Fill Out Your G 49 Form
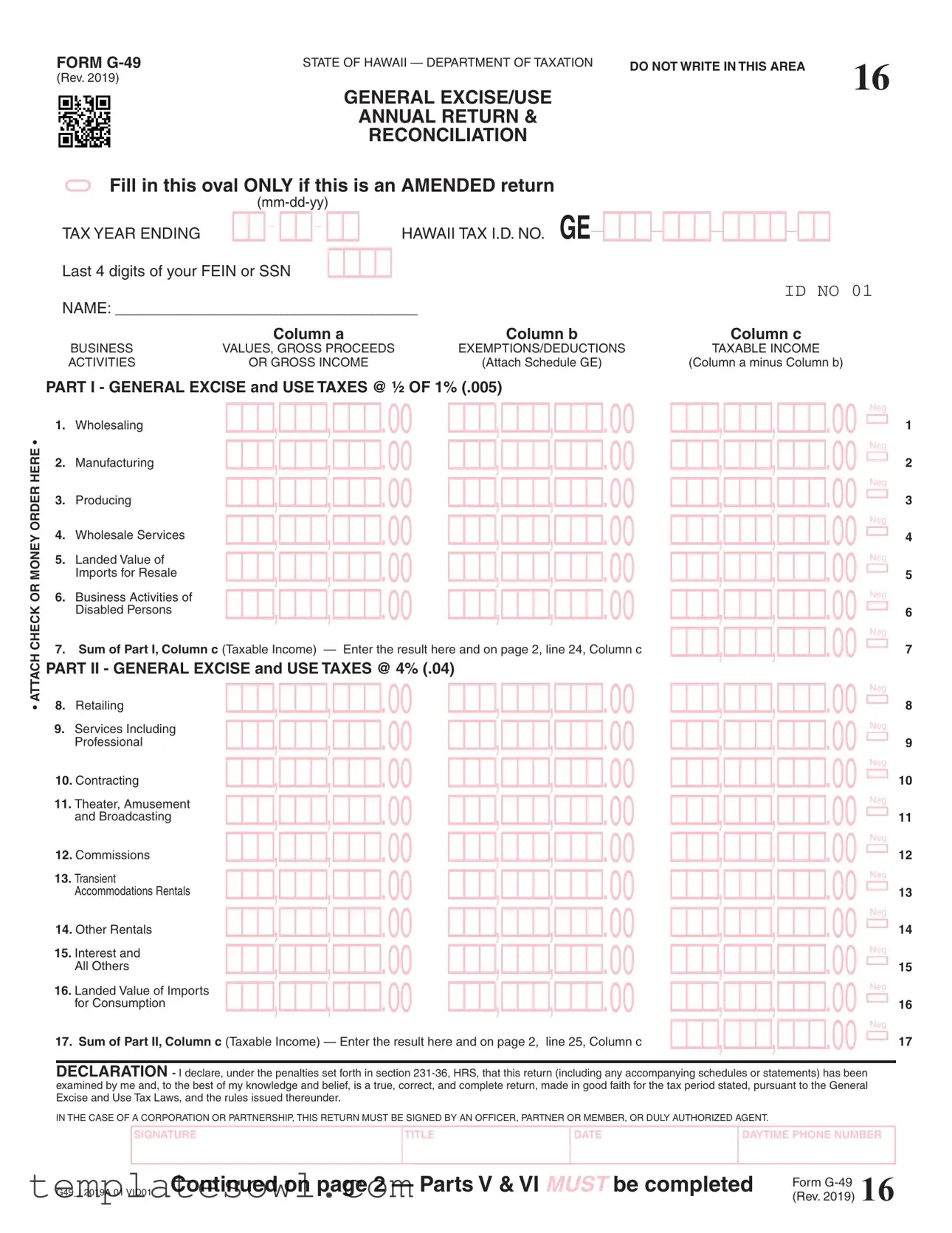
The G-49 form is an essential document for businesses operating in Hawaii. It serves as the annual return and reconciliation for general excise and use taxes. Businesses must provide key information, including their Hawaii Tax I.D. number and the last four digits of their Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or Social Security Number (SSN). The form consists of multiple sections that require detailed disclosures of gross income, deductions, and exemptions. Specifically, it breaks down taxable income across various business activities such as wholesaling, retailing, and professional services. Additionally, businesses must report their insurance commissions and calculate applicable county surcharges. With a structured layout, the form facilitates accurate tax calculations, including tax rates for different activities. It also includes sections for penalties and interest, which are critical for ensuring compliance with Hawaii's tax regulations. Completing the G-49 form correctly is vital for any business to meet its legal obligations and avoid potential penalties.
G 49 Example

FORM |
STATE OF HAWAII — DEPARTMENT OF TAXATION |
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA |
16 |
(Rev. 2019) |
|
|
|
GENERAL EXCISE/USE
ANNUAL RETURN &
RECONCILIATION
= Fill in this oval ONLY if this is an AMENDED return
TAX YEAR ENDING
!!!!
NAME: ___________________________________ |
|
ID NO 01 |
|
|
|
||
|
Column a |
Column b |
Column c |
BUSINESS |
VALUES, GROSS PROCEEDS |
EXEMPTIONS/DEDUCTIONS |
TAXABLE INCOME |
ACTIVITIES |
OR GROSS INCOME |
(Attach Schedule GE) |
(Column a minus Column b) |
• ATTACH CHECK OR MONEY ORDER HERE •
PART I - GENERAL EXCISE and USE TAXES @ ½ OF 1% (.005)
1. |
Wholesaling |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
2. |
Manufacturing |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|||
3. |
Producing |
|||
4. |
Wholesale Services !!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
||
5. |
Landed Value of |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
|
Imports for Resale |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
6. |
Business Activities of |
|||
Disabled Persons
7.Sum of Part I, Column c (Taxable Income) — Enter the result here and on page 2, line 24, Column c
PART II - GENERAL EXCISE and USE TAXES @ 4% (.04) |
||||
8. |
Retailing |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
9. |
Services Including |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
|
Professional |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
10. |
Contracting |
|||
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|||
11. |
Theater, Amusement |
|||
|
and Broadcasting |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
12. |
Commissions |
|||
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|||
13. |
Accommodations Rentals |
|||
Transient |
|
|
||
14. |
Other Rentals |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
15. |
Interest and |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
|
All Others |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
16. |
Landed Value of Imports |
|||
for Consumption
17. Sum of Part II, Column c (Taxable Income) — Enter the result here and on page 2, line 25, Column c
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 Neg
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
DECLARATION - I declare, under the penalties set forth in section
IN THE CASE OF A CORPORATION OR PARTNERSHIP, THIS RETURN MUST BE SIGNED BY AN OFFICER, PARTNER OR MEMBER, OR DULY AUTHORIZED AGENT.
SIGNATURE |
TITLE |
DATE |
DAYTIME PHONE NUMBER |
|
|
|
|
G49_I 2019A 01 VID01 |
Continued on page 2 — Parts V & VI MUST be completed (Rev. 2019) 16 |
|
Form |

FORM
(Rev. 2019) |
Name:___________________________________________________ |
|
||||
Page 2 of 2 |
|
|||||
|
Hawaii Tax I.D. No. |
|
ID NO 01 |
|
||
|
|
|
||||
|
Last 4 digits of your FEIN or SSN !!!! |
TAX YEAR ENDING |
||||
|
|
Column a |
Column b |
|
Column c |
|
BUSINESS |
|
VALUES, GROSS PROCEEDS |
EXEMPTIONS/DEDUCTIONS |
TAXABLE INCOME |
|
|
ACTIVITIES |
|
OR GROSS INCOME |
(Attach Schedule GE) |
|
(Column a minus Column b) |
|
PART III - INSURANCE COMMISSIONS @ .15% (.0015) |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
Enter this amount on line 26, Column c |
|
|||
18. Insurance |
|
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
Neg |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commissions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART IV - COUNTY SURCHARGE — Enter the amounts from Part II, line 17, Column c attributable to each county. Multiply Column c by |
|
|||||
|
|
the applicable county rate(s) and enter the total of the result(s) on Part VI, line 27, Column e. |
|
|||
|
|
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
Neg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19. Oahu (rate = .005) |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
20. Maui |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
||
|
|
Neg |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21. Hawaii (rate = .005) |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
|
||
|
|
Neg |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22. Kauai (rate = .005)
18
19
20
21
22
PART V — SCHEDULE OF ASSIGNMENT OF TAXES BY DISTRICT (ALL taxpayers MUST complete this Part and may be subject to a 10% penalty for noncompliance.) DARKEN the oval of the taxation district in which you have conducted business. IF you did business in MORE THAN ONE district, darken the oval “MULTI” and attach Form
23. |
= Oahu |
= Maui |
= Hawaii |
= Kauai |
= MULTI |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|||
PART VI - TOTAL RETURN AND RECONCILIATION TAXABLE INCOME |
TAX RATE |
TOTAL TAX |
|
|||
|
|
|
Column c |
Column d |
Column e = Column c X Column d |
|
24. |
Enter the amount from Part I, line 7 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
x .005 |
24. |
25. |
Enter the amount from Part II, line 17 |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
x .04 |
25. |
26. |
Enter the amount from Part III line 18, Column c |
!!!,!!!,!!!.00 |
x .0015 |
26. |
27. |
COUNTY SURCHARGE TAX. See Instructions for Part IV. Multi district complete Form |
27. |
||||||
28. TOTAL TAXES DUE. Add column e of lines 24 through 27 and enter result here (but not less than zero). |
||||||||
|
If you did not have any activity for the period, enter “0.00” here |
|
|
28. |
||||
29. |
Amounts Assessed During the Period |
PENALTY $ |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
INTEREST $ |
29. |
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
30. |
TOTAL AMOUNT. Add lines 28 and 29 |
|
|
|
|
30. |
||
31. |
TOTAL PAYMENTS MADE LESS ANY REFUNDS RECEIVED FOR THE TAX YEAR |
|
|
31. |
||||
32. |
CREDIT CLAIMED ON ORIGINAL ANNUAL RETURN. (For Amended Return ONLY) |
|
|
32. |
||||
33. |
NET PAYMENTS MADE. Line 31 minus line 32 |
|
|
|
|
33. |
||
34. |
CREDIT TO BE REFUNDED. Line 33 minus line 30 |
|
|
|
|
34. |
||
35. |
ADDITIONAL TAXES DUE. Line 30 minus line 33 |
|
|
|
|
35. |
||
36. |
FOR LATE FILING ONLY |
PENALTY $ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
INTEREST $ |
|
|
|
36. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
37. |
TOTAL AMOUNT DUE AND PAYABLE (Add lines 35 and 36) |
|
|
37. |
||||
38.PLEASE ENTER THE AMOUNT OF YOUR PAYMENT. If you are NOT submitting a
payment with this return, please enter “0.00” here |
38. |
39. GRAND TOTAL OF EXEMPTIONS/DEDUCTIONS CLAIMED. (Attach Schedule GE) |
If Schedule |
GE is not attached, exemptions/deductions claimed will be disallowed |
39. |
G49_I 2019A 02 VID01
!!!,!!!,!!!.!! Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.!! Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.!! Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.!! Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.!! Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.!! Neg
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.!!
!!!,!!!,!!!.00
Form
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The G-49 form is used by businesses in Hawaii to report General Excise and Use taxes along with annual returns and reconciliations. |
| Governing Laws | This form is governed by the General Excise Tax Law and the Use Tax Law in Hawaii, specifically under Section 231-36, HRS. |
| Eligibility | All businesses operating in Hawaii that receive gross income or gross proceeds from activities subject to the General Excise Tax must file this form annually. |
| Filing Frequency | The G-49 must be filed annually, regardless of whether the business was active or inactive during the tax year. |
| Key Components | The form includes sections for business values, gross proceeds, exemptions/deductions, and taxable income, along with a declaration that the information provided is accurate. |
| Amended Returns | An oval must be filled in to indicate that the return is amended if changes have been made to previously submitted information. |
Guidelines on Utilizing G 49
Completing the G-49 form may seem daunting, but breaking it down into clear steps can make the process manageable. This form is essential for reporting tax information, and getting it right helps avoid any penalties. Here’s how to fill it out.
- Start by entering the last 4 digits of your FEIN or SSN at the top right corner.
- Indicate whether this is an amended return by filling in the oval if it applies.
- Fill in the tax year ending in the specified format (mm-dd-yy).
- Input your Hawaii Tax I.D. Number in the designated area.
- Write your name and ID number where indicated.
- In the section for Part I, accurately list the amounts in Column a (Business Values) and Column b (Exemptions/Deductions) for each activity.
- Calculate Column c (Taxable Income) by subtracting Column b from Column a.
- Repeat this data entry process for Part II and III.
- For Part IV, report amounts for each county by multiplying the amounts from Part II by the respective county rates.
- In Part V, mark the appropriate taxation district in which you conducted business.
- Complete Part VI with totals from the previous sections, ensuring calculations for total taxes due are correct.
- Sign and date the form in the declaration section, entering your title and daytime phone number.
- Attach any necessary documents, such as checks or money orders, to the form.
Once you've completed the form, make sure to double-check your entries for accuracy. Submit it according to the instructions provided, ensuring you've included all required attachments. Staying organized at this step will help keep your tax matters in good standing.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the G-49 form?
The G-49 form is the General Excise/Use Annual Return and Reconciliation for the state of Hawaii. It's a tax form that businesses use to report their gross income, exemptions, and deductions for the year. Understanding how to fill out this form is crucial for compliance with Hawaii's tax laws.
Who needs to file the G-49 form?
Any business operating in Hawaii that is subject to the General Excise Tax must file a G-49 form. This includes corporations, partnerships, sole proprietorships, and other entities engaged in commercial activities. If your business generates income in Hawaii, it's likely you'll need to submit this form annually.
When is the G-49 form due?
The G-49 form is usually due on the last day of the month following the end of the tax year, which for most businesses is December 31. Therefore, the form should typically be submitted by January 31 of the following year. If you operate on a different fiscal year, the deadline will correspond to the end of that fiscal period.
What information do I need to complete the G-49 form?
To fill out the G-49, you'll need several pieces of information. This includes your Hawaii Tax Identification Number, the last four digits of your Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or Social Security Number (SSN), and your total gross income for the year. You’ll also need to report any applicable exemptions or deductions, as well as calculate the taxes owed based on the provided rates.
Can I amend a previously filed G-49 form?
Yes, if you discover an error in your previously filed G-49 form, you can amend it. Make sure to fill in the oval that indicates the return is amended, and include detailed explanations and corrections. Amending your return ensures that any discrepancies are corrected, which helps avoid potential penalties or interest for underreporting your taxes.
What happens if I miss the filing deadline for the G-49?
If you miss the deadline for filing the G-49, you may be subject to penalties and interest on any unpaid taxes. It's important to file as soon as possible to minimize these costs. If you find yourself in this situation, consider contacting a tax professional for guidance on how to proceed.
Common mistakes
When filling out the G-49 form, many individuals make common mistakes that can potentially lead to problems later, ranging from minor issues to significant complications. One frequent error is neglecting to provide the last four digits of the Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or Social Security Number (SSN). This information is essential for identification and processing, so omitting it can delay the return.
Another mistake occurs while entering the tax year. People sometimes forget to specify the correct year in the designated field. Accuracy is crucial, as the tax year dictates the applicable rates and laws. Errors in this section often result in confusion and require additional communication with the tax office.
Additionally, individuals sometimes skip including all necessary business values in Column "a". Omitting entries can lead to understated income, which may affect tax calculations severely. Each revenue source should be recorded accurately to assure compliance and avoid penalties.
Some fill out their exemptions or deductions incorrectly in Column "b". It's essential to ensure that the exemptions and deductions claimed are valid under Hawaii law. Errors here can lead to a misunderstanding of taxable income, which impacts overall tax liability.
People often make mistakes in column calculations, especially when deriving taxable income in Column "c". Calculating Column "c" as Column "a" minus Column "b" needs careful attention. Miscalculations can lead to tax payment discrepancies and potential legal consequences.
Many filers also forget to sign the form. Without a signature, the document may be deemed incomplete. A signature serves as a declaration that the information provided is accurate and truthful, which is an essential part of the filing process.
Some individuals fail to attach the required Schedule GE, which outlines further details about gross income. This omission can result in deductions or exemptions being disallowed, affecting the final tax bill.
Another common oversight involves misreporting the county surcharge. Taxpayers may not calculate the surcharge based on the correct taxable income, leading to inaccuracies in tax owed, which can alter compliance and incur additional costs.
Lastly, many don’t review their completed forms before submission. A thorough review can catch numerous errors, from data entry mistakes to miscalculations, ensuring that the G-49 form reflects accurate information before it is sent in. Thus, giving attention to detail during this process can prevent future complications.
Documents used along the form
The G-49 form for Hawaii's General Excise and Use Tax is often accompanied by several other documents. Each one plays a unique role in the tax reporting process. Below are forms and documents commonly used alongside the G-49.
- Schedule GE: This document lists exemptions and deductions claimed by the taxpayer. It provides details necessary for calculating taxable income and must be attached to the G-49.
- Form G-75: Used for taxpayers engaged in business across multiple districts. This form aids in assigning taxes by district and must be completed if applicable.
- Form G-100: A general form used for reporting income or deductions related to general excise tax. It can simplify the filing process for certain businesses.
- Form G-17: This form is used to report and pay county surcharge taxes separately, often affecting those conducting business in more than one county.
- Taxpayer Notification Letters: These letters may be sent to inform taxpayers of changes in tax laws or obligations. They help ensure compliance with state regulations.
- Payments Documentation: This includes bank statements or receipts showing payments made towards taxes. It serves as proof when substantiating claims or payments.
- Previous Year’s Tax Returns: Past returns provide context and information that may assist in completing the current year's G-49. Review can highlight changes or discrepancies.
- Partnership or Corporate Agreements: These documents detail the structure of the business entity. They may be required for partnerships or corporations to clarify how profits and taxes are handled.
- IRS Forms: Federal tax forms may be needed if applicable, especially if the business has federal tax obligations that align with state requirements.
Filing the G-49 can be complex, and having these documents ready can streamline the process. Ensuring each form is accurately filled out and submitted can reduce errors and potential issues with tax compliance.
Similar forms
The G-49 form, which is used for reporting the General Excise/Use Annual Return and Reconciliation in Hawaii, shares similarities with several other tax-related documents. Here is a list of documents that are analogous to the G-49 form, along with a description of their similarities:
- Form 1040: This is the standard individual income tax return form used in the United States. Like the G-49, it allows individuals to report income and deductions for a specific tax year.
- Form 1120: This form is used by corporations to report income, gains, losses, and deductions. Similar to the G-49, it requires a calculation of taxable income based on various revenues and deductions.
- Form 1065: Partnerships use this form to report their income, deductions, gains, and losses. Just as the G-49 is related to General Excise Tax, this form mandates disclosure of income and expenses related to the partnership's operations.
- Form W-2: Employers use this form to report wages paid to employees and the taxes withheld from those wages. It shares similarities with G-49 in that both require accurate reporting of taxable income.
- Form 941: This quarterly tax return is for employers to report income, social security, and Medicare taxes withheld from employee pay. Like the G-49, it involves reporting on various taxable activities over defined periods.
- Schedule C (Form 1040): Independent contractors and sole proprietors use this to report income and expenses. Both documents require details about sales and tax obligations related to business activities.
- Form 990: This is an informational tax form that most tax-exempt organizations must file annually. It requires detailed reporting of revenue and expenses, akin to the structured reporting required by the G-49.
- Form 1099: Various 1099 forms report different income types, such as nonemployee compensation. Similar to the G-49, they necessitate a declaration of income received, which may be subject to taxation.
- Form G-75: Used in Hawaii for multi-district taxation reporting, this form has a direct relationship with the G-49 in terms of detailing transactions across different districts within the state.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the G-49 form, there are important steps to follow to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here’s a straightforward guide on what to do and what to avoid.
- Do provide the last four digits of your FEIN or SSN on the appropriate line.
- Do indicate if this is an amended return by filling in the corresponding oval.
- Do ensure all numerical entries are accurate and clearly written to prevent errors.
- Do attach any necessary schedules, such as the Schedule GE, before submitting the form.
- Do sign and date the form, as failing to do so can result in processing delays.
- Do not leave any fields blank; fill in all required information completely.
- Do not use pencil; all entries should be made in black or blue ink.
- Do not forget to calculate and include any penalties or interest if applicable.
- Do not neglect to double-check the total taxes due to avoid overpayment or underpayment.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The G-49 form is only for large businesses.
- Misconception 2: Submitting the G-49 form guarantees a tax refund.
- Misconception 3: Filing an amended G-49 form is unnecessary if errors are made.
- Misconception 4: Only certain types of income are reported on the G-49 form.
- Misconception 5: The form does not need to be filed if no business was conducted during the year.
- Misconception 6: The G-49 form can be submitted anytime during the year.
- Misconception 7: Handwritten forms are not accepted.
This form is applicable to all businesses operating in Hawaii, regardless of size. Small businesses must also file it to comply with state tax laws.
While completing and filing the form may lead to a tax refund for some taxpayers, it does not ensure a refund for everyone. Refunds depend on individual tax situations.
If errors occur on the original form, it is essential to file an amended G-49 form to correct those mistakes. This action ensures compliance with tax regulations and prevents potential penalties.
All taxable business activities and income should be reported on the G-49 form. This includes a wide range of activities such as retailing, services, and rentals.
Even if no business activities occurred in a given year, taxpayers are still required to file the G-49 form and indicate that there was no income.
The form must be filed by the Hawaii Department of Taxation's due date, which is typically on or before the end of the fiscal year. Timely submission is crucial to avoid penalties.
While it's generally recommended to submit typed forms for clarity, the G-49 form can be filled out by hand. However, ensuring legibility is crucial for processing.
Key takeaways
1. Complete the G 49 form for the General Excise/Use Annual Return and Reconciliation accurately.
2. Use your Hawaii Tax I.D. Number and last four digits of your FEIN or SSN at the beginning of the form.
3. If you are amending a return, mark the oval that indicates this is an amended return.
4. Clearly itemize your business values, gross proceeds, exemptions, and deductions in the respective columns.
5. Calculate your taxable income by subtracting Column b from Column a for each section.
6. Be aware of the different tax rates specified in the form, such as 0.5% for Part I and 4% for Part II.
7. Fill out Parts V and VI completely to prevent any potential penalties.
8. Ensure an authorized representative signs the declaration section if the return is for a corporation or partnership.
9. Submit any required payment with the form. If no payment is due, enter “0.00.”
Browse Other Templates
Osha 5020 - Confirm if the employee was unable to work for at least one full day.
Subscribed and Sworn to Before Me This Sample - The California Jurat must be kept secure after use.