Fill Out Your Dd 626 Form
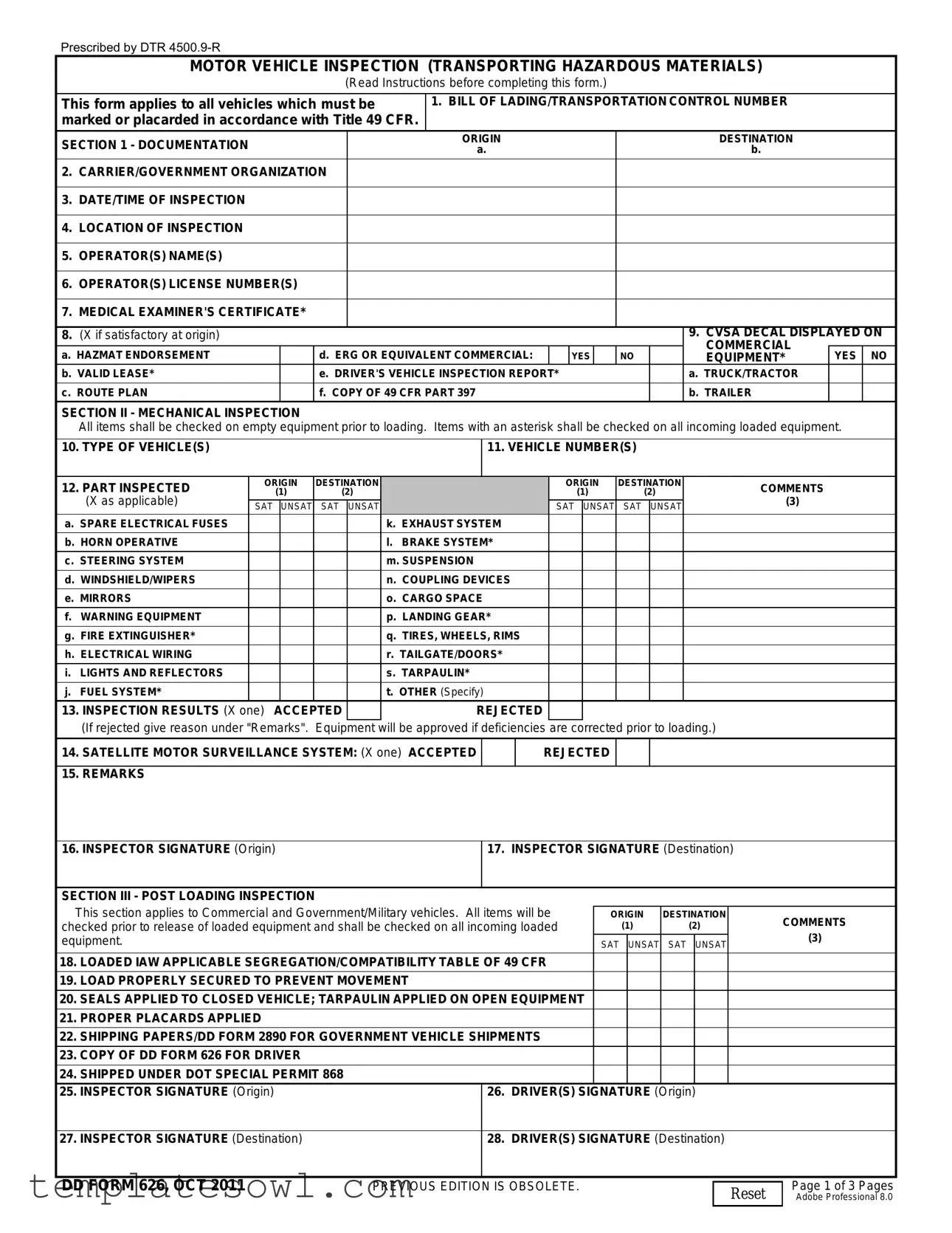
The DD Form 626 is a comprehensive vehicle inspection document explicitly designed for use in the transportation of hazardous materials. It serves various purposes, including ensuring compliance with transportation safety standards as outlined in Title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations. The form requires detailed documentation that includes the origin and destination of the transport, carrier information, and the date and time of inspection. Operators must provide their names, license numbers, and medical examination certification. Various checks must be performed on both empty and loaded vehicles, covering essential mechanical components such as the brake system, tires, and cargo space, to ensure that they are satisfactory before loading. Essential documentation must accompany the vehicle, including shipping papers, emergency response guides, and, where applicable, a copy of the DD Form 626 itself for the driver. The inspection results are prominently displayed on the form, which must be signed by both the inspector and the driver at both origin and destination, thereby creating a transparent record of compliance throughout the transport process.
Dd 626 Example
Prescribed by DTR
MOTOR VEHICLE INSPECTION (TRANSPORTING HAZARDOUS MATERIALS)
(Read Instructions before completing this form.)
This form applies to all vehicles which must be marked or placarded in accordance with Title 49 CFR.
1. BILL OF LADING/TRANSPORTATION CONTROL NUMBER
SECTION 1 - DOCUMENTATION |
ORIGIN |
DESTINATION |
a. |
b. |
2.CARRIER/GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATION
3.DATE/TIME OF INSPECTION
4.LOCATION OF INSPECTION
5.OPERATOR(S) NAME(S)
6.OPERATOR(S) LICENSE NUMBER(S)
7.MEDICAL EXAMINER'S CERTIFICATE*
8. (X if satisfactory at origin) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. CVSA DECAL DISPLAYED ON |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMMERCIAL |
|
|
a. HAZMAT ENDORSEMENT |
|
d. ERG OR EQUIVALENT COMMERCIAL: |
|
YES |
|
NO |
|
EQUIPMENT* |
YES |
NO |
b. VALID LEASE* |
|
e. DRIVER'S VEHICLE INSPECTION REPORT* |
|
|
|
|
a. TRUCK/TRACTOR |
|
|
|
c. ROUTE PLAN |
|
f. COPY OF 49 CFR PART 397 |
|
|
|
|
b. TRAILER |
|
|
|
SECTION II - MECHANICAL INSPECTION
All items shall be checked on empty equipment prior to loading. Items with an asterisk shall be checked on all incoming loaded equipment.
10. TYPE OF VEHICLE(S)
11. VEHICLE NUMBER(S)
12. PART INSPECTED |
ORIGIN |
DESTINATION |
|
|
|
|
ORIGIN |
DESTINATION |
|
COMMENTS |
|||||
|
(1) |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
(1) |
(2) |
|
||||||
(X as applicable) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3) |
SAT |
|
UNSAT |
SAT |
UNSAT |
|
|
|
|
SAT |
UNSAT |
SAT |
UNSAT |
|
||
a. SPARE ELECTRICAL FUSES |
|
|
|
|
|
k. EXHAUST SYSTEM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
b. HORN OPERATIVE |
|
|
|
|
|
l. BRAKE SYSTEM* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
c. STEERING SYSTEM |
|
|
|
|
|
m. SUSPENSION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
d. WINDSHIELD/WIPERS |
|
|
|
|
|
n. COUPLING DEVICES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
e. MIRRORS |
|
|
|
|
|
o. CARGO SPACE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
f. WARNING EQUIPMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
p. LANDING GEAR* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
g. FIRE EXTINGUISHER* |
|
|
|
|
|
q. TIRES, WHEELS, RIMS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
h. ELECTRICAL WIRING |
|
|
|
|
|
r. TAILGATE/DOORS* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
i. LIGHTS AND REFLECTORS |
|
|
|
|
|
s. TARPAULIN* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
j. FUEL SYSTEM* |
|
|
|
|
|
t. OTHER (Specify) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
13. INSPECTION RESULTS (X one) |
ACCEPTED |
|
REJECTED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
(If rejected give reason under "Remarks". Equipment |
will be approved if deficiencies |
are |
corrected prior to loading.) |
|
|||||||||||
14. SATELLITE MOTOR SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM: (X one) ACCEPTED |
|
|
REJECTED |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. REMARKS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16. INSPECTOR SIGNATURE (Origin)
17. INSPECTOR SIGNATURE (Destination)
SECTION III - POST LOADING INSPECTION |
|
|
|
This section applies to Commercial and Government/Military vehicles. All items will be |
ORIGIN |
DESTINATION |
COMMENTS |
checked prior to release of loaded equipment and shall be checked on all incoming loaded |
(1) |
(2) |
|
equipment. |
SAT UNSAT |
SAT UNSAT |
(3) |
18.LOADED IAW APPLICABLE SEGREGATION/COMPATIBILITY TABLE OF 49 CFR
19.LOAD PROPERLY SECURED TO PREVENT MOVEMENT
20.SEALS APPLIED TO CLOSED VEHICLE; TARPAULIN APPLIED ON OPEN EQUIPMENT
21.PROPER PLACARDS APPLIED
22.SHIPPING PAPERS/DD FORM 2890 FOR GOVERNMENT VEHICLE SHIPMENTS
23.COPY OF DD FORM 626 FOR DRIVER
24.SHIPPED UNDER DOT SPECIAL PERMIT 868
25. INSPECTOR SIGNATURE (Origin) |
|
26. |
DRIVER(S) SIGNATURE (Origin) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27. INSPECTOR SIGNATURE (Destination) |
|
28. |
DRIVER(S) SIGNATURE (Destination) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DD FORM 626, OCT 2011 |
PREVIOUS EDITION IS OBSOLETE. |
|
|
Page 1 of 3 Pages |
||
|
Reset |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Adobe Professional 8.0 |
|
INSTRUCTIONS
SECTION I - DOCUMENTATION
General Instructions.
All items (2 through 9) will be checked at origin prior to loading. Items with an asterisk (*) apply to commercial operators or equipment only. Only Items 2 through 7 are required to be checked at destination.
Items 1 through 5. Self explanatory.
Item 6. Enter operator's Commercial Driver's License (CDL) number or Military
Item 7. *Enter the expiration date listed on the Medical Examiner's Certificate.
Item 8.a. Hazardous Materials Certification. In accordance with applicable service regulations, ensure operator has been certified to transport hazardous materials. Check the expiration date on driver's HAZMAT Certification.
b.*Valid Lease. Shipper will ensure a copy of the appropriate contract or lease is carried in all leased vehicles and is available for inspection. (49 CFR 376.12 and 376.11(c)(2)).
c.Route Plan. Prior to loading any Hazard Class/Division 1.1, 1.2, or 1.3 (Explosives) for shipment, ensure that the operator possesses a written route plan in accordance with 49 CFR Part
397.Route Plan requirements for Hazard Class 7 (Radioactive) materials are found in 49 CFR 397.101.
d.Emergency Response Guidebook (ERG) or Equivalent. Commercial operators must be in possession of an ERG or equivalent document. Shipper will provide applicable ERG page(s) to military operators.
e.*Driver's Vehicle Inspection Report. Review the operator's Vehicle Inspection Report. Ensure that there are no defects listed on the report that would affect the safe operation of the vehicle.
f.Copy of 49 CFR Part 397. Operators are required by regulation to have in their possession a copy of 49 CFR Part 397 (Transportation of Hazardous Materials Driving and Parking Rules). If military operators do not possess this document, shipper will provide a copy to operator.
Item 9. *Commercial Vehicle Safety Alliance (CVSA) Decal. Check to see if equipment has a current CVSA decal and mark applicable box. Vehicles without CVSA, check documentation of the last vehicle periodic inspection and perform DD Form 626 inspection.
SECTION II - MECHANICAL INSPECTION
General Instructions.
All items (12.a. through 12.t.) will be checked on all incoming empty equipment prior to loading. All UNSATISFACTORY conditions must be corrected prior to loading. Items with an asterisk (*) shall be checked on all incoming loaded equipment. Unsatisfactory conditions that would affect the safe
SECTION II (Continued)
Item 12.a. Spare Electrical Fuses. Check to ensure that at least one spare fuse for each type of installed fuse is carried on the vehicle as a spare or vehicle is equipped with an overload protection device (circuit breaker). (49 CFR 393.95)
b.Horn Operative. Ensure that horn is securely mounted and of sufficient volume to serve purpose. (49 CFR 393.81)
c.Steering System. The steering wheel shall be secure and must not have any spokes cracked through or missing. The steering column must be securely fastened. Universal joints shall not be worn, faulty or repaired by welding. The steering gear box shall not have loose or missing mounting bolts or cracks in the gear box mounting brackets. The pitman arm on the steering gear output shaft shall not be loose. Steering wheel shall turn freely through the limit of travel in both directions. All components of a power steering system must be in operating condition. No parts shall be loose or broken. Belts shall not be frayed, cracked or slipping. The power steering system shall not be leaking. (49 CFR 396 Appendix G)
d.Windshield/Wipers. Inspect to ensure that windshield is free from breaks, cracks or defects that would make operation of the vehicle unsafe; that the view of the driver is not obscured and that the windshield wipers are operational and wiper blades are in serviceable condition. Defroster must be operative when conditions require. (49 CFR 393.60, 393.78 and 393.79)
e.Mirrors. Every vehicle must be equipped with two rear vision mirrors located so as to reflect to the driver a view of the highway to the rear along both sides of the vehicle. Mirrors shall not be cracked or dirty. (49 CFR 393.80)
f.Warning Equipment. Equipment must include three bidirectional emergency reflective triangles that conform to the requirements of FMVSS No. 125. FLAME PRODUCING DEVICES ARE PROHIBITED. (49 CFR 393.95)
g.Fire Extinguisher. Military vehicles must be equipped with one serviceable fire extinguisher with an Underwriters Laboratories rating of 10 BC or more. (Commercial motor vehicles must be equipped with one serviceable 10 BC Fire Extinguisher). Fire extinguisher must be located so that it is readily accessible for use and securely mounted on the vehicle. The fire extinguisher must be designed, constructed and maintained to permit visual determination of whether it is fully charged. (49 CFR 393.95)
h.Electrical Wiring: Electrical wiring must be clean and properly secured. Insulation must not be frayed, cracked or otherwise in poor condition. There shall be no uninsulated wires, improper splices or connections. Wires and electrical fixtures inside the cargo area must be protected from the lading. (49 CFR 393.28)
DD FORM 626, OCT 2011 |
Page 2 of 3 Pages |
INSTRUCTIONS
SECTION II (Continued)
i.Lights/Reflectors. (Head, tail, turn signal, brake, clearance, marker and identification lights, Emergency Flashers). Inspect to see that all lighting devices and reflectors required are operable, of proper color and properly mounted. Ensure that lights and reflectors are not obscured by dirt or grease or have broken lenses. High/Low beam switch must be operative. Emergency Flashers must be operative on both the front and rear of vehicle. (49 CFR 393.24, 25, and 26)
j.Fuel System. Inspect fuel tank and lines to ensure that they are in serviceable condition, free from leaks, or evidence of leakage and securely mounted. Ensure that fuel tank filler cap is not missing. Examine cap for defective gasket or plugged vent. Inspect filler necks to see that they are in completely serviceable condition and not leaking at joints. (49 CFR 393.83)
k.Exhaust System. Exhaust system shall discharge to the atmosphere at a location to the rear of the cab or if the exhaust projects above the cab, at a location near the rear of the cab.
Exhaust system shall not be leaking at a point forward of or directly below the driver compartment. No part of the exhaust system shall be located where it will burn, char or damage electrical wiring, fuel system or any other part of the vehicle. No part of the exhaust system shall be temporarily repaired with wrap or patches. (49 CFR 393.83)
l.Brake System (to include hand brakes, parking brakes and Low Air Warning devices). Check to ensure that brakes are operational and properly adjusted. Check for audible air leaks around air brake components and air lines. Check for fluid leaks, cracked or damaged lines in hydraulic brake systems. Ensure that parking brake is operational and properly adjusted. Low Air Warning devices must be operative. (49 CFR 393.40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, and 55)
m.Suspension. Inspect for indications of misaligned, shifted or cracked springs, loosened shackles, missing bolts, spring hangers unsecured at frame and cracked or loose
n.Coupling Devices (Inspect without uncoupling). Fifth Wheels: Inspect for unsecured mounting to frame or any missing or damaged parts. Inspect for any visible space between upper and lower fifth wheel plates. Ensure that the locking jaws are around the shank and not the head of the kingpin. Ensure that the release lever is seated properly and safety latch is engaged. Pintle Hook, Drawbar, Towbar Eye and Tongue and Safety Devices: Inspect for unsecured mounting, cracks, missing or ineffective fasteners (welded repairs to pintle hook is prohibited). Ensure safety devices (chains, hooks, cables) are in serviceable condition and properly attached. (49 CFR 393.70 and 71)
o.Cargo Space. Inspect to ensure that cargo space is clean and free from exposed bolts, nuts, screws, nails or inwardly projecting parts that could damage the lading. Check floor to ensure it is tight and free from holes. Floor shall not be permeated with oil or other substances. (49 CFR 393.84)
p.Landing Gear. Inspect to ensure that landing gear and assembly are in serviceable condition, correctly assembled, adequately lubricated and properly mounted.
SECTION II (Continued)
q.Tires, Wheels and Rims: Inspect to ensure that tires are properly inflated. Flat or leaking tires are unacceptable. Inspect tires for cuts, bruises, breaks and blisters. Tires with cuts that extend into the cord body are unacceptable. Thread depth shall not be less than: 4/32 inches for tires on a steering axle of a power unit, and 2/32 inches for all other tires. Mixing bias and radial on the steering axle is prohibited. Inspect wheels and rims for cracks, unseated locking rings, broken, loose, damaged or missing lug nuts or elongated stud holes. (49 CFR 393.75)
r.Tailgate/Doors. Inspect to see that all hinges are tight in body. Check for broken latches and safety chains. Doors must close securely. (49 CFR 177.835(h))
s.Tarpaulin. If shipment is made on open equipment, ensure that lading is properly covered with fire and water resistant tarpaulin. (49 CFR 177.835(h))
t.Other Unsatisfactory Condition. Note any other condition which would prohibit the vehicle from being loaded with hazardous materials.
Item 14. For AA&E and other shipments requiring satellite surveillance, ensure that the Satellite Motor Surveillance System is operable. The DTTS Message Display Unit, when operative, will display the signal "DTTS ON". The munitions carrier driver, when practical, will position the DTTS message display unit in a manner that allows the shipping inspector or other designated shipping personnel to observe the "DTTS ON" message without climbing aboard the cab of the motor vehicle.
SECTION III - POST LOADING INSPECTION
General Instructions.
All placarded quantities items will be checked prior to the release of loaded equipment. Shipment will not be released until deficiencies are corrected. All items will be checked on incoming loaded equipment. De- ficiencies will be reported in accordance with applicable service regulations.
Item 18. Check to ensure shipment is loaded in accordance with 49 CFR Part 177.848 and the applicable Segregation or Compatibility Table of 49 CFR 177.848.
Item 19. Check to ensure the load is secured from movement in accordance with applicable service outload drawings.
Item 20. Check to ensure seal(s) have been applied to closed equipment; fire and water resistant tarpaulin applied on open equipment.
Item 21. Check to ensure each transport vehicle has been properly placarded in accordance with 49 CFR 172.504.
Item 22. Check to ensure operator has been provided shipping papers that comply with 49 CFR 172.201 and 202. For shipments transported by Government vehicle, shipping paper will be DD Form 2890.
Item 23. Ensure operator(s) sign DD Form 626, are given a copy and understand the hazards associated with the shipment.
Item 24. Applies to Commercial Shipments Only. If shipment is made under DOT Special Permit 868, ensure that shipping papers are properly annotated and copy of Special Permit 868 is with shipping papers.
Item 26. Ensure driver/operator signs DD Form 626 at origin.
Item 28. Ensure driver/operator signs DD Form 626 at destination.
DD FORM 626, OCT 2011 |
Page 3 of 3 Pages |
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Fact Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The DD Form 626 is used for motor vehicle inspections related to transporting hazardous materials. |
| Governing Regulation | This form is prescribed by DTR 4500.9-R and applies in accordance with Title 49 CFR. |
| Inspection Requirement | A comprehensive mechanical inspection is required for all vehicles before loading hazardous materials. |
| Documentation | Operators must carry specific documentation, including a Bill of Lading and Medical Examiner's Certificate. |
| Signatures | Signatures of both the inspector and driver are required at the origin and destination of the shipment. |
| Inspection Items | There are several critical items that need inspection, such as brakes, lighting, and tires, among others. |
| Rejection Criteria | If any vehicle inspection item fails, the vehicle must be rejected until deficiencies are corrected. |
| CVSA Decal | A current Commercial Vehicle Safety Alliance (CVSA) decal must be displayed on commercial vehicles. |
| Post-Loading Inspection | A post-loading inspection is required to ensure that the load is properly secured and placarded. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Dd 626
After gathering the necessary information, the next steps involve carefully completing the DD 626 form. This form is critical for ensuring proper documentation and compliance when transporting hazardous materials.
- Begin with Section I. Fill out the Bill of Lading/Transportation Control Number section. Include the origin and destination details.
- Next, enter the Carrier or Government Organization.
- Record the date and time of the inspection.
- Indicate the location of the inspection.
- List the name(s) of the operator(s).
- Fill in the operator(s) license number(s), ensuring it's accurate.
- Provide the expiration date from the Medical Examiner's Certificate.
- Mark as satisfactory at origin if applicable; check the necessary boxes for CVSA Decal and other requirements.
- In Section II, specify the type of vehicle(s) being inspected and the vehicle number(s).
- Inspect and document the condition of the parts listed; mark SAT (satisfactory) or UNSAT (unsatisfactory) as applicable.
- Report the inspection results by choosing ACCEPTED or REJECTED, and include any remarks if rejected.
- In Section III, perform a post-loading inspection. Check items such as load security and proper placarding.
- Ensure the inspector and driver(s) sign in the appropriate sections at both origin and destination.
Completing the DD 626 form accurately is essential for compliance with transportation regulations. Double-check all entries to ensure they are correct before submission.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the DD Form 626?
The DD Form 626 serves as a comprehensive inspection form for vehicles transporting hazardous materials. It ensures that essential safety checks are performed on vehicles before they are loaded and released for transportation. This form is vital for compliance with federal regulations, specifically those outlined in Title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), which governs the safe transport of hazardous materials. By documenting the inspection process, the form provides a record that the vehicle meets safety standards and is suitable for carrying hazardous materials.
What information do I need to provide in Section I of the DD Form 626?
In Section I, you must fill out several fields related to the vehicle documentation. This includes details about the origin and destination, carrier or government organization, date and time of inspection, and the operator’s name and license number. You will also need to indicate whether the operator has a valid Medical Examiner's Certificate and if all necessary paperwork, such as the Hazardous Materials Certification and the Driver’s Vehicle Inspection Report, is in order. The inclusion of a route plan for certain hazardous materials is also mandatory, as is certification regarding emergency response documentation.
What items are checked during the mechanical inspection in Section II?
Section II requires a thorough mechanical inspection of the vehicle. Inspectors will check items like the steering system, brakes, tires, and lights to ensure they are in proper working condition. Each component is marked as either satisfactory (SAT) or unsatisfactory (UNSAT). If any component is deemed unsatisfactory, it must be corrected before loading the vehicle with hazardous materials. The goal is to ensure that the vehicle is safe for operation and meets all necessary regulations.
What should I do if my vehicle is rejected during the inspection?
If your vehicle is rejected due to unsatisfactory conditions, it is crucial to address the identified issues promptly. The vehicle cannot be loaded with hazardous materials until all deficiencies have been rectified. The inspector will provide remarks detailing the reasons for the rejection, which should guide the necessary repairs. After corrections have been made, a follow-up inspection can occur to verify that the vehicle now complies with safety standards.
How does post-loading inspection differ from pre-loading inspection?
The post-loading inspection outlined in Section III focuses specifically on ensuring that the load has been secured properly and that all placarding and shipping documentation are in order before the vehicle can be released. Inspectors will verify that the hazardous materials are loaded according to regulations and that all seals and placards are correctly placed. This step is vital to prevent incidents during transportation and ensures compliance with safety procedures related to the handling of hazardous materials.
Common mistakes
Completing the DD Form 626 is essential for ensuring the safety and compliance of vehicles transporting hazardous materials. However, individuals often make several common mistakes that can lead to complications or delays. Awareness of these errors can significantly streamline the inspection process.
One prevalent mistake involves failing to thoroughly check the operator's license number. This detail must include the full Commercial Driver's License (CDL) number or the Military OF-346 License Number. Leaving out digits, or entering an incorrect number, can create significant issues during inspection. Properly verifying the license ensures that the operator is authorized to manage hazardous materials.
Another frequent error occurs with the Medical Examiner's Certificate. This certificate has an expiration date that needs to be documented correctly. If individuals neglect to check the certificate’s validity or mistakenly enter an expired date, they may risk non-compliance with federal regulations. It’s crucial to keep track of such certificates to avoid operational disruptions and legal penalties.
Moreover, many users do not provide adequate detail in the remarks section when items are marked as "Rejected." Simply indicating that an item was unsatisfactory without specifying the issue or corrective actions can lead to confusion. This lack of detail not only hampers the inspection process but can also prolong the time required to clear the vehicle for loading, as inspectors need a clear understanding of the presented issues.
Lastly, individuals often overlook confirming that all necessary documentation accompanies the inspection form. For instance, ensuring that the Emergency Response Guidebook or equivalent documentation is readily available is a crucial part of the process. Without this documentation, the operator may fail to adhere to safety protocols during transport, exposing everyone to unnecessary risks. By being mindful of these common mistakes, individuals can facilitate a smoother and more effective inspection process.
Documents used along the form
The DD Form 626 is essential for inspecting vehicles transporting hazardous materials. However, it is often accompanied by several other documents to ensure compliance and safety. Below are important forms that work together with the DD Form 626.
- Bill of Lading: This document serves as a receipt for the goods shipped. It contains information about the origin, destination, and details of the shipment, ensuring that all parties are informed about the cargo.
- Driver's Vehicle Inspection Report: This report details the vehicle's mechanical condition before operation. It highlights any issues that could impact safety and ensures that the vehicle is compliant with regulations.
- Emergency Response Guidebook (ERG): The ERG is an essential reference for emergency responders. It provides crucial information on hazardous materials, including handling instructions and emergency measures.
- Copy of 49 CFR Part 397: This document outlines federal regulations pertaining to the transportation of hazardous materials. It includes rules on driving and parking that operators must follow.
- Shipping Papers (DD Form 2890): Required for government vehicle shipments, this document contains shipping information that complies with federal regulations, including details relevant to hazardous materials.
Having these documents on hand is crucial for maintaining safety and regulatory compliance in the transportation of hazardous materials. Make sure to keep them organized and readily accessible during inspections and transport operations.
Similar forms
Bill of Lading: This document serves as a receipt for the goods being transported, detailing the type and quantity of items along with their destination. It outlines the contractual obligations of the carrier and shipper, similar to how the DD 626 ensures compliance for vehicles transporting hazardous materials.
Driver's Vehicle Inspection Report (DVIR): The DVIR is used to document the condition of a vehicle before and after use. Like the DD 626, it mandates inspections to ensure safety and compliance, specifically focusing on vehicle operability and road-worthiness.
Emergency Response Guidebook (ERG): The ERG contains vital information on handling hazardous materials in emergencies. It is similar to the DD 626 as both documents aim to enhance safety protocols for transporting dangerous goods.
Shipping Papers (DD Form 2890): This form specifically applies to government vehicle shipments and includes details about cargo being transported. It parallels the DD 626 by ensuring that the shipment adheres to regulatory requirements regarding hazardous materials.
Commercial Vehicle Safety Alliance (CVSA) Decal: A certification indicating that the vehicle has passed a safety inspection, much like the inspection required in the DD 626, which assesses a vehicle’s readiness for transporting hazardous materials.
Route Plan: This document outlines the designated path for transporting hazardous materials, ensuring safety through appropriate routes. Similar to the DD 626, it is critical for regulatory compliance and minimizes risk during transportation.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the DD Form 626, there are several important practices to keep in mind. Here are eight things you should do, as well as a few things to avoid.
- Review the instructions carefully before starting the form. Understanding all sections can help prevent errors.
- Provide accurate information for the operator’s name and license number. This ensures clear identification.
- Check all required documentation, such as medical examiner's certificates and hazardous materials certifications, to confirm they are current.
- Clearly indicate inspection results in the designated sections. This helps streamline the approval process.
- Ensure compliance with regulations for vehicle inspections prior to loading. This includes checking for any mechanical issues.
- Obtain necessary signatures from inspectors and drivers at both origin and destination points to validate the inspection process.
- Maintain a copy of the form for your records. This can serve as proof of compliance in future audits.
- Double-check all responses before submitting the form. A second review can catch potential mistakes.
- Do not leave any sections blank, as this can lead to delays in processing the form.
- Avoid using outdated information, particularly regarding licenses or certificates, as it may result in rejection.
- Do not overlook mechanical inspections. Any unsatisfactory conditions must be corrected before loading.
- Refrain from skipping required signatures. Incomplete documentation can lead to regulatory issues.
- Do not falsify any information on the form. Providing inaccurate data can have serious legal consequences.
- Avoid submitting the form without necessary supporting documents, as this may result in disapproval.
- Do not assume all items passed inspection without verification. Each must be checked and documented.
- Refrain from using ambiguous language or notes in the comments section. Clarity is crucial for understanding.
Misconceptions
Misconception 1: The DD Form 626 is only for military vehicles.
This form is applicable to all vehicles that transport hazardous materials, not just military ones. Commercial vehicles must adhere to the same regulations and complete this form where required.
Misconception 2: Completing the DD Form 626 is optional for hazardous materials transport.
It is essential to understand that filling out this form is a mandatory requirement. Compliance with Title 49 CFR regulations is vital to ensure safety in the transportation of hazardous materials.
Misconception 3: Only the inspector needs to sign the DD Form 626.
Both the inspector and the driver must sign the form. This ensures that the driver acknowledges and understands the inspections performed and the associated hazards.
Misconception 4: The DD Form 626 only covers the initial inspection of the vehicle.
The form encompasses multiple inspection phases, including pre-loading, post-loading, and emergency equipment readiness. Each section must be completed for comprehensive compliance and safety assurance.
Key takeaways
1. The DD Form 626 is essential for documenting the mechanical inspection of vehicles transporting hazardous materials.
2. Complete all sections accurately, focusing on the documentation, mechanical inspection, and post-loading inspection sections.
3. Ensure the vehicle is empty during the initial inspection to address any possible mechanical flaws.
4. Pay close attention to items marked with an asterisk (*); these are mandatory checks for commercial operations and loaded equipment.
5. Record deficiencies and provide clear remarks for any rejected inspections, as corrections must be made before loading can occur.
6. Both copy and original of the DD Form 626 must be signed by the inspector and the driver at both origin and destination locations.
7. Validate all required documentation before commencing transport, including the driver’s certifications and necessary permits.
8. Remember that the shipment cannot proceed if any safety deficiencies are present or if the form is incomplete.
Browse Other Templates
Pa Child Abuse History Certification - Previous names used since 1975 should be listed for identification verification.
Un Geoscheme - The original form should be submitted to the local UST regulatory agency.