Fill Out Your Food Protection Training Manual Form
The Food Protection Training Manual is an essential resource aimed at enhancing food safety knowledge among food service operators in New York City. This manual covers a wide range of topics that are crucial for anyone involved in food handling, from receiving and storing food to understanding microbiology and the common foodborne illnesses that can arise from improper practices. Starting with an introduction to food safety principles, it guides readers through various sections addressing topics like hazards to health, food allergies, personal hygiene, and safe food preparation techniques. The manual emphasizes the importance of maintaining safe temperatures during cooking and holding food, as well as the need for proper cleaning and sanitizing procedures. Specialized areas such as the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Food Protection System, pest control, and local laws specific to New York City further equip readers with the knowledge needed to operate within compliance. Importantly, the manual includes practical tools like quizzes, worksheets, and essential contact numbers to facilitate learning and adherence to best practices. Through a structured approach, this manual not only serves as a guide for training but also as a critical reference for food service professionals aiming to ensure the safety and health of the public in their establishments.
Food Protection Training Manual Example

C I T Y O F N E W Y O R K
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction 1
Introduction to Food Safety 2
Receiving Foods 4
Storage of Food 8
Hazards to Our Health 11
Food Allergies 12
Microbiology of Foods 13
Common Foodborne Illnesses 18
Personal Hygiene 22
Food Preparation 24
Cooking, Hot Holding,
Cooling & Reheating 25
Cleaning and Sanitizing 31
HACCP Food Protection System 35
Pest Control 38
Plumbing 48
Operating a Temporary Food
Service Establishment 51
Required Postings 53
Reduced Oxygen Packaging 55
Local Laws 56
NYC Health Code Extracts 58
Food Defense Strategies 60
Trans Fat 62
Workplace Safety and Health 66
Form 198E Food Establishment
Inspection Report 69
Quizzes 75
Numbers to Remember 79
Work Sheets 83
foDEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & MENTALdHYGIENE
P R O T E C T I O N
T R A I N I N G
M A N U A L
R E V I S E D E D I T I O N , 2 0 1 3

fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
If you have questions or com- ments regarding this manual,
please call the Health Academy at
(917)
If you wish to contact:
OATH – HEALTH TRIBUNAL 66 John Street, 11th Floor
NY, NY 10038
☎(212)
BUREAU OF FOOD SAFETY &
COMMUNITY SANITATION
125 Worth Street, 9th & 10th Floors Box
☎(212)
☎(212)
CITYWIDE
LICENSING CENTER
42Broadway NY, NY 10004
☎(212)
HEALTH ACADEMY 413 East 120 Street 2nd Floor
NY, NY 10035
☎(917)
INSPECTOR GENERAL
80 Maiden Lane NY, NY 10005
☎(212)
RESTAURANT WORKER
SAFETY AND HEALTH
☎(212)
REVISED EDITION 2013
Published by the
New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene
Division of Environmental Health
125 Worth Street
New York, NY 10013
ii
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E

fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene has the jurisdiction to regulate all matters affecting health in the city and to perform all those
functions and operations that relate to the health of the people of the city.
this certification may be needed at an establishment to have coverage dur- ing all shifts, vacations or illnesses.
The Food Protection Manual has been designed to assist participants of the course to better understand the principles of safe food handling. It serves as a reference for food ser- vice operators and it includes the necessary information to pass the final examination.
The Health Code
These are regulations that were formulated to allow the Department to effectively protect the health of the population. Among the rules embodied in the Health Code is Article 81 which regulates the oper- ations of food establishments for the purpose of preventing public health hazards.
Environmental Health Division
The Division of Environmental Health is the Commission within the Health Department that is concerned with public health and works to eliminate the incidence of injury and illness caused by environmental factors.
There are several Offices and Bureaus within this division. One of these is the Bureau of Food Safety and Community Sanitation that has the responsibility for con- ducting inspections of food service and food processing establishments. These inspections are performed by Public Health Sanitarians.
All Sanitarians have Department of Health and Mental Hygiene badges and identification cards which they must display whenever it is requested of them.
It is illegal to offer a Sanitarian any bribe, gratuity or reward for official misconduct; this is a crime
that can result in fines, and /or imprisonment, and the revocation of permits. Also, Sanitarians are not authorized to conduct any monetary transactions on behalf of the Department.
Inspector General
This is an office that exists within the Health Department with the responsibility of investigating any incidence of alleged corrupt activity. Investigations may be conducted as a result of complaints by employees of the Department or members of the public.
Health Academy
The Health Academy is an office within the Division of Environmental Health. One of its responsibilities is to provide training and certification courses for individuals from the public as mandated by the Health Code.
The Food Protection Course is one of the courses taught here. The Food Protection Course is required by the Health Code for supervisors of food service establishments and
The Food Protection Course in English, Spanish and Chinese is now also available
Register for Health Academy Classes
You may now register and pay online for courses offered at the Department of Health and Mental Hygiene’s Health Academy, includ- ing the Food Protection Course for restaurants. This new service allows you to avoid going to the Citywide Licensing Center to register for a course. You may also use the
How does it work?
Go to the registration web page, nyc.gov/healthacademy, select a course and date, pay the appropriate fee and receive confirmation.
You will be asked to provide some personal information before regis- tering. In most cases, you will be able to select from a list of course dates. If you don’t see a date that is convenient, check back as new course dates are added frequently.
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
1 |
|
|
|

fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
QUICK REVIEW
1.All food service establishments must have a current and valid permit issued by the NYC Health Department.
TRUE FALSE
2.Health Inspectors have the right to inspect a food service or food processing establishment as long as it is in operation. Inspectors must be given access to all areas of establishment during an inspection. TRUE FALSE
3.Health Inspectors are authorized to collect permit fees and fines on behalf of the Department. TRUE FALSE
4.Health Inspectors must show their photo identification and badge to the person in charge of an establishment.
TRUE FALSE
5.According to the NYC Health Code, who is required to have a Food Protection Certificate? ________________________________.
INTRODUCTION TO FOOD SAFETY
What are Potentially Hazardous
Foods (PHF)?
The United States has one of the safest food safety systems in the world, yet millions of Americans still get sick each year from eating contami- nated foods; hundreds of thousands are hospitalized; and several thou- sand die. This means that there is still tremendous room for improve- ment in food safety standards.
Most
Sick food worker
Poor personal Hygiene/Bare hand contact
Improper holding temperatures
Improper cooling
Inadequate cooking and reheating
Cross contamination
Use of food from unknown source
What is
Any illness that is caused by food is called
|
|
This expression refers to those foods |
|
|
|
that provide suitable conditions for |
|
viruses, parasites, fungi etc. Injury |
rapid growth of microorganisms. |
||
and illness caused by foreign objects, |
These include foods that are high in |
||
dangerous chemicals and/or allergens |
protein like raw or cooked animal |
||
in food is also considered a food- |
products such as meats, poultry, |
||
borne illness. |
fish, shellfish (mollusks as well as |
||
Who is at Risk? |
crustaceans), milk and milk products |
||
(cheese, butter milk, heavy cream etc.,), |
|||
We are all at risk of getting a food |
|||
plant protein such as tofu, and |
|||
borne illness; however, the effects are |
|||
starches such as cooked rice, cooked |
|||
more severe for certain categories of |
|||
pasta, cooked beans and cooked |
|||
individuals: |
|||
vegetables like potatoes, cut melons, |
|||
Children whose immune system |
|||
cut leafy greens, cut tomatoes or |
|||
(human body’s defense system |
|||
mixtures of cut tomatoes, as well as |
|||
against diseases) is not fully devel- |
|||
oped yet. |
raw seed sprouts and garlic in oil. |
||
Elderly individuals because their |
Exceptions: Those foods that have a |
||
immune system is not robust any- |
low water activity (.85 or less) or those |
||
more and has weakened due to old |
|||
that are highly acidic with a pH of |
|||
age. |
|||
4.6 or below. |
|||
Pregnant women where the threat |
|||
eggs with shells intact. |
|||
is both to the mother and the fetus. |
|||
|
|||
Individuals with com- |
|
||
promised immune sys- |
|
|
|
|
Potentially Hazardous Foods |
||
tems e.g., Patients with |
|
||
AIDS, cancer or indi- |
|
|
|
viduals who are diabet- |
|
|
|
ics, etc. |
|
|
|
People on medication |
|
|
|
(antibiotics, immunosup- |
|
|
|
pressant, etc.). |
|
|
|
What is food? |
|
|
|
Food is any edible sub- |
|
|
|
stance, ice, beverage, or |
|
|
|
ingredient intended for use |
|
|
|
and used or sold for |
|
|
|
human consumption. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
2 |
|
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
|
|
fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
What is |
necessary permits to operate. The use of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Any food product that does not |
foods prepared at home or in an unli- |
|
212° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
need additional heat treatment or |
censed establishment is prohibited. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
washing is called |
|
|
|
|
|
|
165° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Extra care must be taken to ensure |
The Temperature Danger Zone? |
|
140° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
the safety of these foods. |
|
Most microorganisms that cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Where do we purchase foods? |
foodborne illness typically grow best |
|
|
|
DANGER |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZONE |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
between temperatures of 41°F and |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
All foods must be purchased from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
140°F. This is commonly referred to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
approved sources. These are manu- |
|
|
|
41° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
as the temperature danger zone. One |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
facturers and suppliers who comply |
|
32° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
with all the rules and regulations that |
of the basic and simplest ways to keep |
|
|
|
|
Temperature |
|
|
|
||||||||
food safe is by keeping it out of the |
|
|
|
|
Danger |
|
|
|
|||||||||
pertain to the production of their |
|
|
|
0° |
|
|
|
||||||||||
temperature danger zone. |
|
|
|
|
Zone |
|
|
|
|||||||||
product, including having the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How do we store potentially |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
hazardous foods? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All foods must be kept free from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
adulteration, spoilage, filth or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
other contamination in order to be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
suitable for human consumption. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Potentially hazardous foods are of |
|
|
|
|
|
Thermocouple |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cold temperature |
|||||||
particular concern because they |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Thermometer |
|
|
Thermometer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
reading calibration |
|||||
provide the conditions suitable for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
the growth of microorganisms. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
These foods must be kept either hot or |
Also, it is available within the range |
in 50/50 solution of ice and water |
|||||||||||||||
cold to prevent microorganisms from |
of 0° to 220°F making it ideal for |
or boiling water, and hitting the |
|||||||||||||||
growing. Hot means 140°F or above |
measuring the required tempera- |
“reset” button will automatically |
|||||||||||||||
and cold means 41°F or below. The |
tures in a food establishment. |
calibrate the thermometer. |
|||||||||||||||
temperature range between 41°F and |
|
Another thermometer in use is |
stem thermometers may be calibrated |
||||||||||||||
140°F is known as the temperature |
the thermocouple which is very accu- |
by two methods: |
|||||||||||||||
danger zone. It is within this range |
rate but fairly expensive. Lastly, there is |
||||||||||||||||
that microorganisms are comfortable |
a thermometer called thermistor, |
||||||||||||||||
and will grow rapidly. At 41°F and |
which has a digital read out and is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
below, the temperature is cold |
commonly called "digital thermometer." |
||||||||||||||||
enough to retard or slow down the |
|
These thermometers are used by |
Bring water to a boil. |
||||||||||||||
growth of microorganisms, while |
inserting the probe into the thickest |
Place the thermometer probe (stem) |
|||||||||||||||
above 140°F most of the microor- |
part or the geometric center of the |
into the boiling water. Make sure |
|||||||||||||||
ganisms which cause foodborne ill- |
food item being measured. The stem |
that the thermometer probe does |
|||||||||||||||
ness begin to die. |
thermometer must remain in the food |
not touch the bottom or sides of |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
until the indicator stops moving before |
the pan. Wait until the indicator |
||||||||||||||
Thermometers |
stops moving, then record the |
||||||||||||||||
the reading is taken and must be re- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
The only safe way to determine |
temperature. |
||||||||||||||||
calibrated periodically to assure accuracy. |
|||||||||||||||||
that potentially hazardous foods are |
If the temperature is 212°F, do |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
kept out of the temperature danger |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Calibration |
|
|
nothing, the thermometer is accurate. |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
zone is by the use of thermometers. |
|
Thermometers must be calibrated |
(This is the temperature of boiling |
||||||||||||||
There are several different types of |
to ensure their accuracy. For thermo- |
water at sea level.) |
|||||||||||||||
thermometers. The |
couple thermometers, follow the |
If the temperature is not 212°F, |
|||||||||||||||
the most popular type. It is fairly |
instructions provided by the manu- |
rotate the |
|||||||||||||||
inexpensive, easy to use, accurate to |
facturer. For some thermistor ther- |
a wrench or other tool until the |
|||||||||||||||
+ or – 2°F and easy to |
mometers, placing the thermometer |
indicator is at 212°F. |
|||||||||||||||
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
3 |
|
|
|
fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
Fill a container with ice and water to |
make a 50/50 ice water slush. |
Stir the slush. |
RECEIVING FOODS
Place the thermometer probe so |
that it is completely submerged in |
the |
not to touch the sides or the bot- |
tom. Wait until the indicator nee- |
dle stops moving, then record the |
temperature. |
If the temperature is 32°F, do |
nothing, the thermometer is |
accurate. (A 50/50 ice water slush |
will always have a temperature of |
32°F at |
ture is not 32°F, rotate the hex- |
adjusting nut until the indicator |
needle is at 32°F. |
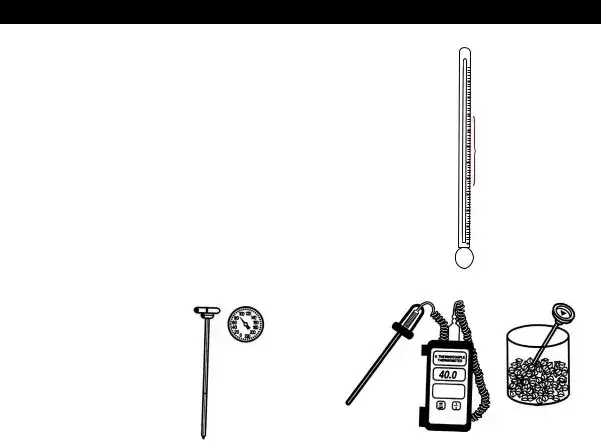
How to use a Thermometer
The following describes the proper method of using thermometers:
Sanitize the probe by the use of |
alcohol wipes. This is a fairly safe |
and common practice. Other |
methods such as immersion in |
water with a temperature of 170°F |
for 30 seconds or in a chemical |
sanitizing solution of 50 PPM for |
at least one minute, or swabbing |
with a chlorine sanitizing solution |
of 100 PPM are also acceptable. |
Measure the internal product |
temperature by inserting the probe |
into the thickest part or the center |
of the product. It is recommend- |
ed that the temperature readings |
be taken at several points. |
Whenever using a |
thermometer, ensure that the |
entire sensing portion – from the |
tip of the probe to the indenta- |
tion on the stem, is inserted in to |
the food product. |
The first opportunity one has to ensure that food is safe is at the point of receiving. At this point care
must be taken to ensure that all products come from approved sources and/or reliable and rep- utable suppliers. Incoming supplies must be received at a time when it is convenient to inspect them and place them into storage promptly. There are various qualities and con- ditions one should look for in dif- ferent food items.
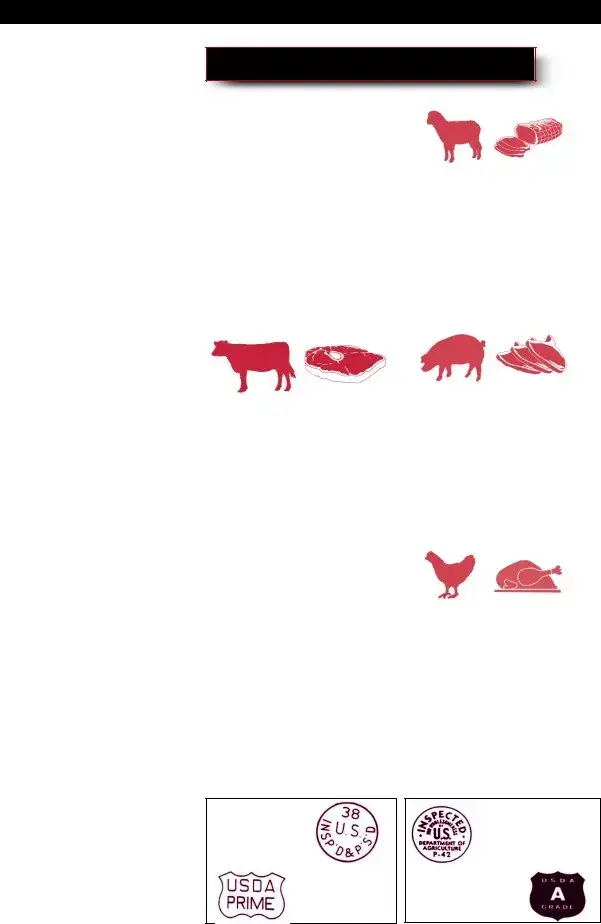
Beef
Incoming supplies of beef can be received either fresh or frozen. Fresh beef should be at 41°F or below while frozen beef should be at 0°F or below. Beef should be bright to dark red in color with no objection- able odor. To ensure that the supply is from an approved source, look for the United States Department of Agriculture inspection stamp. This can be found on the sides of the beef carcass or on the box when receiving portions of the carcass. This inspection is mandatory and the stamp indicates that the meat is sanitary, wholesome and fit for human consumption. Also found may be a grade stamp which attests to the quality of the meat and will certainly have an impact on its price. The inspection stamp is the more important of the two stamps.
Lamb
Lamb, like beef, may have an inspection stamp as well as a grade stamp. When fresh, it is light red in color and has no objectionable odor and the flesh is firm and elastic. Fresh lamb is received at 41°F and frozen at or below 0°F. (See stamps below)
Pork
Pork is also subject to USDA inspection. The flesh is light colored while the fat is white. A good way to check for spoilage is to insert a knife into the flesh all the way to the bone and check the blade for any off odors. (See stamps below)
Chicken and Poultry
Chicken and poultry are subject to USDA inspection which must be verified by the inspection stamp. (See stamps below) These must be received either fresh at 41°F and below or frozen at 0°F or less, as they are naturally contaminated with the
Wait for roughly 15 seconds or |
until the reading is steady before |
recording it. |
Clean and sanitize the thermometer |
for later use. |
USDA Meat |
USDA Poultry |
Inspection Stamp |
Inspection Stamp |
|
USDA Poultry |
USDA Meat |
|
Grade Stamp |
Grade Stamp |
|
|
4 |
|
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
|
|

fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
Fresh fish
There is no inspection for fresh fish other than what can be done by sight and touch and one’s sense of smell. This makes it more impor- tant to purchase supplies from rep- utable and reliable suppliers. Fresh fish must be received cold and on ice, 41°F or less, with no objection- able odor. The eyes must be clear and bulging, the gills bright red and the flesh firm and elastic. Fish that is spoiling will have a fishy odor; the eyes cloudy, red rimmed and sunken; the gills grey or greenish; the flesh will pit on pressure and can easily be pulled away from the bones; the scales are loose.
Smoked fish
Smoked fish provide ideal condi- tions for the growth of Clostridium botulinum spores if left at room temperature. Therefore, upon receipt, all smoked fish must be stored at 38°F or below.
It is important to adhere to the temperature requirements stated on the label.
Shellfish
Shellfish is the term used to describe clams, mussels, and oysters. These belong to the family of mol- lusks. They are filter feeders, that is, they absorb water from their envi- ronment, filter out whatever nutri- ents are there and then expel the water. Feeding in this manner causes them to absorb and accumulate harmful microorganisms from pollut- ed waters. Since the whole shellfish is eaten either raw or partially cooked, it is critical to ensure that they are harvested from safe waters. It is important to buy shellfish from reputable suppliers who can provide the shipper’s tags which identify the source of the shellfish. These tags supply the following information:
The name of the product
The name of the original shipper
The address of the original shipper
The interstate certificate number of the original shipper
The location of the shellfish har- vesting area.
When purchasing small amounts from a retailer, a tag must be pro- vided. This is a
has all the information that is on the original tag.
The shellfish tag is required to be kept together with the product, then whenever the product is used up, it must be kept for 90 days in order of delivery. The virus Hepatitis A is associated with shellfish.
Check if the shellfish is alive. An opened shell may be an indication of dead shellfish. Gently tap on the shell, if the shell closes then it is alive otherwise it’s dead and should be discarded. Both alive as well as shucked shellfish (shellfish that has been removed from its shell) must only be accepted if delivered at a temperature of 41°F or below. Following conditions would auto- matically be grounds for rejection:
Slimy, sticky or dry texture
Strong fishy odor
Broken shells
Other Shellfish
Lobsters, crabs and shrimps belong to the family of crustaceans. Fresh lobsters and crabs must be alive at the time of delivery. As with other seafood, a strong fishy odor is an indication of spoilage. The shell of the shrimp must be intact and firm- ly attached. All processed crustacean must be delivered at 41°F or below.
Split Lot Tag |
Shellfish Tag |
|
It is strongly recommended that the invoices be kept with the tags to aid in tracing the lot’s history.
Eggs
Eggs produced outside of New York State are inspected by the U.S. Department of Agriculture while those produced within the State are inspected by the New York State Department of Agriculture and Markets. In either case, inspected eggs will be identified by a stamp on the carton. Eggs have long been
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
5 |
|
|
|
fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
associated with the
Eggs should be bought from sup- pliers who deliver them in refriger- ated trucks and upon receipt, these eggs must be kept refrigerated at an ambient temperature of 45°F until they are used.
pasteurized milk and milk products must not exceed 45 days from date of ultra pasteurization.
Upon receipt, these products must be checked to ensure that they are well within the expiration period and that they are at 41°F or below. This temperature must be main- tained until the product is used up.
watermelons, cantaloupes, honey dews and all varieties of melons, oranges, etc. Only potable running water should be used to thoroughly wash these produce, and the use of produce scrubbing brushes is strongly recommended.
Egg Cartons Stamps
Pasteurized Eggs
Pasteurization is a method of heating foods to destroy harmful microorganisms. Pasteurized eggs come in many forms: intact shell eggs, liquid eggs, frozen eggs, or in pow- dered form. Even though these have been pasteurized, they still require refrigeration to slow down growth of spoilage microorganisms to extend the shelf life. Only the powdered pasteurized eggs may be held at room temperature.
Milk and Milk Products
Only accept Grade A pasteurized milk and milk products. Harmful pathogens such as Listeria monocy- togenes, E.coli 0157:H7 and Salmonella spp. are commonly asso- ciated with
The expiration date on pasteur- ized milk and milk products must not exceed nine calendar days from date of pasteurization, while ultra
|
|
|
Canned Goods |
|
||
|
|
|
It is a simple task to inspect |
|||
|
|
|
canned goods and remove from cir- |
|||
|
|
|
culation those cans that can cause |
|||
Fresh Fruits and Vegetables |
|
foodborne illness. The first step is |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
The acceptable condition of fruits |
to ensure that home canned foods |
|||||
are not used in a food service estab- |
||||||
and vegetables vary from one item |
|
|||||
|
lishment. All canned foods must be |
|||||
to another. As a general rule of thumb, |
||||||
commercially processed. A good can |
||||||
only accept those that do not show |
||||||
is free from rust and dents, properly |
||||||
any signs of spoilage. Reject any |
|
|||||
|
sealed and labeled and slightly con- |
|||||
produce that shows signs of decay, |
|
|||||
|
cave at both ends. |
|
||||
mold, mushiness, discoloration, |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
wilting, and bad odors. |
|
A can with a dent on any of the |
||||
A recent study done by the center |
|
|||||
|
three seams (top, bottom or side) |
|||||
for Science in the Public Interest |
|
|||||
|
must be removed from circulation. |
|||||
(CSPI) found that contaminated fruits |
||||||
The same requirement is true for |
||||||
and vegetables are causing more food- |
||||||
severely rusted, severely dented, leak- |
||||||
borne illness among Americans than |
||||||
ing and cans with swollen ends. Bad |
||||||
raw chicken and eggs combined. |
|
|||||
|
cans may be rejected at delivery or seg- |
|||||
Most fresh produce may become |
|
|||||
|
regated and clearly labeled for return |
|||||
contaminated with Salmonella and |
|
|||||
|
to the supplier. |
|
||||
E.coli 0157:H7 due to the |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
use of manure fertilizer |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(more common in South |
|
|
|
|
|
|
and Central America, which |
|
|
|
|
|
|
is a major source of fresh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
produce to the United |
|
|
|
|
|
|
States). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fresh produce must be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
thoroughly washed prior to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
being served raw. This |
|
|
|
|
|
|
includes all kinds of fruits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
and vegetables including |
|
swollen |
severe dents |
slight rust |
||
produce that has a hard |
|
critical |
major |
minor |
||
rind that is typically not |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
consumed, for example, |
|
|
|
|
||
6 |
|
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
|
|
fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
Modified Atmosphere
Packaged Foods
Various food items are packaged under special conditions to prolong their shelf life. These conditions include the following:
Food is placed in a package and all the air is withdrawn: vacuum packaging.
Food is placed in a package, all the air is withdrawn and gases are added to preserve the contents – modified atmosphere packaging.
Food is placed in a package, all the air is withdrawn and the food
is cooked in the package: sous vide packaging.
Because of the absence of air, foods packaged in this manner provide ideal conditions for the growth of the clostridium botulinum
These products must be provided by approved sources and care taken to preserve the packaging during handling and when taking the tem- perature.
Food establishments interested in making “modified atmosphere pack- aged foods” must first obtain per- mission from NYC DOHMH.
For more information , please see Page 54.
Dry Foods
Dry foods such as grains, peas,
beans, flour and sugar are to be dry at the time of receiving. Moisture will cause growth of molds and the deterioration of these products. Broken and defective packages will indicate contamination; as will the evidence of rodent teeth marks.
Whenever these products are removed from their original con- tainers, they must be stored in tightly covered,
Refrigerated and Frozen
Processed Foods
For convenience as well as cutting down on costs, there has been a greater shift towards using prepared pre- packaged refrigerated or frozen foods. These routinely include deli and luncheon meats, refrigerated or frozen entrees, etc. Care should be taken when receiving these products to ensure quality as well as safety. Following are some guidelines:
Ensure that refrigerated foods are delivered at 41°F or below. (Except, as noted previously, smoked fish must be received at 38° F or lower.)
Ensure that frozen foods are delivered at 0°F or lower.
All packaging must be intact.
Any frozen food packaging that shows signs of thawing and refreezing should be rejected. Signs include liquid or frozen liquids on the outside packaging, formation of ice crystals on the packaging or on the product, and water stains.
QUICK REVIEW
1.The term "potentially hazardous food" refers to foods which do not support rapid growth of microorganisms. TRUE FALSE
2.Home canned food products are allowed in commercial food establishments. TRUE FALSE
3.The Temperature Danger Zone is between 41°F and 140°F.
TRUE FALSE
4.Within the Temperature Danger Zone, most harmful microorganisms reproduce rapidly. TRUE FALSE
5.Shellfish tags must be filed in order of delivery date and kept for a period of _______ days.
6.Fresh shell eggs must be refrigerated at an ambient temperature of: ______°F.
7.Foods in Modified Atmosphere Packages provide ideal conditions for the growth of: _______
8.The recommended range of
9.Meat inspected by the U.S. Dept. of Agriculture must have a/an:
____________ stamp.
10.Chicken and other poultry are most likely to be contaminated with: _______
11.Smoked fish provide ideal conditions for the growth of Botulinum spores. Therefore, this product must be stored at: ______°F
12.Safe temperatures for holding potentially hazardous foods are: ______°F or below and ______°F or above
13.What are the four types of defective canned products that must be removed from circulation? ______, ______, _____, _____
14.Which of the following is an indication that fish is not fresh?:
clear eyes fishy odor firm flesh
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
7 |
|
|
|

fo d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
d P R O T E C T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
STORAGE OF FOOD
fter receiving the foods proper |
Storage Containers |
||
Aly, they must be immediately |
It is always best to store food in |
||
their original packaging; however, |
|||
moved to appropriate storage areas. |
|||
The most common types of food |
when it is removed to another con- |
||
storage include: |
tainer, take extra care to avoid cont- |
||
Refrigeration storage |
amination. Only use food containers |
||
that are clean, |
|||
Freezer storage |
|||
are made from |
|||
Dry storage |
|||
intended for such use. Containers |
|||
Storage in Ice |
|||
made from metal may react with |
|||
|
|||
We will discuss each of these |
certain type of high acid foods such |
||
individually; however, certain |
as sauerkraut, citrus juices, tomato |
||
aspects are common for all types of |
sauce, etc. Plastic |
||
storage and are described below. |
tainers are the best choice for these |
||
FIFO |
types of foods. Containers made of |
||
copper, brass, tin and galvanized metal |
|||
An important aspect of food stor- |
|||
should not be used. The use of such |
|||
age is to be able to use food products |
|||
products is prohibited. |
|||
before their |
|||
|
|
||
date. In this regard, stock rotation is |
|||
very important. The common sense |
store cooked foods is also a source |
||
approach of First in First out (FIFO) |
of contamination. Lining containers |
||
method of stock rotation prevents |
with newspapers, menus or other |
||
waste of food products and ensures |
publication before placing foods is |
||
quality. The first step in implement- |
also prohibited as chemical dyes from |
||
ing the FIFO method of stock rota- |
these can easily leach into foods. |
||
tion is to date products. Marking the |
Storage Areas |
||
products with a date allows food |
|||
Foods should only be stored in |
|||
workers to know which product was |
|||
designated areas. Storing foods in |
|||
received first. This way, the older stock |
|||
passageways, rest rooms, garbage |
|||
is moved to the front, and the newly |
|||
areas, utility rooms, etc. would sub- |
|||
received stock is placed in the back. |
|||
ject these to contamination. Raw |
|||
|
|||
|
|
foods must always be stored |
|
Cross Contamination |
|
below and away from cooked |
|
When harmful microorganisms are |
|
foods to avoid cross contami- |
|
transferred from one food item to |
|
nation. |
|
another, typically, from raw foods to |
|
Refrigerated Storage |
|
cooked or ready to eat foods, it is |
|
||
|
This type of storage is typi- |
||
termed cross contamination. This |
|
||
|
cally used for holding potential- |
||
expression also applies in any situa- |
|
||
tion where contamination from one |
|
ly hazardous foods as well as |
|
object crosses over to another. Cross |
|
perishable foods for short peri- |
|
contamination may also occur between |
|
ods of |
|
two raw products, for instance, |
|
few days. |
|
poultry juices falling on raw beef |
|
An adequate number of effi- |
|
will contaminate it with Salmonella, |
|
||
|
cient refrigerated units are |
||
which is typically only associated |
|
||
|
required to store potentially |
||
with poultry and raw eggs. |
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
hazardous cold foods. By keeping cold foods cold, the microorganisms that are found naturally on these foods are kept to a minimum. Cold
temperature does not kill microor- ganisms, however, it slows down their growth.
Fresh meat, poultry and other potentially hazardous foods must be stored at 41°F or below, while frozen foods must be stored at 0°F or below. For foods to be maintained at these temperatures, refrigerators and freezers must be operating at tem- peratures lower than 41°F and 0°F., respectively. Thermometers placed in the warmest part of a refrigerated unit are necessary to monitor the temperature of each unit.
The rule of storage, First In First Out (FIFO) ensures that older deliveries are used up before newer ones. In practicing FIFO, the very first step would be to date all prod- ucts as they are received. The next step is to store the newer products behind the older ones.
The following rules are important in making sure that foods are safe during refrigerated storage:
Store cooked foods above raw foods to avoid
Keep cooked food items covered unless they are in the process of cooling, in which case they must be covered after being cooled to 41°F.
Avoid placing large pots of hot foods in a refrigerator. This will cause the temperature of the refrigerator to rise and other foods will be out of temperature.
8 |
|
N E W Y O R K C I T Y D E P A R T M E N T O F H E A L T H & M E N T A L H Y G I E N E |
|
|
|
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Title | The form is titled "Food Protection Training Manual" and is published by the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. |
| Purpose of the Manual | This manual is designed to assist food service operators and staff in understanding safe food handling practices. |
| Mandatory Certificate | Supervisors of food service establishments must hold a Food Protection Certificate as mandated by the NYC Health Code, specifically Article 81. |
| Online Course Availability | The Food Protection Course is available online, offering flexibility for individuals with busy schedules. |
| Inspection Rights | Health inspectors have the authority to inspect any food service or food processing establishment at any time during hours of operation. |
| Pest Control | The manual covers pest control measures to protect food establishments from health hazards. |
| Temperature Danger Zone | The manual defines the temperature danger zone as the range between 41°F and 140°F, where microorganisms grow rapidly. |
| Emergency Contact Numbers | The document provides several important phone numbers for various services related to food safety and health regulations. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Food Protection Training Manual
Completing the Food Protection Training Manual form involves gathering necessary information and accurately filling in specific sections. Each entry is critical for ensuring compliance and understanding of food safety practices. Follow the steps below to successfully navigate the form.
- Begin by selecting the appropriate language for the course: English, Spanish, or Chinese.
- Provide your personal details, including your full name, address, phone number, and email address.
- Enter the name of your food establishment accurately, along with its address and phone number.
- Specify the type of food service establishment you are operating.
- Indicate the number of employees at your establishment who will require Food Protection Certification.
- List any relevant experience or training related to food safety you have completed previously.
- Review the specific regulations that apply to your type of establishment and ensure you understand them.
- Sign and date the form to confirm that all information provided is true to the best of your knowledge.
- Submit the completed form online or deliver it to the designated department as per provided instructions.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the Food Protection Training Manual form and why is it important?
The Food Protection Training Manual form is an essential resource published by the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. It provides guidelines and best practices for safe food handling in various food service establishments. This manual is crucial as it assists food service operators, supervisors, and employees in understanding health regulations and hygiene requirements necessary to prevent foodborne illnesses. Proper training ensures compliance with local health laws and promotes public health safety.
Who is required to take the Food Protection Course?
The Food Protection Course is mandated for individuals who supervise food service operations. This includes managers and supervisors in both retail and non-retail food processing establishments. To operate legally, these individuals must complete the training and pass an examination to obtain a Food Protection Certificate. Having a certified supervisor on site during all hours of operation is necessary to maintain food safety compliance.
What topics are covered in the Food Protection Training Manual?
The manual covers a wide range of topics vital for effective food safety management. Key sections include safe food handling practices, storage and receiving of food, personal hygiene, cleaning and sanitizing, foodborne illness prevention, and the principles of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) systems. Additional subjects, such as pest control and food defense strategies, are also included, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of safety in food service operations.
Is the Food Protection Course available online?
Yes, the Food Protection Course is available online, providing flexibility for those with busy schedules. Participants can study at their convenience and complete the course material in English, Spanish, or Chinese. After finishing the online training, candidates are required to schedule the final examination at the Health Academy. This option allows individuals to pursue certification without needing to attend in-person classes.
What should I do if I have questions regarding the manual or course?
If you have questions or comments about the Food Protection Training Manual or the associated course, you can contact the Health Academy directly at (917) 492-6990. The Health Academy provides assistance and guidance related to food safety training and can address any concerns you may have. Additionally, contact information for various departments related to food safety is also available within the manual.
How can I register for the Food Protection Course and is there a fee?
Registration for the Food Protection Course can be done online at the Department of Health and Mental Hygiene's Health Academy website. Participants can select a convenient course date, pay the associated fee, and receive a confirmation of their registration. The fee varies and should be paid at the time of registration. This online system streamlines the process, eliminating the need for in-person visits to the Citywide Licensing Center.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Food Protection Training Manual form can seem straightforward, but many people make common mistakes that could delay their certification or even lead to complications later on. One frequent error is neglecting to provide accurate personal information. It’s essential to ensure that your name, address, and contact details are spelled correctly. This information is crucial for your certification and any communication from the Health Department.
Another mistake often encountered involves the incorrect selection of course details. Many individuals fail to pay close attention to the specific course they are registering for, which can result in enrolling in the wrong session. Always double-check that you choose the relevant course and date to avoid unnecessary hassle.
Providing incomplete responses during the quiz section is another pitfall. Students may feel rushed and skip questions or fail to provide thorough answers. Remember, these quizzes are designed to test your knowledge of food safety, and providing detailed answers can help reinforce your understanding of best practices.
People also commonly overlook the requirement for supporting documents. For some courses or certifications, additional documentation may be needed. This could include previous certificates or proof of work experience. Lacking these documents can lead to delays or rejection of your application.
Additionally, many candidates fail to read the instructions carefully. The form comes with specific guidelines that need to be followed. Not adhering to these instructions can result in filing an incomplete form. Take the time to read all directions to ensure you submit a complete document.
Another frequent error involves financial transactions. Some applicants do not verify the payment details. Errors in payment amounts or incorrect credit card information can lead to rejected registrations. Always confirm that your payment method is correct and that you have received a confirmation after payment.
Furthermore, people often forget about deadlines. Registration for the Food Protection Course has specific dates, and failing to register on time can mean missing an opportunity to attend the course. Setting reminders can help ensure that you do not miss these important deadlines.
Lastly, some individuals do not take the time to prepare for the exam adequately. The course materials are there to help, but skimming through them might not be enough. Engaging with the content, taking notes, and reviewing all sections can significantly improve your chances of passing the final examination.
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can navigate the registration process more efficiently and successfully secure your Food Protection Certificate. Taking these steps will not only enhance your understanding of food safety but also ensure that you meet all the necessary requirements for your establishment.
Documents used along the form
When managing food service operations, several essential forms and documents complement the Food Protection Training Manual. Each of these documents plays a vital role in ensuring compliance with health regulations, maintaining safety standards, and improving operational efficiency. Here’s an overview of some of the most commonly used forms:
- Food Establishment Inspection Report: This document outlines the findings of health inspections conducted at food service establishments. It details any violations, health risks, and necessary corrective actions.
- Certificate of Occupancy: This form confirms that a building complies with local zoning laws and safety regulations. It is crucial for any food establishment to ensure it is legally permitted to operate within a specific location.
- Food Protection Certificate: This certification is essential for individuals who complete the Food Protection Course. It verifies that a supervisor is knowledgeable about safe food handling practices.
- Employee Health Declaration: Employees must complete this form to disclose health conditions that could affect food safety. It helps identify those who may pose a risk to public health while handling food.
- Temperature Log: This document is used to record the temperatures at which food is stored and prepared. It ensures that foods remain outside the temperature danger zone, thereby reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Pest Control Report: A record of pest control measures taken within the establishment. This report identifies the services performed and any pest-related issues addressed, ensuring a safe food environment.
- Cleaning Schedule: This document details routines for cleaning kitchen equipment, food prep areas, and dining spaces. Regular cleaning schedules help maintain hygiene standards and prevent cross-contamination.
- Maintenance Log: A record of any maintenance or repairs made to kitchen equipment and facilities. Keeping this log helps to ensure that all systems are functioning correctly and that food safety equipment is operational.
- Supplier Verification Forms: These forms are used to document the sourcing of food products. They ensure that foods are purchased from approved suppliers, complying with safety regulations.
Utilizing these forms and documents alongside the Food Protection Training Manual not only enhances food safety practices but also ensures compliance with public health regulations. Establishments must prioritize these documents' accuracy and completeness to safeguard public health and maintain operational integrity.
Similar forms
The Food Protection Training Manual form has similarities to several other documents that serve regulatory and educational purposes in food safety. Each of these documents addresses key aspects of food safety and health standards. Here are five documents similar to the Food Protection Training Manual:
- Health Code Regulations: Like the Food Protection Training Manual, the Health Code outlines essential regulations for food service establishments. It establishes requirements that help ensure safe food handling and operations to protect public health.
- Food Safety Guidelines: These guidelines offer practical advice and checklists on safe food handling practices. Similar to the training manual, they are designed to educate food service workers about preventing foodborne illnesses.
- HACCP Plans: Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) plans are strategies that assist establishments in identifying and managing food safety hazards. This document parallels the manual by focusing on systematic processes that promote food protection.
- Food Establishment Inspection Report: This report is utilized by health inspectors during their evaluations of food service establishments. It shares the same goal as the training manual: to ensure compliance with food safety standards and help prevent health risks.
- Temporary Food Service Guidelines: These guidelines provide specific instructions for operating temporary food service establishments. They closely mirror the training manual's intent to educate and inform operators about safety standards.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Food Protection Training Manual form, there are clear dos and don'ts to follow. Here is a list to guide you.
- Do double-check the name and contact information provided.
- Do complete all sections accurately and thoroughly.
- Do use a blue or black pen for handwritten entries.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records.
- Do read the instructions carefully before starting.
- Don't leave any fields blank unless specified.
- Don't use correction fluid or tape to fix errors.
- Don't submit the form without reviewing it for accuracy.
- Don't provide false information, as it may lead to penalties.
- Don't forget to sign and date the form before submission.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The Food Protection Training Manual is only for restaurant owners.
- Misconception 2: Completing the food protection course is optional.
- Misconception 3: Once certified, there is no need for ongoing education or training.
- Misconception 4: Health inspectors cannot conduct inspections without notice.
- Misconception 5: The food protection manual only covers food handling procedures.
This manual is relevant not just for restaurant owners, but also for all food service employees. Everyone working in a food establishment benefits from understanding food safety practices.
In fact, the training course is mandatory for supervisors of food service establishments. A valid Food Protection Certificate must be obtained to comply with local health regulations.
Food safety standards can change over time. Regular updates and refresher courses are essential to staying informed about the latest food safety practices and regulations.
Health inspectors have the right to inspect food establishments at any time while they are operational. They must be granted access to all areas during an inspection.
The manual includes a broad range of topics, such as personal hygiene, pest control, and workplace safety. It serves as a comprehensive guide to maintaining public health standards in food service operations.
Key takeaways
- The Food Protection Training Manual is a comprehensive resource designed to educate food service operators on safe food handling practices.
- All food service establishments must possess a current, valid permit from the NYC Health Department to operate legally.
- The manual includes critical information on various topics, from food safety basics to personal hygiene and proper food storage.
- Completing the online Food Protection Course, which is available in English, Spanish, and Chinese, can be done at one’s convenience.
- A final examination is required after course completion to earn a certification which must be present during all food preparation activities.
- Potentially hazardous foods must be stored properly at specific temperatures to prevent the growth of microorganisms.
- Use of calibrated thermometers is essential to monitor temperatures in food service to avoid foodborne illnesses.
- The Health Academy provides certification courses and regulates educational standards for individuals in the food industry.
- Health Inspectors can access any area of a food establishment during inspections and must display identification upon request.
- Violating health codes can lead to legal repercussions, including fines or permit revocation, emphasizing the importance of compliance with regulations.
Browse Other Templates
Adt Police Response Cost - Residential applicants fifty-five or older may qualify for fee exemptions.
How Do I Avoid Taxes When Buying a Boat? - The Illinois Department of Revenue offers assistance for completing the form.
