Fill Out Your Food Allergy Action Plan Form
The Food Allergy Action Plan form is an essential document designed to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals with food allergies. This form captures critical information such as the individual's name, date of birth, and specific allergens to which they are allergic. A section is dedicated to health background, including the individual’s weight and asthma status, which can significantly affect the management of allergic reactions. It provides detailed steps to follow in the event of an allergic reaction, categorizing symptoms into severe and mild categories. The plan emphasizes the importance of using epinephrine promptly, providing clear instructions on when and how to administer it. Additionally, emergency contacts are included to facilitate swift communication in critical situations. This form is not just a record; it’s a proactive measure to protect against life-threatening situations that can arise from food allergies. With a clear structure, it guides caregivers and emergency responders alike, ensuring preparedness and informed action when every second counts.
Food Allergy Action Plan Example
|
|
|
|
Name:__________________________________________________________________________ D.O.B.:_____________________ |
|
PLACE |
|
|
|
PICTURE |
|
Allergic to:__________________________________________________________________________________________________ |
|
HERE |
|
Weight:_________________ lbs. Asthma: □ Yes (higher risk for a severe reaction) □ No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: Do not depend on antihistamines or inhalers (bronchodilators) to treat a severe reaction. USE EPINEPHRINE. |
|
|
|
Extremely reactive to the following allergens:_________________________________________________________
THEREFORE:
□If checked, give epinephrine immediately if the allergen was LIKELY eaten, for ANY symptoms.
□If checked, give epinephrine immediately if the allergen was DEFINITELY eaten, even if no symptoms are apparent.
FOR ANY OF THE FOLLOWING:
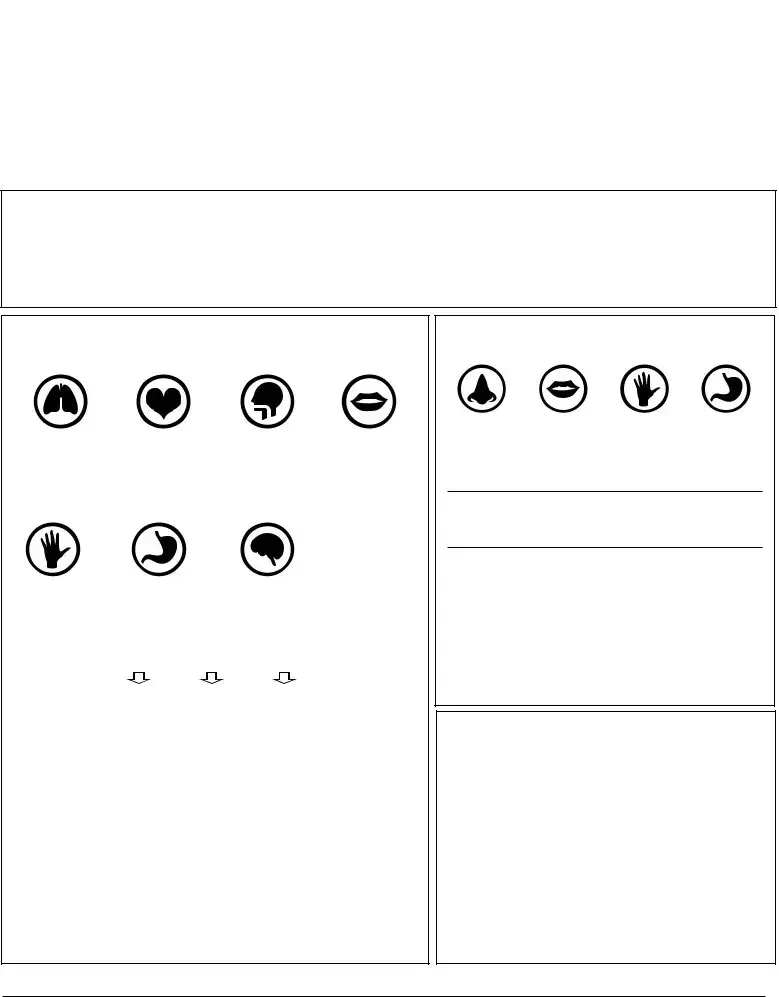
SEVERE SYMPTOMS
LUNG |
HEART |
THROAT |
MOUTH |
Shortness of |
Pale or bluish |
Tight or hoarse |
Significant |
breath, wheezing, |
skin, faintness, |
throat, trouble |
swelling of the |
repetitive cough |
weak pulse, |
breathing or |
tongue or lips |
|
dizziness |
swallowing |
|
|
|
|
OR A |
SKIN |
GUT |
OTHER |
COMBINATION |
of symptoms |
|||
Many hives over |
Repetitive |
Feeling |
from different |
body, widespread |
vomiting, severe |
something bad is |
body areas. |
redness |
diarrhea |
about to happen, |
|
|
|
anxiety, confusion |
|
1.INJECT EPINEPHRINE IMMEDIATELY.
2.Call 911. Tell emergency dispatcher the person is having
anaphylaxis and may need epinephrine when emergency responders arrive.
•Consider giving additional medications following epinephrine:
»Antihistamine
»Inhaler (bronchodilator) if wheezing
•Lay the person flat, raise legs and keep warm. If breathing is difficult or they are vomiting, let them sit up or lie on their side.
•If symptoms do not improve, or symptoms return, more doses of epinephrine can be given about 5 minutes or more after the last dose.
•Alert emergency contacts.
•Transport patient to ER, even if symptoms resolve. Patient should remain in ER for at least 4 hours because symptoms may return.
MILD SYMPTOMS
NOSE |
MOUTH |
SKIN |
GUT |
Itchy or |
Itchy mouth |
A few hives, |
Mild |
runny nose, |
|
mild itch |
nausea or |
sneezing |
|
|
discomfort |
FOR MILD SYMPTOMS FROM MORE THAN ONE
SYSTEM AREA, GIVE EPINEPHRINE.
FOR MILD SYMPTOMS FROM A SINGLE SYSTEM
AREA, FOLLOW THE DIRECTIONS BELOW:
1.Antihistamines may be given, if ordered by a healthcare provider.
2.Stay with the person; alert emergency contacts.
3.Watch closely for changes. If symptoms worsen, give epinephrine.
MEDICATIONS/DOSES
Epinephrine Brand or Generic: _________________________________
Epinephrine Dose: □ 0.1 mg IM □ 0.15 mg IM □ 0.3 mg IM
Antihistamine Brand or Generic:_ _______________________________
Antihistamine Dose:___________________________________________
Other (e.g.,
____________________________________________________________
PATIENT OR PARENT/GUARDIAN AUTHORIZATION SIGNATURE |
DATE |
PHYSICIAN/HCP AUTHORIZATION SIGNATURE |
DATE |
FORM PROVIDED COURTESY OF FOOD ALLERGY RESEARCH & EDUCATION (FARE) (FOODALLERGY.ORG) 5/2020
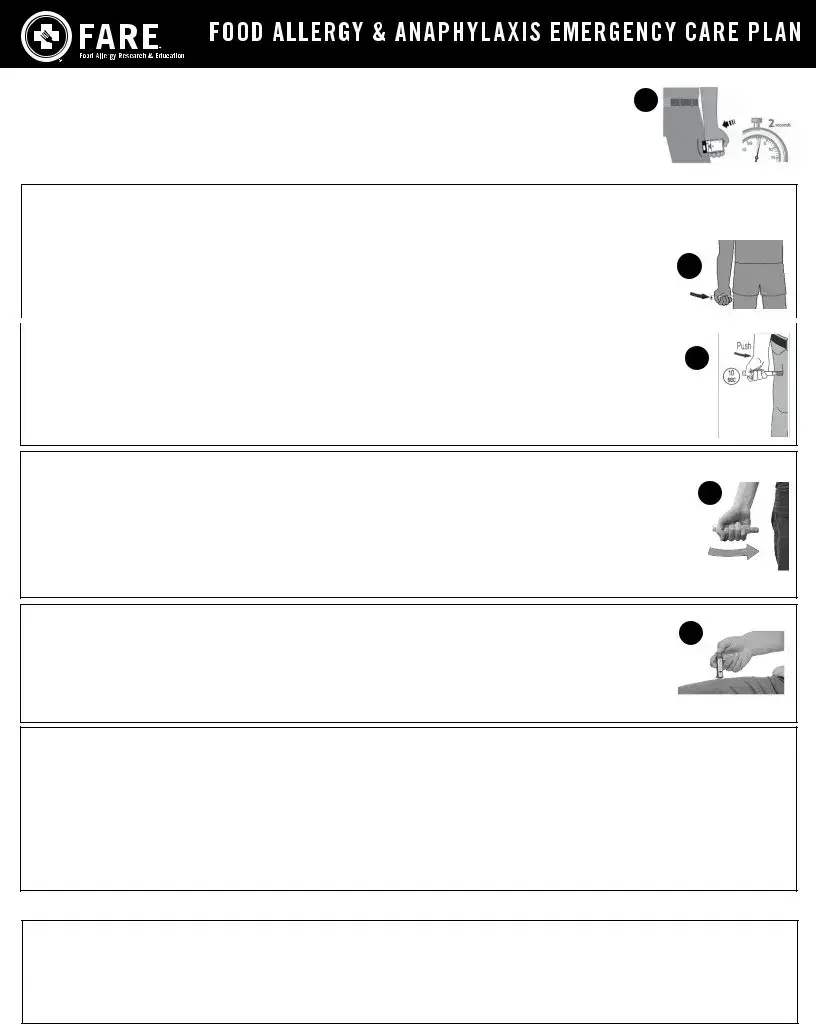
HOW TO USE |
3 |
||
1. |
Remove |
||
|
|||
2. |
Place black end of |
|
|
3. |
Press firmly until you hear a click and hiss sound, and hold in place for 2 seconds. |
|
|
4. |
Call 911 and get emergency medical help right away. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HOW TO USE EPIPEN®, EPIPEN JR® (EPINEPHRINE)
1. |
Remove the EpiPen® or EpiPen Jr® |
|
|
2. |
Grasp the |
|
|
|
remove the blue safety release by pulling straight up. |
4 |
|
3. |
Swing and push the |
||
|
|||
|
3 seconds (count slowly 1, 2, 3). |
|
|
4. |
Remove and massage the injection area for 10 seconds. Call 911 and get emergency medical help right away. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
HOW TO USE IMPAX EPINEPHRINE INJECTION (AUTHORIZED GENERIC OF ADRENACLICK®), |
|
||
USP |
5 |
||
1.Remove epinephrine
2.Pull off both blue end caps: you will now see a red tip. Grasp the
3.Put the red tip against the middle of the outer thigh at a
4.Remove and massage the area for 10 seconds. Call 911 and get emergency medical help right away.
HOW TO USE TEVA’S GENERIC EPIPEN® (EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP) |
|
TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES |
5 |
1. Quickly twist the yellow or green cap off of the |
2.Grasp the
3.Place the orange tip against the middle of the outer thigh at a right angle to the thigh.
4.Swing and push the
5.Remove and massage the injection area for 10 seconds. Call 911 and get emergency medical help right away.
HOW TO USE SYMJEPI™ (EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP)
1. When ready to inject, pull off cap to expose needle. Do not put finger on top of the device. |
2 |
2.Hold SYMJEPI by finger grips only and slowly insert the needle into the thigh. SYMJEPI can be injected through clothing if necessary.
3.After needle is in thigh, push the plunger all the way down until it clicks and hold for 2 seconds.
4.Remove the syringe and massage the injection area for 10 seconds. Call 911 and get emergency medical help right away.
5.Once the injection has been administered, using one hand with fingers behind the needle slide safety guard over needle.
ADMINISTRATION AND SAFETY INFORMATION FOR ALL
1.Do not put your thumb, fingers or hand over the tip of the
2.If administering to a young child, hold their leg firmly in place before and during injection to prevent injuries.
3.Epinephrine can be injected through clothing if needed.
4.Call 911 immediately after injection.
OTHER DIRECTIONS/INFORMATION (may
Treat the person before calling emergency contacts. The first signs of a reaction can be mild, but symptoms can worsen quickly.
EMERGENCY CONTACTS — CALL 911 |
OTHER EMERGENCY CONTACTS |
RESCUE SQUAD: _______________________________________________________________________ |
NAME/RELATIONSHIP:_____________________________________ PHONE: ____________________ |
|
|
DOCTOR:__________________________________________________ PHONE: ____________________ |
NAME/RELATIONSHIP:_____________________________________ PHONE: ____________________ |
PARENT/GUARDIAN: _______________________________________ PHONE: ____________________ |
NAME/RELATIONSHIP:_____________________________________ PHONE: ____________________ |
|
FORM PROVIDED COURTESY OF FOOD ALLERGY RESEARCH & EDUCATION (FARE) (FOODALLERGY.ORG) 5/2020
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient Information | The Food Allergy Action Plan form requires essential patient details, including name, date of birth, weight, and allergens. This information helps ensure proper care during an allergic reaction. |
| Severe Symptoms Protocol | In cases of severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or significant swelling, epinephrine must be administered immediately, followed by a call to emergency services. |
| Legal Framework | In the United States, different states have specific laws governing the use of allergy action plans. For example, California's Education Code Section 49414 outlines requirements for schools to establish plans for students with severe allergies. |
| Administration of Medications | The form specifies the appropriate epinephrine dosage and allows for additional medications, such as antihistamines, to be listed. This versatility can be vital in responding to different symptoms or situations. |
| Mild Symptoms Management | Mild symptoms like hives or a runny nose can be monitored. However, if symptoms worsen or additional reactions occur, epinephrine should be administered without delay. |
| Emergency Contacts | The form emphasizes the importance of maintaining a list of emergency contacts, including doctors and family members. Quick access to this information can facilitate prompt medical attention during a crisis. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Food Allergy Action Plan
The Food Allergy Action Plan form is a critical tool for managing food allergies effectively. It collects essential information needed for quick response during allergic reactions and facilitates communication among caregivers, parents, and healthcare professionals. Follow the steps below to complete the form accurately.
- Begin by filling in the patient’s Name at the top of the form.
- Next, write the patient’s Date of Birth (D.O.B.) next to the name.
- Attach a recent Picture of the patient in the designated area.
- List the food or substances the patient is Allergic to in the provided space.
- Record the patient’s Weight in pounds.
- Indicate if the patient has Asthma by checking the appropriate box (□ Yes or □ No).
- If applicable, detail any allergies the patient is Extremely reactive to in the specified section.
- Select the appropriate Epipen instructions based on symptoms and check the relevant options regarding when to administer epinephrine.
- Fill in any noted SEVERE SYMPTOMS witnessed in the patient in the appropriate sections.
- For MILD SYMPTOMS, follow the instructions and provide the necessary information about medications here:
- Record the Epinephrine Brand or Generic and corresponding Dose.
- Specify the Antihistamine Brand or Generic and the appropriate Dose.
- Provide details for any Other medications or treatments that may be necessary.
- Have the Patient or Parent/Guardian sign, date the form, and attach the physician or healthcare provider’s authorization signature.
- Complete the emergency contact information, including names and phone numbers.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is a Food Allergy Action Plan?
A Food Allergy Action Plan is a document designed to guide individuals and caregivers in responding to allergic reactions. It outlines critical information specific to a person's allergies, including the allergens involved, symptoms to watch for, and emergency procedures to follow in case of an allergic reaction.
Why is it important to have a Food Allergy Action Plan?
Having a Food Allergy Action Plan is essential because it provides clear instructions for managing allergic reactions. This plan helps caregivers and educators respond appropriately and quickly, which is crucial since food allergies can lead to severe reactions, including anaphylaxis.
Who should use a Food Allergy Action Plan?
This plan is beneficial for anyone diagnosed with food allergies. It is especially important for children in school settings or at daycare and for adults with allergies who may require assistance from others in the event of a reaction.
What information should be included in the Food Allergy Action Plan?
The plan should include the individual's name, date of birth, allergies, emergency medications, dosage details, and emergency contacts. It also lists symptoms that may indicate a mild or severe reaction and clear steps on what to do if a reaction occurs.
How should epinephrine be administered according to the plan?
Epinephrine should be injected into the outer thigh immediately if there are severe symptoms or if it’s known that an allergen was consumed. Hold the injector in place for a specified time, typically around 3 seconds. After administering, call 911 right away.
What should I do if mild symptoms occur?
If mild symptoms appear, follow the directions provided for mild reactions. Consider administering antihistamines as directed and monitor the situation closely. Always be ready to act quickly if the symptoms worsen.
Is it necessary to go to the emergency room after a reaction?
Yes, individuals should go to the emergency room even if symptoms improve. Doctors recommend remaining at the ER for at least four hours, as symptoms can return after an initial reaction.
Can individuals self-carry their epinephrine auto-injectors?
Yes, individuals can self-carry their epinephrine auto-injectors if they are capable of recognizing their symptoms and know how to use the injectors. It is vital for them to be educated and trained on administering the injection correctly.
Who should I contact in case of an emergency?
In case of an emergency, first call 911. Then, contact the designated emergency contacts listed on the Food Allergy Action Plan. Keeping a list of these contacts nearby is recommended in case of an emergency.
How often should I update the Food Allergy Action Plan?
Regularly review and update the plan, especially when there are changes in allergies, medications, or contacts. Annually checking with a healthcare provider can ensure that the information remains accurate and up-to-date.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Food Allergy Action Plan form is a critical task that directly impacts the safety and well-being of individuals with food allergies. However, there are several common mistakes that people make which can lead to serious consequences. One common error is failing to provide accurate and complete information about the individual's allergies. For example, if someone lists "nuts" but doesn’t specify the type of nuts, this vagueness might create confusion during an emergency situation. It’s essential to be as precise as possible when detailing allergies.
Another frequent mistake is neglecting to include recent medical information. The form specifically asks for the weight of the individual and whether they have asthma. Forgetting to include current weight can affect the dosage of medication to administer during an allergic reaction. Asthma can increase the severity of allergic reactions, so noting its presence is crucial. Skipping these details can put the individual at risk.
Some people also mistakenly overlook the section concerning symptoms. The instructions are clear regarding the need for immediate action based on the severity of symptoms encountered. Many individuals may not realize that mild symptoms, when presented in combination, require epinephrine. When the information is incomplete or misunderstood, it can lead to delayed treatment during critical situations.
In addition to not identifying all allergens, failing to check the appropriate boxes for administering epinephrine can also pose a danger. The form can be easily misinterpreted, and by not marking the relevant boxes, individuals may hesitate in administering epinephrine, putting the person at risk for severe reactions.
Lastly, people often forget to update the form regularly. Changes in allergies, medications, or emergency contacts necessitate updating the form. If this is ignored, the emergency responders may be unaware of the risks or specific medications available, leading to inadequate care. Keeping the Food Allergy Action Plan current is as important as completing it accurately in the first place.
Documents used along the form
The Food Allergy Action Plan form is an essential document for managing food allergies, but it is often used alongside other important forms and documents. Each of these documents serves a specific purpose in promoting health and safety for individuals with food allergies.
- Medication Authorization Form: This document allows a parent or guardian to authorize school personnel to administer specific medications, including epinephrine, to a child in case of an allergic reaction.
- Emergency Contact Information Form: This form provides a list of emergency contacts, including family members and doctors, ensuring quick communication during a medical emergency.
- Health History Form: A comprehensive document detailing a patient’s medical history, allergies, and any past reactions. This can help healthcare providers make informed decisions during treatment.
- Individualized Health Plan: This plan outlines specific health needs for a student in an educational setting. It includes details about allergies, triggers, and emergency procedures.
- Consent for Release of Information Form: This document grants permission to share a patient’s medical information with relevant parties, such as schools or camp organizations, to ensure safety and preparedness.
- Food Allergy Disclosure Form: This form is used to inform caregivers and staff about specific allergies and necessary avoidance strategies for individuals at camps or schools.
- Incident Report Form: This document is used to record any allergic reactions that occur, documenting details such as the time, symptoms, actions taken, and any follow-up required.
- Nutritional Information Sheet: This sheet provides important information about allergens found in various foods, helping individuals and caregivers make safe dietary choices.
- Emergency Action Plan: A detailed plan that outlines the steps to take if an individual experiences an allergic reaction. It specifies when and how to administer medications like epinephrine.
Using these documents in conjunction with the Food Allergy Action Plan can enhance safety and preparedness in managing food allergies effectively. Each form plays a critical role in ensuring that individuals with food allergies receive the care and attention they need in emergencies.
Similar forms
The Food Allergy Action Plan form shares common features with several other important documents used in emergency situations. Understanding the similarities can enhance awareness and preparedness. Here are eight documents that are similar:
- Individual Health Plan (IHP): Like the Food Allergy Action Plan, an IHP outlines specific medical needs and emergency protocols for an individual, ensuring that essential information is readily available to caregivers and first responders.
- Emergency Medical Information Form: This form provides crucial health details about an individual that medical personnel may require in emergencies. Both documents aim to facilitate quick and effective care during critical situations.
- Asthma Action Plan: Similar to the Food Allergy Action Plan, the Asthma Action Plan details symptoms, medication dosages, and emergency procedures. Both highlight the importance of timely intervention and clear steps to take during an allergic or asthmatic emergency.
- Seizure Action Plan: This plan contains guidelines for handling seizure episodes. Just as the Food Allergy Action Plan provides a clear course of action, the Seizure Action Plan offers essential instructions for caregivers unsure of how to respond effectively in the moment.
- Diabetes Management Plan: This document outlines daily care and emergency measures for individuals with diabetes. Both forms prioritize understanding the medical condition to ensure the safety and health of the person affected.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): The MAR tracks medications given to a patient, similar to how the Food Allergy Action Plan specifies which medications to administer during allergic reactions. Both promote accountability and accurate treatment information.
- Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP): A BIP helps to identify strategies and interventions for specific behavioral challenges. While focused on behavior rather than medical emergencies, both documents require careful planning and proactive measures to ensure the safety and well-being of the individual.
- School Emergency Response Plan: This plan outlines how schools should respond to various emergencies involving students. Like the Food Allergy Action Plan, it emphasizes the need for quick response and clear communication among staff and first responders.
Awareness of these documents can empower caregivers, educators, and medical personnel to act swiftly and effectively during emergencies, ultimately supporting the well-being of individuals at risk.
Dos and Don'ts
- Do ensure all fields are accurately completed, including the patient’s name, date of birth, and specific allergies.
- Do attach a recent photograph of the patient to help with quick identification in emergencies.
- Do check the section regarding asthma, as it indicates a higher risk for severe reactions.
- Do clearly indicate if the patient is extremely reactive to certain allergens.
- Do have a plan for accessing emergency contacts and call 911 immediately when anaphylaxis occurs.
- Don’t wait for symptoms to improve; administer epinephrine as directed if allergens are likely or definitely eaten.
- Don’t substitute antihistamines or inhalers for epinephrine during a severe allergic reaction.
- Don’t assume mild symptoms will remain mild; escalate treatment if symptoms worsen.
- Don’t skip the signature sections for both patient/guardian and physician; this indicates approval and understanding of the allergy plan.
Misconceptions
-
Only those with severe allergies need a Food Allergy Action Plan. This is not true. Anyone with any level of food allergy can benefit from having a plan. Even mild allergies can lead to serious allergic reactions, so a plan helps ensure safety at all times.
-
Antihistamines can replace epinephrine in emergencies. This is a common misconception. Antihistamines are not effective in treating severe allergic reactions. Epinephrine is the first-line treatment and should be administered immediately if severe symptoms occur.
-
Once symptoms improve, it's okay to skip the emergency room. This is dangerous thinking. Even if symptoms resolve, the individual should still go to the emergency room. Symptoms can return, and monitoring is essential.
-
The Food Allergy Action Plan is only for school use. This is incorrect. While it is critical for schools to have this plan, it is also important to have it at home, at gatherings, and anywhere the individual may encounter allergens.
Key takeaways
- Fill out all necessary fields, including the child's name, date of birth, and allergens.
- Attach a recent photo of the child to the form for easy identification.
- Indicate the child’s weight and whether they have asthma, as this impacts emergency response.
- Clearly list all allergens to which the child is extremely reactive.
- Understand the importance of using epinephrine immediately in case of a severe reaction.
- Know the signs of a severe reaction such as difficulty breathing, skin changes, or confusion.
- Always call 911 after administering epinephrine, as emergency help is critical.
- For mild symptoms, follow instructions for antihistamines and monitor closely for changes.
- Keep emergency contacts readily available and inform them of the action plan.
- Ensure that the child understands their own allergy plan, if appropriate for their age.
Browse Other Templates
Explore Rate Authorization Form - Keep in mind that discrepancies could affect the guest’s experience.
Set Up Direct Deposit - Direct deposit is a convenient way to receive your payments without paper checks.
