Fill Out Your Fannie Mae 1037 Form
The Fannie Mae 1037 form serves as an essential tool for borrowers and lenders when calculating rental income from a principal residence or a 2- to 4-unit property. This form guides users in determining the monthly qualifying rental income that can be utilized in the mortgage application process. To initiate this assessment, individuals must provide required documentation, such as IRS Form Schedule E or a lease agreement, to support their rental income claims. The form outlines a systematic approach, starting with evaluating the number of months the property has been in service, then moving on to how to accurately calculate the monthly qualifying rental income based on either tax filings from Schedule E or details from a lease agreement. Each method provides a clear pathway to assess income while accounting for expenses and potential losses, which can ultimately affect the debt-to-income ratio and overall qualification for a mortgage. By following the structured steps laid out in the form, those involved in real estate transactions can find clarity and reassurance in what may otherwise be a complicated process.
Fannie Mae 1037 Example
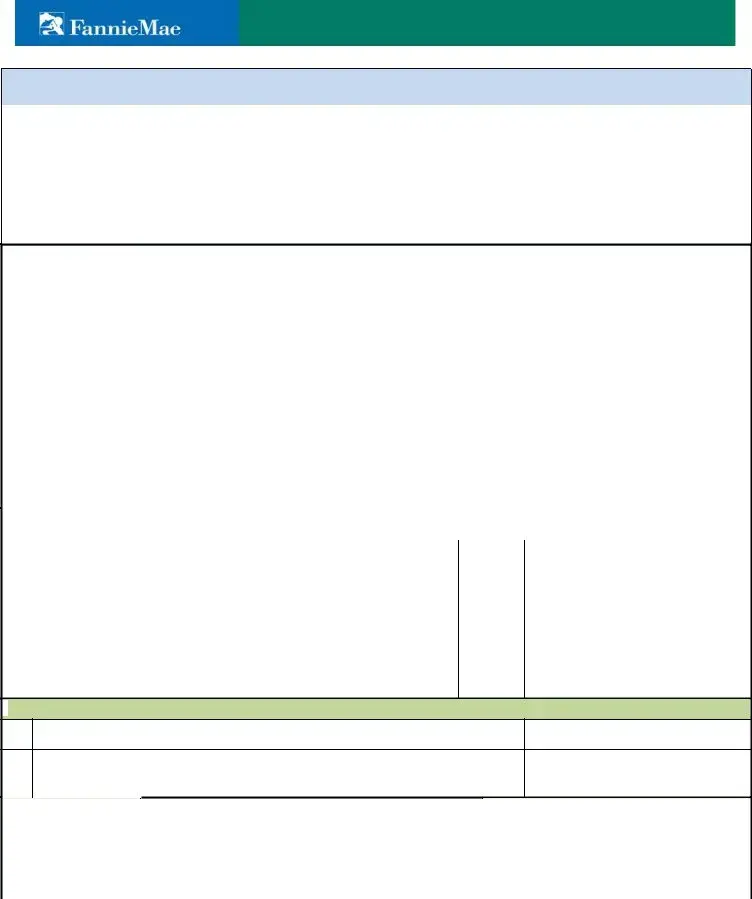
Rental Income Worksheet
Principal Residence, 2- to
Documentation Required: |
|
Address of Principal Residence: |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
Schedule E (IRS Form 1040) OR |
|
|
|
|
||
Enter |
Rental Unit |
Rental Unit |
Rental Unit |
|||
|
Lease Agreement or Fannie Mae Form 1025 |
|||||
|
_________ |
_________ |
_________ |
|||
|
|
|
||||
Step 1 When using Schedule E, determine the number of months the property was in service by dividing the Fair Rental Days by 30. If Fair Rental Days are not reported, the property is considered to be in service for 12 months unless there is evidence of a shorter term of service.
Step 1. Result: The number of months the property was in service: |
Result |
|
|
|
Step 2 Calculate the monthly qualifying rental income using Step 2A: Schedule E OR Step 2B: Lease Agreement or Form 1025.
|
|
|
Step 2 A. Schedule E - Part I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 |
Enter total rents received (from the |
Enter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
May enter rent from individual unit(s) or combine. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
Subtract total expenses. |
Subtract |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A3 |
Add back insurance expense. |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A4 |
Add back mortgage interest paid. |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A5 |
Add back tax expense. |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A6 |
Add back homeowners’ association dues. |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This expense must be specifically identified on Schedule E in order to add it back. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A7 |
Add back depreciation expense or depletion. |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A8 |
Add back any |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
must be evidence of the nature of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equals adjusted rental income. |
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A9 |
Divide by the number of months the property was in service (Step 1 Result). |
Divide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 2A. Result: Monthly qualifying rental income: |
Result |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 2 B. Lease Agreement or Fannie Mae Form 1025 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
This method is used when the transaction is a purchase or the property was acquired subsequent to the most recent tax filing. |
|
|
||||
|
|
B1 |
Enter gross monthly rent (from the lease agreement) or |
Enter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
market rent (from Form 1025) for the applicable rental unit. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B2 |
Multiply gross monthly rent or market rent by 75% (.75). The remaining 25% |
Multiply |
x .75 |
|
x .75 |
|
|
|
|
|
accounts for vacancy loss, maintenance, and management expenses. |
|
x .75 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equals monthly rental income per unit. |
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B3 |
Combine the monthly rental income of all |
Add |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(up to a maximum of 3 rental units since rental income is not eligible on the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
unit occupied by the borrower). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 2B. Result: Monthly qualifying rental income: |
Result |
|
|
|
|
|
 Step 3. Determine the qualifying impact using the combined result of Step 2A or Step 2B.
Step 3. Determine the qualifying impact using the combined result of Step 2A or Step 2B.
3A Add the monthly qualifying rental income to the borrower’s monthly qualifying income.
3B Identify the full amount of the PITIA as the borrower’s primary housing expense and include it in the
Use proposed PITIA when the subject property; existing PITIA when not the subject property.
|
|
DU Data Entry |
Monthly Income and Combined Housing Expenses |
|
Mortgage Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Subject Property |
Enter the amount of the monthly qualifying income in |
|
Include as the borrower’s primary housing |
|
|
|
|
“Subject Net Cash.” |
|
expense. For refinance transactions, identify |
|
|
|
|
|
|
the mortgage as a subject property lien. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enter the amount of the monthly qualifying income in “Net |
|
Include as the borrower’s primary housing |
|
|
|
|
|
Rental.” |
|
expense. |
|
Refer to the Rental Income topic in the Selling Guide for additional guidance.
Fannie Mae Form 1037 |
09.30.2014 |
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Fannie Mae 1037 form is used to calculate rental income for a principal residence that is a 2- to 4-unit property. |
| Documentation Requirements | To complete the form, you need either Schedule E from IRS Form 1040 or a lease agreement or Fannie Mae Form 1025. |
| Property Service Period | The property is considered in service for 12 months unless documented evidence shows a shorter rental period. |
| Monthly Income Calculation | The form allows for adjustments based on expenses like insurance, mortgage interest, and homeowners’ association dues. |
| Rental Agreement Method | The lease agreement or Form 1025 method is used for properties acquired after the last tax filing. |
| PITIA Inclusion | PITIA (Principal, Interest, Taxes, Insurance, and Association dues) must be included in the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio analysis. |
| Governing Law | The Fannie Mae 1037 form is governed by federal law, but state-specific laws may also apply to rental income calculations. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Fannie Mae 1037
Completing the Fannie Mae 1037 form requires attention to detail and an understanding of your rental income situation. Following these steps will help ensure that the form is filled out accurately, providing a clear picture of your rental income.
- Step 1: Determine how many months the property was in service. If you have Fair Rental Days, divide that number by 30. If Fair Rental Days are not reported, assume the property was in service for 12 months, unless you can prove a shorter duration.
- Step 2: Calculate your monthly qualifying rental income.
- Step 2A: If using Schedule E:
- A1: Enter total rents received from non-owner-occupied units.
- A2: Subtract total expenses.
- A3: Add back insurance expense if specifically identified on Schedule E.
- A4: Add back mortgage interest paid.
- A5: Add back tax expense.
- A6: Add back homeowners’ association dues, if applicable.
- A7: Add back depreciation or depletion expense.
- A8: Add back any one-time extraordinary expense, making sure to provide evidence.
- A9: Divide the adjusted rental income by the number of months the property was in service (result from Step 1).
- Step 2B: If using a Lease Agreement or Fannie Mae Form 1025:
- B1: Enter gross monthly rent or market rent for the rental unit.
- B2: Multiply gross monthly rent by 75% to account for vacancy loss and expenses.
- B3: Combine the monthly rental income for all non-owner-occupied units, up to three units.
- Step 3: Determine the qualifying impact of your rental income.
- 3A: Add the monthly qualifying rental income to the borrower’s monthly qualifying income.
- 3B: Identify the full amount of the PITIA as the primary housing expense and include it in the debt-to-income ratio.
After completing these steps, you should have all the information needed to provide a comprehensive understanding of your rental income, which will be crucial for your lenders and financial assessments. Take your time to ensure accuracy, especially with the figures and supporting documentation you provide.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the Fannie Mae 1037 form used for?
The Fannie Mae 1037 form is primarily a Rental Income Worksheet designed for two to four-unit properties that qualify as principal residences. It assists lenders in calculating the monthly qualifying rental income for these properties. Accurate calculations are essential for assessing borrower eligibility and determining debt-to-income ratios. Without this form, evaluating rental income can be inefficient and less reliable.
What documents are required when completing the Fannie Mae 1037 form?
When filling out the Fannie Mae 1037 form, you will need either Schedule E from the IRS Form 1040 or a Lease Agreement (or Fannie Mae Form 1025). Schedule E includes detailed financial information about the rental property, while a Lease Agreement provides the terms of rental occupancy. These documents help establish the income generated by the property to calculate qualifying rental income accurately.
How is the monthly qualifying rental income calculated?
To calculate monthly qualifying rental income, follow one of two paths: using Schedule E or the Lease Agreement/Fannie Mae Form 1025. If using Schedule E, you first calculate your adjusted rental income by accounting for various expenses and then divide that amount by the number of months the property was in service. If using the Lease Agreement or Form 1025, gross monthly rent is multiplied by 75% to account for potential vacancies and expenses. The calculated figures help determine your monthly rental income.
What should I do if Fair Rental Days are not reported?
If Fair Rental Days are not included in the documentation, assume that the property is in service for 12 months. However, if there is evidence indicating a shorter rental period, adjust the calculation accordingly. This assumption helps ensure that your calculations remain as accurate as possible even when data is incomplete.
Is there a maximum number of rental units that can be included in the calculation?
Yes, when calculating monthly qualifying rental income, you may include rental income from up to three non-owner-occupied rental units. Income from the unit occupied by the borrower cannot be considered. This limitation safeguards lenders against inflated income calculations and provides a more accurate assessment of the borrower’s financial situation.
How does the qualifying impact of rental income affect the borrower’s financial evaluation?
The qualifying impact of rental income directly influences the borrower’s financial evaluation and debt-to-income ratio. To determine the impact, combine the monthly qualifying rental income with the borrower’s monthly qualifying income. Additionally, the full amount of the PITIA (Principal, Interest, Taxes, Insurance, and Association dues) must be included in the borrower’s housing expenses. This process ensures that all financial obligations are accurately accounted for during the lending process.
Common mistakes
Completing the Fannie Mae 1037 form is an important task for many seeking to establish rental income. However, several common mistakes can lead to complications or inaccuracies in the documentation. It is essential to pay attention to detail and understand the requirements to avoid these pitfalls.
One mistake frequently made is improper documentation of rental income. Many individuals rely solely on personal records or informal agreements, failing to provide the required Schedule E or lease agreements. Without proper documentation, the income may be deemed unverifiable, which can negatively impact loan approval chances. It is crucial to submit official documents that reflect actual rental activity.
Another common error involves miscalculating the number of months the property has been in service. Individuals often neglect to check the Fair Rental Days reported on Schedule E. If this figure is not available, it is assumed the property was in service for 12 months, potentially leading to an inflated rental income calculation. Applicants must ensure they accurately account for the rental service period to reflect realistic income figures.
Many also struggle with accurately calculating the monthly qualifying rental income. When using Schedule E, for example, failing to identify and subtract all applicable expenses can inflate the rental income. It is important to meticulously record all expenses, such as insurance, tax, and HOA dues, as these directly affect the adjusted rental income calculation. A lack of attention to this step may yield a misleading representation of the financial situation.
Additionally, errors can occur during the interpretation of net rental income derived from lease agreements or Fannie Mae Form 1025. Some mistakenly assume that merely providing the gross monthly rent suffices. It is vital to apply the 75% adjustment to account for vacancies and maintenance expenses. This adjustment is crucial in obtaining a realistic figure that lenders will consider.
Finally, many overlook the importance of properly integrating the rental income into the overall financial picture when determining qualifying impacts. It is essential to combine the monthly qualifying rental income with the borrower’s qualifying income accurately. Misrepresenting this total can lead to complications in debt-to-income calculations and affect the final loan outcome.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking the necessary steps to avoid them, individuals can emerge with accurate and favorable rental income documentation. Thorough preparation and attention to detail will serve to benefit them in the long run.
Documents used along the form
The Fannie Mae 1037 form is essential for documenting rental income for a principal residence that is a 2- to 4-unit property. Alongside this form, several other documents are commonly used to ensure accurate assessment and compliance. Below is a brief overview of these important forms and documents.
- Schedule E (IRS Form 1040): This form details rental income and expenses for different rental properties, allowing property owners to report profits or losses on their tax returns.
- Lease Agreement: A legal contract between the landlord and tenant specifying the terms of rent, duration, and the responsibilities of both parties. It provides essential data like rental amounts and lease duration.
- Fannie Mae Form 1025: This form provides a detailed analysis of the rental property’s market rent. It helps in determining the potential monthly income based on the property's location and condition.
- Mortgage Note: A document that outlines the borrower's promise to repay the loan according to specified terms. It includes the interest rate, payment schedule, and consequences of default.
- Property Appraisal Report: An assessment prepared by a licensed appraiser that evaluates the property's market value. This report is vital for determining both its rental and sale potential.
- Insurance Policy Documentation: These documents outline the type of insurance coverage held on the property. They may be required to protect against potential damage or liability claims.
- Tax Returns: The borrower’s previous tax returns help verify income reported from rental units and ensure consistency with Schedule E information.
- Verification of Employment (VOE): A form used to verify a borrower’s employment status and income. This can help the lender confirm financial stability in conjunction with rental income documentation.
These documents play a crucial role in the assessment process for rental income. Together, they help establish a clear financial picture of the property and the borrower, facilitating a smoother transaction for everyone involved.
Similar forms
- Schedule E (IRS Form 1040): This form is used to report rental income and expenses on personal tax returns. It serves to calculate the net rental income, similar to how the 1037 form estimates monthly qualifying rental income.
- Lease Agreement: A formal contract between a landlord and tenant, detailing the rental period and conditions. The rental income from the lease agreement can be calculated in a manner similar to the method specified in the 1037 form.
- Fannie Mae Form 1025: This form provides market rent data for properties. It is used similarly to the 1037 form to assess rental income for underwriting purposes.
- Rental Property Operating Expenses Worksheet: This document lists various expenses related to rental properties. Like the 1037 form, it captures necessary financial details to determine qualifying rental income.
- Form 8825 (IRS): Used for reporting rental real estate income and expenses by partnerships or S corporations. This form similarly breaks down rental finances, aiding in income validation like the 1037 form.
- Net Income Calculation Sheet: An internal document used by mortgage companies to summarize rental income and expenses. It functions similarly to the 1037 form in that it calculates net qualifying income.
- Profit and Loss Statement: A financial report that summarizes revenues, costs, and expenses to show net profit or loss. This can be used in conjunction with the 1037 form to provide a broader view of rental income operations.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing the Fannie Mae 1037 form, adherence to guidelines ensures accuracy and avoids delays. Below is a concise list of actions to take and to avoid during this process.
- Do: Use Schedule E or a lease agreement to accurately document rental income.
- Do: Clearly identify all expenses on Schedule E to ensure proper adjustments are made to rental income.
- Do: Divide Fair Rental Days by 30 to determine the number of months the property was in service.
- Do: Ensure that the property is evaluated according to the correct guidelines for the number of rental units.
- Don't: Skip providing evidence for extraordinary expenses; always include documentation.
- Don't: Ignore the requirement to account for vacancy loss and maintenance expenses when calculating rental income.
- Don't: Enter information without double-checking for accuracy and completeness.
- Don't: Assume that all expenses can be added back without verifying their eligibility on Schedule E.
Misconceptions
- Fannie Mae Form 1037 is only for single-family homes. This form can be used for 2- to 4-unit properties, not just single-family residences.
- You must have a Schedule E to calculate rental income. While Schedule E can assist, it is not the only method. Lease agreements or Fannie Mae Form 1025 can also be used.
- Rental income is calculated the same way for all properties. The calculation varies based on if you are using Schedule E or a lease agreement.
- You cannot include any expenses when calculating rental income. Certain expenses can be added back when determining adjusted rental income, as specified in the form.
- Only landlords can use Form 1037. This form is available to any borrower who has qualifying rental income, not just landlords.
- The number of months a property is in service must always be 12. If fair rental days are not reported, it is typically considered in service for 12 months unless evidence indicates otherwise.
- All rental units must be included in the income calculation. Only up to three non-owner-occupied rental units should be included when calculating rental income.
- Fannie Mae Form 1037 is only for new purchases. This form is applicable for purchases and also for properties acquired after the most recent tax filing.
- All rental income sources are treated the same. Income from non-owner-occupied units is treated differently than income from owner-occupied ones.
- Qualifying rental income is determined solely by subtracting expenses from gross rent. The calculation is more complex and includes multiple steps and adjustments.
Key takeaways
Key Takeaways for Filling Out the Fannie Mae 1037 Form:
- Determine the number of months the property was in service by dividing Fair Rental Days by 30. If not reported, assume 12 months unless you have evidence of less.
- Use either Schedule E or a lease agreement to calculate monthly rental income. This step is crucial for accurately reflecting income from rental properties.
- Add back certain expenses like insurance and mortgage interest when using Schedule E, as they can help adjust the rental income figure higher.
- When using a lease agreement, multiply the gross monthly rent by 75% to account for potential vacancy and maintenance costs, allowing for a more realistic rental income estimate.
Browse Other Templates
Comed Customer Service - Understanding the requirements for evidence will strengthen your claim submission.
Usa Draft - The intention to resolve this matter positively is made clear.
How to File Contempt of Court for Child Support in California - The document must include specifics about the context of the alleged violations.