initial the form.
- Line Number: Complete the line number associated with this entry, if applicable.
After filling out all sections, review the form carefully for any errors or missing information before submitting it with your DA Form 1306 as required. Keeping accurate records is essential for your military service documentation.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the DA Form 1307?
The DA Form 1307, also known as the Individual Jump Record, is a document used by military personnel to record jump activities. It serves as a permanent part of the personnel record and provides a detailed history of parachute jumps performed by an individual. This form must be completed according to the guidelines set forth in Army Regulation 600-8-22.
Who needs to fill out the DA Form 1307?
This form is typically filled out by military personnel who are involved in parachute operations. It is essential for soldiers who participate in jumps to ensure that their records are accurate and up-to-date, as the form is part of their official military documentation.
What information is required on the DA Form 1307?
The form requires basic personal information, such as the soldier's name and grade. Additionally, it includes columns for detailing the type of jumps performed, location, type of aircraft, and pay period covered. Soldiers must present the DA Form 1306 to have jumps entered on the DA Form 1307.
What types of jumps are recorded on the DA Form 1307?
The form accommodates various jump types, indicated by codes. For instance, 'T' stands for Tactical jumps, while 'N' indicates Night jumps. Mixed codes can also be recorded to show specific jump characteristics, such as combining Tactical and Night designations.
How does the DA Form 1307 relate to other forms?
The DA Form 1307 works in conjunction with the DA Form 1306, which is needed to authenticate the jumps recorded. Each entry on the DA Form 1307 relies on the information documented on the DA Form 1306, ensuring that the records are consistent and verified.
Is the DA Form 1307 a temporary or permanent document?
The DA Form 1307 is a permanent document. It becomes a part of a soldier's personnel file, which is maintained throughout their military career. This permanence underscores the importance of accurate entries, as it documents the soldier's parachuting experience and qualifications.
Are there any consequences for incomplete or incorrect entries on the DA Form 1307?
Yes, incorrect or incomplete entries can lead to issues with verifying jump experience, which may impact training, promotions, and other career opportunities. Accurate documentation is vital in the military, especially concerning qualifications for airborne operations.
Who is responsible for ensuring the accuracy of the DA Form 1307?
The individual soldier is primarily responsible for ensuring that the entries on the DA Form 1307 are correct. However, the Personnel Line Officer also plays a crucial role in reviewing and verifying the information entered before it is finalized in the records.
When should the DA Form 1307 be updated?
The DA Form 1307 should be updated promptly after each jump. Soldiers should ensure that their jump experiences are recorded as soon as possible following an event, ideally presenting their DA Form 1306 to have the jumps updated on their Individual Jump Record.
Where can soldiers obtain the DA Form 1307?
The DA Form 1307 can be obtained through military channels, typically from unit administrative offices or online military resources. It is advisable for soldiers to work closely with their personnel section to ensure they have the latest version of any form required for their records.
Common mistakes
Filling out the DA 1307 form may seem straightforward, but many individuals make common errors that can lead to complications in their military records. One significant mistake is failing to accurately complete the personal information section. This section requires the full name, including the last name, first name, and middle initial of the individual. Missing or incorrect information here can create confusion and lead to delays in processing the form.
Another frequent error occurs in the jump types coded in Column B. Participants often overlook the specific codes to indicate the type of jump performed. For instance, not distinguishing between Tactical (T) or Night (N) jumps might result in incorrect categorization. Each code serves a crucial purpose for record-keeping and can affect training and deployment assessments. Ensure you are familiar with the available codes before submission.
Moreover, many individuals neglect to confirm the confirmation of the jump with DA Form 1306. The DA 1307 is designed to be completed only after this verification is presented, as outlined in AR 600-8-22. Failing to attach or reference this documentation renders the jump record incomplete and potentially invalid. Always double-check that all necessary supporting forms are in order.
Lastly, ensuring the initials of the personnel officer are present is often an afterthought for many. This signature signifies that an authorized individual has reviewed the jump record. Without it, the form may not be considered complete and can lead to administrative issues. Taking a few extra moments to secure all required signatures and checks can save significant time and hassle down the road.
Documents used along the form
The DA Form 1307, known as the Individual Jump Record, is a crucial document for military personnel involved in airborne operations. It tracks the details of each jump made by a soldier and serves as a permanent record of their airborne training and experience. Alongside this form, several other documents are often needed for comprehensive record-keeping and operational clarity. Here is a list of related forms that typically accompany the DA 1307.
- DA Form 1306: This is the Jump Approval Record. It is required for documenting the completion of a jump before the DA Form 1307 can be filled out. This form certifies that the jump has been authorized and provides necessary details about the jump.
- DA Form 2-1: This form is the Personnel Qualification Record. It stores an individual's complete military record, including qualifications and training accomplishments, which is essential for leadership evaluations and career progression.
- DA Form 1059: The Academic Evaluation Report is used to assess the performance of soldiers in formal training courses. In conjunction with the DA Form 1307, it may highlight a soldier’s proficiency in airborne training.
- DA Form 4187: This is a Request for Personnel Action. It allows soldiers to request administrative changes, such as a change in airborne status, and serves as a formal request for updates that impact jump records.
- DA Form 3126: The Airborne Jump Record is a supplemental document that tracks airborne jumps in terms of airborne school requirements. It aids in maintaining a soldier’s operational readiness for airborne assignments.
- DD Form 214: This is the Certificate of Release or Discharge from Active Duty. It serves as official documentation of a service member’s time served and includes key information about training and qualifications received during service, including airborne training.
- AR 600-8-22: This regulation outlines the policies for military awards, which can include decorations for airborne operations. Understanding this regulation helps soldiers know how their airborne accomplishments might be recognized.
- AF Form 250: This form is the Air Force Jump Personnel Record. It is used by Air Force personnel to log jumps and is similar in function to the DA Form 1307, maintaining records of airborne missions.
These forms and documents work together to ensure that the airborne operations records are complete, accurate, and easily accessible. They play an essential role in maintaining a soldier's training history and operational capability, supporting personnel decisions and facilitating awards and promotions. Each document carries its own significance, providing a comprehensive view of a soldier's airborne experience.
Similar forms
The DA 1307 form, known as the Individual Jump Record, serves a specialized purpose within military personnel documentation. However, several other forms share similarities in their function or structure. Here are five examples:
- DA Form 1306 - This form is used to record parachuting training and jump qualifications. Like the DA 1307, it provides essential information about the individual’s jump achievements. The DA 1306 is typically required before data can be entered into the DA 1307.
- DA Form 4980-14 - This is the Army award certificate for service members qualifying for parachutist badges. Both forms document achievements related to airborne operations, with the DA 4980-14 serving as proof of recognition for jump qualifications reflected in the DA 1307.
- DA Form 1059 - This academic evaluation form is used for documenting the completion of military schools, including airborne training. Similar to the DA 1307, it records significant milestones in a service member's training and is also retained in the personnel records.
- DA Form 4100 - This form tracks individual training records. Both the DA 4100 and DA 1307 are vital for maintaining comprehensive personnel records, capturing essential training and experience that impacts a soldier’s career trajectory.
- DA Form 2-1 - Also known as the Personnel Qualification Record, this document compiles extensive data about a service member’s career. Similar to the DA 1307, it is a crucial part of a service member's official record, capturing various qualifications and experiences.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the DA 1307 form, there are important actions to take into account. Below is a list of dos and don'ts to ensure accurate completion.
- Do: Clearly print your name in the specified format: Last, First, Middle Initial.
- Do: Ensure that all jump information is recorded only after presenting DA Form 1306.
- Do: Use the proper jump code symbols that accurately reflect the type of jump performed.
- Do: Double-check the date and place of jump for accuracy.
- Don't: Leave any fields blank; incomplete entries may lead to issues in record-keeping.
- Don't: Forget to include your initials as the Personnel Line Officer in the designated section.
Misconceptions
Understanding the DA Form 1307, or Individual Jump Record, is essential for military personnel involved in airborne operations. However, several misconceptions exist regarding this form. Here are some clarifications:
- Misconception 1: The DA Form 1307 is optional.
- Misconception 2: Only experienced jumpers need to fill it out.
- Misconception 3: The information on the DA Form 1307 is not regularly reviewed.
- Misconception 4: The DA Form 1307 can be filled out without presenting a DA Form 1306.
- Misconception 5: The form is only for airborne operations.
- Misconception 6: All information on the DA Form 1307 is entered by the jumper themselves.
- Misconception 7: The DA Form 1307 expires after a set period.
- Misconception 8: The DA Form 1307 has no impact outside of parachuting records.
In reality, this form is mandatory and serves as a permanent record of jumps. It is essential for tracking an individual's airborne experience.
All personnel who perform jumps, regardless of their experience level, must complete this form to maintain accurate records.
Contrary to this belief, the data entered is subject to periodic review by superiors to ensure compliance and accuracy.
To properly document jumps, a DA Form 1306 must be presented first. The 1307 only captures jumps documented through this prerequisite.
While it primarily serves airborne personnel, the form may also include other relevant parachuting activities.
This form requires initial input from the observer, typically a jumpmaster or qualified personnel, to ensure the recorded information is accurate.
This form does not expire. It remains a permanent part of an individual's personnel records throughout their military career.
The details on this form can influence an individual’s career progression, assignments, and eligibility for airborne-related opportunities.
Clarifying these misconceptions can enhance understanding and facilitate proper record-keeping in military airborne operations.
Key takeaways
Filling out the DA Form 1307 is crucial for maintaining accurate jump records.
- Complete All Fields: Ensure that each section of the form, including name, grade, and type of jump, is filled out accurately.
- Permanent Record: This form becomes part of the official personnel records jacket, so accuracy is essential.
- Jump Codes: Use the specified codes to indicate the nature of the jump. For example, use “T” for Tactical and “N” for Night jumps.
- Authorization Required: Jumps can only be entered after presenting the DA Form 1306, which verifies the details of the jump.
- Initials of Officer: Include the initials of the personnel officer next to each jump entry, ensuring accountability.
- Multiple Jumps: You can document more than one jump on the same form, as long as all required details are included for each.
- Review Before Submission: It's important to double-check for any errors or omissions prior to submitting the form.
- Validity of the Form: Note that previous editions are obsolete; always use the most current version, as specified on the form.
Completing the DA Form 1307 carefully can support personnel evaluations and other military processes. Adhering to these guidelines will facilitate accurate record-keeping.
Browse Other Templates
Bank Application Form - Record the name of your employer or business for income verification.
Decedent's Estate Hearing Notification,Notice of Estate Administration Hearing,Probate Status Report Notice,Hearing Reminder for Decedent's Estate,Notice of Trust Proceedings,Hearing Announcement for Estate Matters,Decedent Trust Notification Form,Es - The DE-120 form reinforces the importance of adhering to legal deadlines in estate matters.
How to Fight a Ticket in Michigan - Follow up if you do not receive a response within the specified time frame.