Fill Out Your 1010 Form
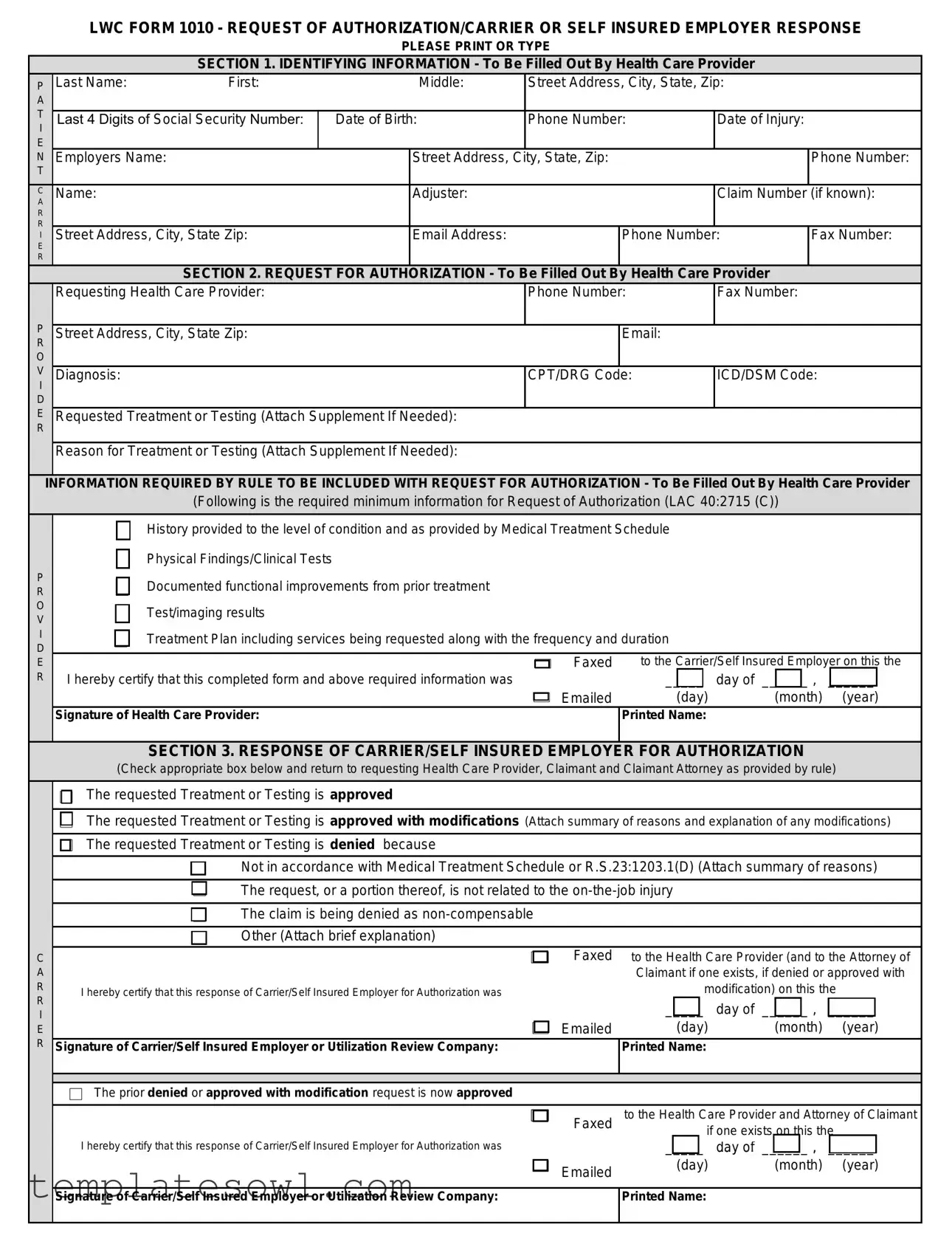
The LWC Form 1010 is a critical tool in the healthcare and workers' compensation systems, serving as a formal request for authorization regarding medical treatment or testing. This form is primarily filled out by health care providers when they seek approval for essential medical services needed by injured workers. It requires detailed identifying information, including personal and employment details of the claimant, the provider's contact information, and specifics about the injury. The health care provider must also submit comprehensive information about the diagnosis, requested treatment, and supporting medical history, which helps justify the necessity of the treatment. Once the request is submitted, the form also facilitates a structured response from the carrier or self-insured employer, indicating whether the treatment is approved, approved with modifications, or denied, along with the reasons for such decisions. Additionally, if there is an appeal or an information suspension, the form outlines the necessary steps to address these issues. The procedure to complete and process Form 1010 emphasizes a clear line of communication between health care providers, employers, and insurers, enhancing the efficiency of treatment authorization in the context of workplace injuries.
1010 Example

LWC FORM 1010 - REQUEST OF AUTHORIZATION/CARRIER OR SELF INSURED EMPLOYER RESPONSE
PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE
SECTION 1. IDENTIFYING INFORMATION - To Be Filled Out By Health Care Provider
P |
Last Name: |
First: |
|
Middle: |
Street Address, City, State, Zip: |
|
||
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last 4 Digits of Social Security Number: |
Date of Birth: |
Phone Number: |
Date of Injury: |
|
||||
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
Employers Name: |
|
|
Street Address, City, State, Zip: |
|
Phone Number: |
||
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
Name: |
|
|
Adjuster: |
|
|
Claim Number |
(if known): |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
Street Address, City, State Zip: |
|
Email Address: |
|
Phone Number: |
Fax Number: |
||
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION 2. REQUEST FOR AUTHORIZATION - To Be Filled Out By Health Care Provider |
|
|||||
|
Requesting Health Care Provider: |
|
|
Phone Number: |
Fax Number: |
|
||
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Street Address, City, State Zip: |
|
|
|
Email: |
|
|
||
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
Diagnosis: |
|
|
|
CPT/DRG Code: |
ICD/DSM Code: |
||
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
Requested Treatment or Testing (Attach Supplement If Needed): |
|
|
|
|
|||
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Reason for Treatment or Testing (Attach Supplement If Needed): |
|
|
|
|
|||
INFORMATION REQUIRED BY RULE TO BE INCLUDED WITH REQUEST FOR AUTHORIZATION - To Be Filled Out By Health Care Provider
(Following is the required minimum information for Request of Authorization (LAC 40:2715 (C))
P R O V I D E R
History provided to the level of condition and as provided by Medical Treatment Schedule
Physical Findings/Clinical Tests
Documented functional improvements from prior treatment
Test/imaging results
Treatment Plan including services being requested along with the frequency and duration
Faxed |
to the Carrier/Self Insured Employer on this the |
||
I hereby certify that this completed form and above required information was |
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
Signature of Health Care Provider: |
Printed Name: |
|
|
SECTION 3. RESPONSE OF CARRIER/SELF INSURED EMPLOYER FOR AUTHORIZATION
(Check appropriate box below and return to requesting Health Care Provider, Claimant and Claimant Attorney as provided by rule)
C A R R I E R
The requested Treatment or Testing is approved
The requested Treatment or Testing is approved with modifications (Attach summary of reasons and explanation of any modifications)
The requested Treatment or Testing is denied because
Not in accordance with Medical Treatment Schedule or R.S.23:1203.1(D) (Attach summary of reasons)
The request, or a portion thereof, is not related to the
The claim is being denied as
Other (Attach brief explanation)
Faxed to the Health Care Provider (and to the Attorney of
Claimant if one exists, if denied or approved with
I hereby certify that this response of Carrier/Self Insured Employer for Authorization was |
modification) on this the |
||||
|
|
|
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
|
|
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
Signature of Carrier/Self Insured Employer or Utilization Review Company: |
Printed Name: |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The prior denied or approved with modification request is now approved |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Faxed |
to the Health Care Provider and Attorney of Claimant |
||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
if one exists on this the |
||
I hereby certify that this response of Carrier/Self Insured Employer for Authorization was |
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
||
|
|
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signature of Carrier/Self Insured Employer or Utilization Review Company: |
Printed Name: |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION 4. FIRST REQUEST
(Form 1010A is required to be filled out by Carrier/Self Insured Employer and Health Care Provider)
C |
The requested Treatment or Testing is delayed because minimum information required by rule was not provided |
|||||
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faxed |
to the Health Care Provider on this the |
||||
R |
|
|||||
I hereby certify that this First Request and accompanying Form 1010A was |
|
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
||
R |
|
|||||
I |
|
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
|
E |
Signature of Carrier/Self Insured Employer or Utilization Review Company: |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
Faxed |
to the Carrier/Self Insured Employer on this the |
|||
R |
I hereby certify that a response to the First Request and |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
O |
|
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
||
accompanying Form 1010A was |
|
|||||
V |
|
|||||
|
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
||
I |
|
|||||
D |
Signature of Health Care Provider: |
|
Printed Name: |
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION 5. SUSPENSION OF PRIOR AUTHORIZATION DUE TO LACK OF INFORMATION
|
Suspension of Prior Authorization Process due to Lack of Information |
|
|
||
C |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
The requested Treatment or Testing is delayed due to a Suspension of Prior Authorization Due to Lack of Information |
||||
R |
|||||
R |
|
|
|
|
|
Faxed |
to the Health Care Provider on this the |
||||
I |
|||||
I hereby certify that this Suspension of Prior Authorization was |
_____ day of |
______ , |
______ |
||
E |
|||||
R |
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
|
|
Signature of Carrier/Self Insured Employer or Utilization Review Company: |
Printed Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Appeal of Suspension to Medical Services Section by Health Care Provider |
|
|
||
P |
|
|
|
|
|
OR |
I hereby certify that this form and all information previously submitted to Carrier/Self Insured Employer |
|
|
||
|
was faxed to OWCA Medical Services (Fax Number: |
||||
V |
|||||
I |
|
|
|
|
|
Faxed to the Carrier/Self Insured Employer on this the |
|||||
D |
|||||
E |
I hereby certify that this Appeal of Suspension of Prior Authorization was |
_____ day of |
______ , |
______ |
|
R |
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
|
|
Signature of Health Care Provider: |
Printed Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION 6. DETERMINATION OF MEDICAL SERVICES SECTION
O W C A
The required information of LAC40:2715(C) was not provided
The required information of LAC40:2715(C) was provided
Faxed |
to the Health Care Provider & Carrier/Self |
|||
Insured Employer on this the |
||||
I hereby certify that a written determination was |
||||
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
||
|
||||
Emailed |
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
|
Signature: |
Printed Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION 7. HEALTH CARE PROVIDER RESPONSE TO MEDICAL SERVICES DETERMINATION
P R O V I D E R
Faxed to the Carrier/Self Insured Employer on this the
I hereby certify that additional information, pursuant to the determination of |
|
|
|
|
Medical Services Section, was |
Emailed |
_____ |
day of ______ , |
______ |
|
|
(day) |
(month) |
(year) |
Signature of Health Care Provider: |
|
Printed Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Form 1010 | The LWC Form 1010 is used to request authorization for medical treatment or testing for injured workers. |
| Governing Law | This form is governed by Louisiana Administrative Code 40:2715(C), which outlines the requirements for request of authorization. |
| Sections Included | The Form 1010 has several key sections, including identifying information, request for authorization, response from the carrier, and appeal procedures. |
| Submission Requirements | Healthcare providers must provide specific information, such as diagnoses, treatment plans, and clinical findings when submitting the form. |
| Response Timeline | The carrier or self-insured employer must respond within a specified time frame after receiving the authorization request. |
| Denials | If treatment is denied, the carrier must provide a summary explaining the reasons for the denial, according to set regulations. |
| Appeal Process | Healthcare providers can appeal denials by submitting additional information and following outlined procedures for reconsideration. |
Guidelines on Utilizing 1010
Completing the 1010 form requires careful attention to detail. This form is essential for health care providers submitting a request for authorization. It's important to provide accurate information as the next steps depend on the information submitted.
- Gather necessary information: Before you begin filling out the form, collect all required details such as names, addresses, contact numbers, and relevant medical codes.
- Start with Section 1: Fill in the identifying information for both the patient and the employer. This includes the patient’s name, Social Security number, and date of injury.
- Complete Section 2: Enter details about the requesting health care provider, diagnosis, and proposed treatment. Ensure that you attach any additional necessary documents.
- Address required information: In Section 2, provide the clinical history, physical findings, and treatment plan as specified. Make sure it meets all requirements as outlined.
- Sign and date: After completing the form, the health care provider must sign and certify that the information is accurate. Include the date and method of submission (fax or email).
- Carrier/Self Insured Employer response: If applicable, the carrier or self-insured employer will need to check the appropriate box in Section 3 and provide their response to the request.
- Complete Sections 4-7, if necessary: If the request is denied or suspended, fill out the relevant sections about the first request or suspension of authorization.
- Submit the form: Finally, ensure that the completed form is sent to the appropriate parties, including the health care provider, claimant, and their attorney, if necessary.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the LWC Form 1010?
The LWC Form 1010 is used to request authorization for medical treatment or testing related to a workplace injury. Health care providers fill it out to provide necessary details about the patient, the injury, and the proposed treatment. It ensures that both the provider and the insurance carrier are on the same page regarding treatment plans for injured workers.
Who is responsible for filling out the 1010 form?
The 1010 form should be completed by the health care provider requesting authorization. It includes details such as patient information, diagnosis, requested treatment or testing, and relevant medical history. Accurate information helps facilitate the review process and ensures that the right treatments are approved efficiently.
What happens after the 1010 form is submitted?
Once the 1010 form is submitted, the carrier or self-insured employer reviews the request for authorization. They can approve the requested treatment, modify it, deny it, or request additional information. The health care provider and the claimant will receive a response detailing the outcome. This process is essential to determine whether the requested medical services will be covered.
What should a health care provider do if the authorization is denied?
If the authorization for treatment is denied, the health care provider has the option to appeal the decision. The provider may resubmit the necessary information or additional documentation that supports the request. The appeal must follow the guidelines specified by the insurance carrier, including timelines for submitting the appeal and required documentation.
What information is necessary to include with the authorization request?
Common mistakes
Filling out the Form 1010 can be a straightforward process, but common mistakes can lead to delays or denials of requests. A prevalent error is failing to provide complete identifying information in Section 1. Health care providers must ensure that all fields, including names, addresses, and social security numbers, are filled out accurately. Incomplete data can hinder the processing of the request and further communication.
Another mistake relates to not including the diagnosis and relevant codes in Section 2. It's crucial to fill out the CPT/DRG and ICD/DSM codes correctly. Omissions or inaccuracies in this area can result in a denial due to insufficient information, delaying critical treatment for the injured party.
Inadequate explanations for requested treatments often surface as an issue. In Section 2, it's essential to provide detailed reasons for treatment or testing. Failure to attach supplemental documents when necessary may lead to complications. This information must clearly outline the rationale, demonstrating the need for the requested services.
Another frequent mistake is not certifying the date of submission. In multiple sections, including Section 2, the certifying signature must include the correct date. Any inaccuracies here can delay the request, as it may be flagged for further verification.
Neglecting to communicate with involved parties is another critical error. Health care providers should ensure that the form is sent to all appropriate parties listed throughout the document. This includes sending necessary notifications to the claimant and their attorney when applicable. Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings and further delays in treatment approval.
In addition, many providers fail to double-check the fax and email addresses entered. Incorrect contact details can result in important information not reaching its destination. Prior to submission, review each address thoroughly to ensure that communications are received by all involved parties.
Finally, overlooking the necessity for the required supplemental information as prescribed by LAC 40:2715 (C) can be detrimental. The request for authorization needs a complete history and documentation. Inadequate information may prompt a suspension of the prior authorization process, thus prolonging care for the injured worker.
Documents used along the form
The LWC Form 1010 serves as a cornerstone for requesting authorization related to health care services in the context of workers' compensation cases. Several other documents often accompany this form, each serving a specific purpose in the authorization process. Below is a list of such documents, highlighting their roles and relevance.
- Form 1010A: This form is filled out by the Carrier or Self-Insured Employer and the Health Care Provider when the initial request for authorization lacks the minimum required information. It facilitates communication regarding the deficiencies in the request.
- Claimant’s Authorization Form: This document grants permission for the health care provider to share pertinent medical information with the insurance carrier. It is essential for compliance with privacy regulations and ensures the confidentiality of medical records.
- Medical Report: A detailed report prepared by the health care provider, outlining the diagnosis, treatment plan, and any relevant medical history. This report supports the request for authorization by providing a comprehensive view of the patient’s condition.
- Utilization Review Summary: When a utilization review is conducted, this summary outlines the findings and recommendations pertaining to the requested treatment. This document is vital for the carrier’s decision-making process regarding approvals or denials.
- Appeal Form: In cases where treatment authorization is denied, a formal appeal form can be filed. This document outlines the reasons for the appeal and requests a reconsideration of the original decision.
Navigating the complexities of workers’ compensation and health care authorization requires clear communication and thorough documentation. Each of these documents plays a critical role in ensuring that relevant information is obtained and shared, facilitating appropriate decision-making in the best interest of the claimant.
Similar forms
-
Form W-2 - This document is used to report annual wage and tax information for employees. Similar to the 1010 form, it collects personal identifying information and pertains to healthcare and employer responsibilities. Employers must submit this form to both employees and the IRS.
-
Form 1099-MISC - This form reports payments made to independent contractors and other non-employees. Like the 1010 form, it includes details about the payer and recipient, ensuring accountability and proper documentation of financial transactions.
-
Authorization for Release of Health Information - This document is crucial for allowing health care providers to share a patient's medical records with other parties. It shares similarities with the 1010 form, as both require identifiable information and aim to formalize communication regarding health services.
-
Health Insurance Claim Form (CMS-1500) - The CMS-1500 is utilized by health care providers to bill Medicare and other insurers for services rendered. Like the 1010 form, it necessitates detailed service descriptions and provider information.
-
Certificate of Creditable Coverage - This document verifies an individual's prior health coverage, often needed when transitioning between insurance plans. It parallels the 1010 form by providing essential information about coverage history and personal details for the individual.
-
Claim Appeal Forms - When a health care provider seeks to challenge a denial of services, they submit a claim appeal form. Much like the 1010 form, it necessitates the inclusion of comprehensive details surrounding patient care and service validation.
Dos and Don'ts
Here are some important dos and don'ts when filling out the 1010 form:
- Do: Ensure all personal information is accurate, including names, addresses, and contact numbers.
- Do: Fill out the form completely. Missing information can delay processing.
- Do: Provide supporting documents when necessary, such as diagnosis and treatment plans.
- Do: Review the form for errors before submitting it to avoid unnecessary back-and-forth.
- Don't: Use abbreviations that may confuse the reviewer. Be clear and concise.
- Don't: Forget to sign and date the form. An unsigned form may be rejected.
Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about the 1010 form can lead to confusion when requesting authorizations for medical treatment. Here are four common misconceptions:
- It's just a simple form for any medical request. The 1010 form is specifically designed for worker's compensation cases. It includes detailed requirements aimed at certifying the necessity of treatment related to a workplace injury, which is different from standard medical authorization forms.
- Anyone can fill out the 1010 form. Only healthcare providers are authorized to complete the sections related to patient diagnosis and proposed treatment. Properly filling out the form requires understanding specific medical codes and treatment guidelines.
- Submitting the form guarantees approval of treatment. Approval is not automatic. The form is subject to review, and the carrier may deny or modify a request based on the information provided or compliance with state regulations.
- Once submitted, there is no need for follow-up. Follow-up is crucial. The healthcare provider should ensure that the carrier acknowledges receipt of the request and that the authorization process is progressing. Delays can occur, and proactive communication can prevent roadblocks.
Key takeaways
When filling out and using the LWC Form 1010, consider these essential takeaways:
- Clarity is key: Ensure that all information, such as names and addresses, is printed clearly to avoid any misunderstandings.
- Complete all sections: Each part of the form must be thoroughly filled out, including identifying information and details about the requested treatment or testing.
- Include all required documentation: Attach all necessary supplements to support your request for authorization. This ensures that the carrier or self-insured employer has the full context.
- Check for accuracy: Review the form for errors before submission, particularly Social Security numbers, dates, and medical codes.
- Submission method matters: Submit the form via fax or email as indicated on the form to ensure it reaches the intended recipient promptly.
- Know the approval process: Familiarize yourself with the potential responses from carriers, including full approval, modified approval, or denial.
- Understanding timelines: Be aware of the time frames associated with responses to your requests. Prompt follow-up may be necessary.
- Respond to denials: If authorization is denied, take note of the reasons provided and consider submitting additional information for reconsideration.
- Be proactive in communication: Maintain open lines of communication with both the health care provider and the carrier for any questions or clarifications needed during the process.
Browse Other Templates
Nj Court Forms - Directly contact legal aid services if you need help and cannot afford a lawyer.
Alabama Cr - Ensuring the form is filled out correctly protects defendants' rights.
Wells Fargo Letterhead - This handbook outlines company policies and resources available to staff.