Fill Out Your Employee Earnings Record Form
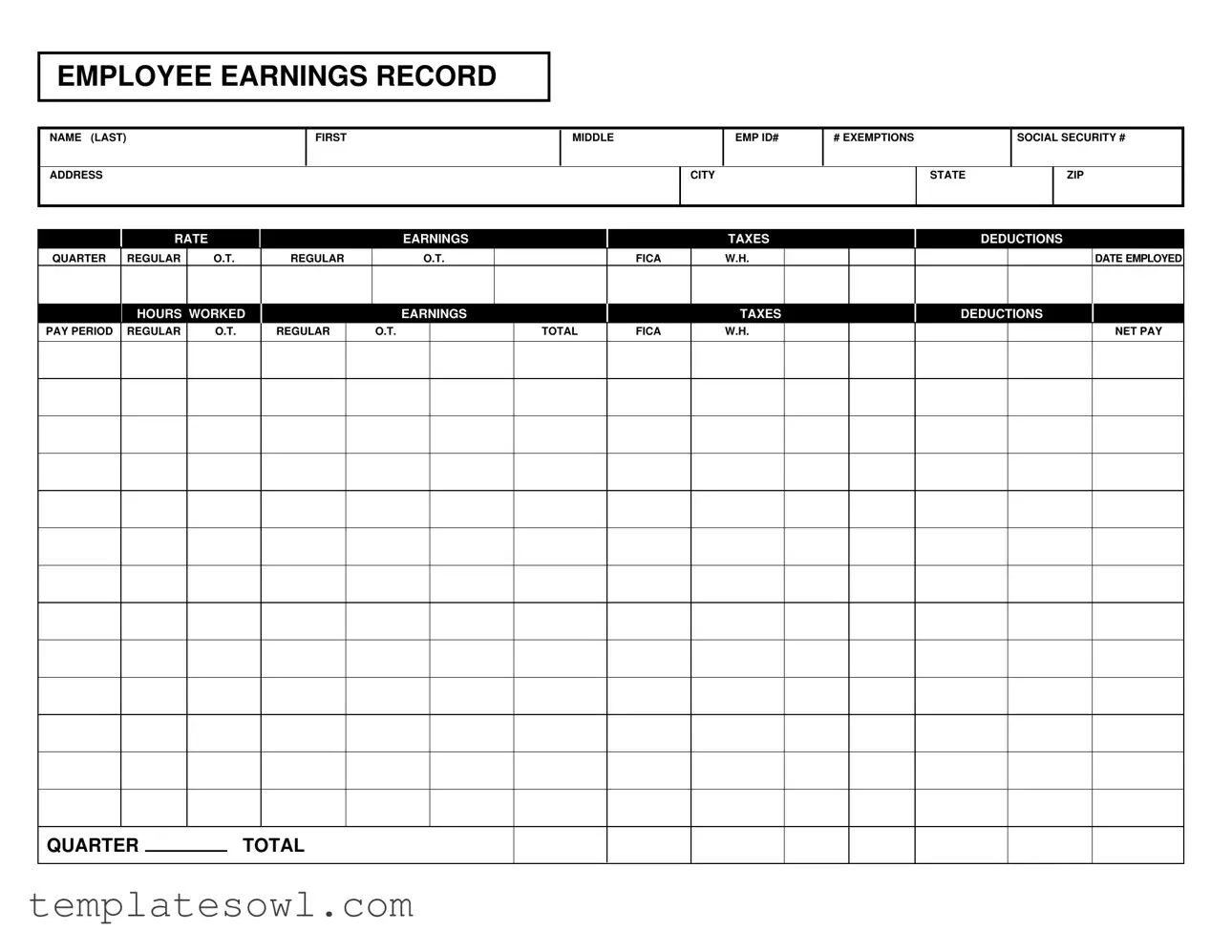
The Employee Earnings Record form serves as an essential tool for tracking employees' earnings and deductions throughout the year. Each record captures vital information such as the employee's name, identification number, and contact details, making it easy for both employers and employees to reference. Key sections include salary rates, hours worked, and overtime pay, providing a comprehensive view of compensation during each pay period. Taxes withheld, including FICA contributions, are also documented, ensuring accurate records for tax reporting. Additionally, the form details any deductions taken, allowing employees to understand their net pay clearly. By summarizing earnings on a quarterly basis, this form not only helps manage payroll effectively but also supports employees in monitoring their financial standing over the course of their employment.
Employee Earnings Record Example
EMPLOYEE EARNINGS RECORD
NAME (LAST)
ADDRESS
FIRST |
|
MIDDLE |
EMP ID# |
# EXEMPTIONS |
SOCIAL SECURITY # |
|||
|
||||||||
|
|
|
CITY |
|
|
STATE |
|
ZIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RATE |
|
|
|
EARNINGS |
|
|
TAXES |
DEDUCTIONS |
|
QUARTER |
REGULAR |
|
O.T. |
REGULAR |
O.T. |
|
FICA |
W.H. |
DATE EMPLOYED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HOURS |
WORKED |
|
|
EARNINGS |
|
|
TAXES |
DEDUCTIONS |
|
PAY PERIOD |
REGULAR |
|
O.T. |
REGULAR |
|
O.T. |
TOTAL |
FICA |
W.H. |
NET PAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QUARTERTOTAL
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Employee Earnings Record form is designed to document individual earnings, tax withholdings, and deductions throughout the employment period. |
| Information Included | This form captures essential employee information such as name, address, Social Security number, and employment identification number. |
| Tax Deductions | It outlines various tax deductions, including FICA, federal withholding (W.H.), and state taxes, ensuring compliance with tax laws. |
| Record Keeping | Employers are required to maintain this record for each employee, as it is crucial for tax reporting and payroll audits. |
| Governing Laws | Specific state forms may be governed by state employment laws, which outline the requirements for recordkeeping and reporting. |
| Hours Worked | The form tracks both regular and overtime hours worked, enabling accurate calculation of total earnings for each pay period. |
| Net Pay Calculation | It includes a section for calculating net pay after accounting for all deductions, which is critical for employee financial outcomes. |
| Quarterly Reporting | Employers may use the earnings record for quarterly reporting purposes, summarizing total earnings, taxes, and deductions for each quarter. |
| Important Dates | Key dates are captured on the form, including the employee's date of employment and the specific pay period dates, aiding in compliance and tracking. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Employee Earnings Record
Filling out the Employee Earnings Record is a straightforward process that requires precision to ensure accurate tracking of an individual's earnings throughout the pay period. Once completed, the form provides valuable information for payroll and tax reporting, contributing to effective financial management.
- Section 1: Employee Information
In the first section, enter the employee's last name, first name, and middle name. Next, fill in their Employee ID number and Social Security number. Provide the address, including the city, state, and ZIP code. - Section 2: Employment Details
Indicate the date employed. Then, input the rate of pay, followed by the number of hours worked during the pay period. - Section 3: Earnings and Taxes
Specify the earnings for both regular and overtime hours. Make sure to also record the associated taxes and deductions. This includes FICA and Withholding (W.H.) amounts. - Section 4: Pay Period Summary
Sum up the total earnings, including regular and overtime components. Calculate the overall deductions and the final net pay for the quarter. - Section 5: Exemptions
If applicable, note the number of exemptions claimed by the employee in the designated area.
By following these steps accurately, the Employee Earnings Record can be filled out effectively, ensuring clarity in payroll processing and compliance with tax regulations.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the Employee Earnings Record form?
The Employee Earnings Record form is a document used by employers to keep track of an employee's earnings, taxes, deductions, and other important financial information. It serves as a record of how much an employee has earned during a specific pay period, including regular and overtime hours.
Why is the Employee Earnings Record important?
This form is crucial for both employers and employees. For employers, it ensures compliance with tax regulations and assists in reporting earnings accurately. Employees can use this record to verify their payments, track their earnings over time, and view the deductions taken from their paychecks.
What information is included in the Employee Earnings Record?
The form includes various pieces of important information: the employee's name, address, employee ID number, total earnings, categorization of earnings (regular and overtime), tax information, deductions, and net pay. It also lists the pay periods and hours worked.
Who is responsible for maintaining the Employee Earnings Record?
Employers are primarily responsible for maintaining accurate records. However, employees should regularly check their earnings records for accuracy to ensure they are receiving the correct payments and deductions. An open line of communication regarding this record can help prevent issues.
How often should the Employee Earnings Record be updated?
The Employee Earnings Record should be updated with each pay period. This regular updating allows for real-time tracking of earnings and deductions, which is essential for tax purposes and personal financial management.
What are the key components listed on this form?
Key components of the form include the employee's name, pay rate, hours worked (both regular and overtime), earnings summary, tax withheld, deductions, and net pay. Each section is vital for understanding the employee's overall compensation package.
How does overtime pay work in the Employee Earnings Record?
Overtime pay is recorded separately on the form. It’s typically calculated at a higher rate than regular hours, and employers must ensure that the correct amount is reflected in the earnings section. Accurate recording is essential for compliance with labor laws.
What should I do if I notice an error on the Employee Earnings Record?
If you spot an error on your Employee Earnings Record, promptly notify your employer or the HR department. Discussing it as soon as possible can help resolve the issue quickly and ensure that any necessary corrections are made in a timely manner.
Is the Employee Earnings Record used for tax purposes?
Yes, the Employee Earnings Record plays a significant role in preparing for tax filings. It provides a detailed summary of your earnings and withheld taxes, which you will need when filing your annual tax returns. Always keep a copy for your records.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Employee Earnings Record form is crucial for accurate payroll processing. However, many individuals make mistakes that can lead to complications down the line. One common error involves omitting vital personal information, such as the *last name* or *employee identification number*. This information is essential for proper record-keeping and can hinder the processing of earnings if missing.
Another frequent mistake is incorrectly entering the *social security number*. A simple typographical error in this field can create significant issues for tax reporting and benefits eligibility. It is important to double-check this number, as discrepancies can lead not only to delays but also to potential penalties.
Many people also misunderstand the exemptions section. Filling it out accurately is key to determining withholding amounts. Overestimating exemptions can result in under-withholding, leading to unexpected tax liabilities at the end of the year. Conversely, underestimating exemptions could mean losing out on take-home pay unnecessarily.
Some individuals fail to record their *earnings* correctly under the designated categories of regular and overtime pay. This mistake can distort their financial records and affect calculations for taxes and other deductions. Accurate entries in these fields ensure that the employee receives appropriate compensation for all hours worked.
The *deductions* section often sees errors as well. Missing or inaccurately recorded deductions can impact net pay calculations. It is essential to ensure that all relevant deductions, such as those for benefits or retirement contributions, are accounted for and correctly inputted, as even minor errors can lead to financial discrepancies.
Lastly, individuals sometimes neglect to update their forms when there are changes in employment status or personal information. Failure to report changes, such as a change in address or a new tax filing status, can hinder effective communication with payroll departments. Keeping records current not only ensures compliance but also protects against potential problems in the future.
Documents used along the form
The Employee Earnings Record form is an essential document for tracking an employee's earnings, taxes, and deductions over a specific period. However, several other forms and documents often accompany it to ensure comprehensive payroll accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. These related documents collectively help organize and manage employee information effectively.
- W-2 Form: This form provides a summary of an employee's annual wages and the taxes withheld. Employers must issue this tax document to their employees by January 31 each year. Employees use it to file their personal income tax returns.
- Payroll Register: This document serves as a detailed report of all payroll transactions for a specific period. It includes information about gross pay, deductions, and net pay for each employee, allowing employers to verify and reconcile payroll-related financial data.
- Time Sheets: These documents track the hours worked by employees during a pay period. They provide evidence of attendance and hours worked, which is crucial for accurately calculating wages and ensuring compliance with labor laws.
- Employee Tax Withholding Certificate (W-4): Employees complete this form to indicate their tax withholding preferences. It helps employers calculate the correct amount of federal income tax to withhold from employees’ paychecks, based on their deductions and exemptions.
- Direct Deposit Authorization Form: This form allows employees to authorize electronic payments of their wages directly into their bank accounts. It simplifies the payroll process for employers and provides convenience for employees, ensuring timely access to funds.
By utilizing these documents alongside the Employee Earnings Record form, employers can more accurately manage payroll, remain compliant with tax regulations, and ensure that employees receive their rightful earnings in a timely manner.
Similar forms
-
Pay Stubs: Pay stubs are similar because they provide a detailed breakdown of an employee’s earnings for a specific pay period. This document lists gross pay, deductions, and net pay, much like the Employee Earnings Record.
-
W-2 Forms: W-2 forms summarize an employee's annual earnings and taxes withheld. Like the Employee Earnings Record, they are essential for tax reporting and reflect cumulative earnings over the year.
-
1099 Forms: For independent contractors, 1099 forms capture earnings similar to Employee Earnings Records. They also summarize income but are geared towards those who are not classified as employees.
-
Payroll Journals: Payroll journals are records maintained by employers that log each payroll transaction. This document, much like the Employee Earnings Record, provides details about hours worked, earnings, and deductions.
-
Employment Contracts: Employment contracts outline the terms of employment including salary and benefits. While more comprehensive, they share common elements with the Employee Earnings Record in detailing financial compensation.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Employee Earnings Record form, it is important to follow guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Below is a list of dos and don'ts to help you complete the form correctly.
- Do include your full name, as it appears on official documents.
- Do double-check your Social Security number to avoid discrepancies.
- Do specify the correct pay rate for both regular and overtime hours.
- Do accurately report the number of exemptions claimed.
- Do carefully calculate total earnings for the pay period, including all applicable taxes and deductions.
- Don't leave any sections blank; provide all required information.
- Don't use nicknames or abbreviations for your name or address.
- Don't include any incorrect or outdated employment information.
- Don't forget to sign and date the form as required.
Misconceptions
The Employee Earnings Record form is a critical document for tracking an employee's earnings and deductions, yet many misconceptions surround it. Understanding these misconceptions can help provide clarity for both employees and employers alike. Here’s a list of ten common misconceptions regarding the Employee Earnings Record form:
-
It is only for tax purposes.
While the Employee Earnings Record does play a role in tax calculations, it serves many functions. This form also helps track hours worked, earnings, and deductions, making it essential for both administrative and record-keeping purposes.
-
Only employers need to fill it out.
Employees should be involved in reviewing this record. Their engagement ensures the accuracy of the information recorded, including hours and earnings.
-
It is a one-time document.
The form is actually updated regularly. It should reflect each pay period's earnings, deductions, and hours, making it a living document that evolves throughout employment.
-
All deductions are voluntary.
This is not completely true. While some deductions, like retirement contributions, may be optional, others, such as taxes, are required by law.
-
It's the same across all states.
The Employee Earnings Record can differ depending on state regulations. Specific requirements and deductions may vary, so staff should be aware of their state’s guidelines.
-
FICA deductions are optional.
FICA taxes, which fund Social Security and Medicare, are mandatory for most employees. Everyone employed in the United States is subject to these deductions unless specifically exempted.
-
Overtime pay is automatically calculated.
Calculating overtime pay depends on the employer’s policies and the employee's classification. While the form may help track hours, employers must ensure correct calculations based on labor laws.
-
Only full-time employees have an Employee Earnings Record.
Both part-time and full-time employees should have this record. Any worker earning wages needs an accurate account of their earnings and deductions.
-
There are no implications for inaccuracies.
Inaccuracies can lead to serious consequences, including discrepancies in paychecks, tax filing issues, or even penalties. Proper record-keeping is essential for compliance with tax laws.
-
It is a private document with no need for review.
This form should be regularly reviewed by employees to ensure that the data is accurate. Maintaining transparency promotes trust and can prevent disputes over discrepancies in compensation.
Becoming informed about these common misconceptions can empower employees and employers alike to navigate payroll processes more effectively. Staying educated fosters better financial awareness and compliance with regulations.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the Employee Earnings Record form effectively ensures accurate tracking of employee compensation and deductions. Here are five key takeaways:
- Accurate Information: Fill in all sections carefully, including name, address, and other personal identifiers. Inaccuracies can lead to payroll errors.
- Social Security Number: Provide the correct Social Security number. This is crucial for tax reporting and benefiting from Social Security.
- Tax Calculations: Keep track of taxes withheld such as FICA and federal withholding. Proper documentation helps in preparing tax returns.
- Regular and Overtime Hours: Record both regular and overtime hours worked. This ensures proper pay and compliance with labor laws.
- Maintain Privacy: Safeguard the information on the form. Sensitive details like Social Security numbers should be protected to prevent identity theft.
Using the form correctly sets a solid foundation for payroll management and employee record-keeping.
Browse Other Templates
El Super Application - State your age if you are not yet 18 years old.
Sonicare Rebates - The offer is void if not compliant with provided terms and conditions.