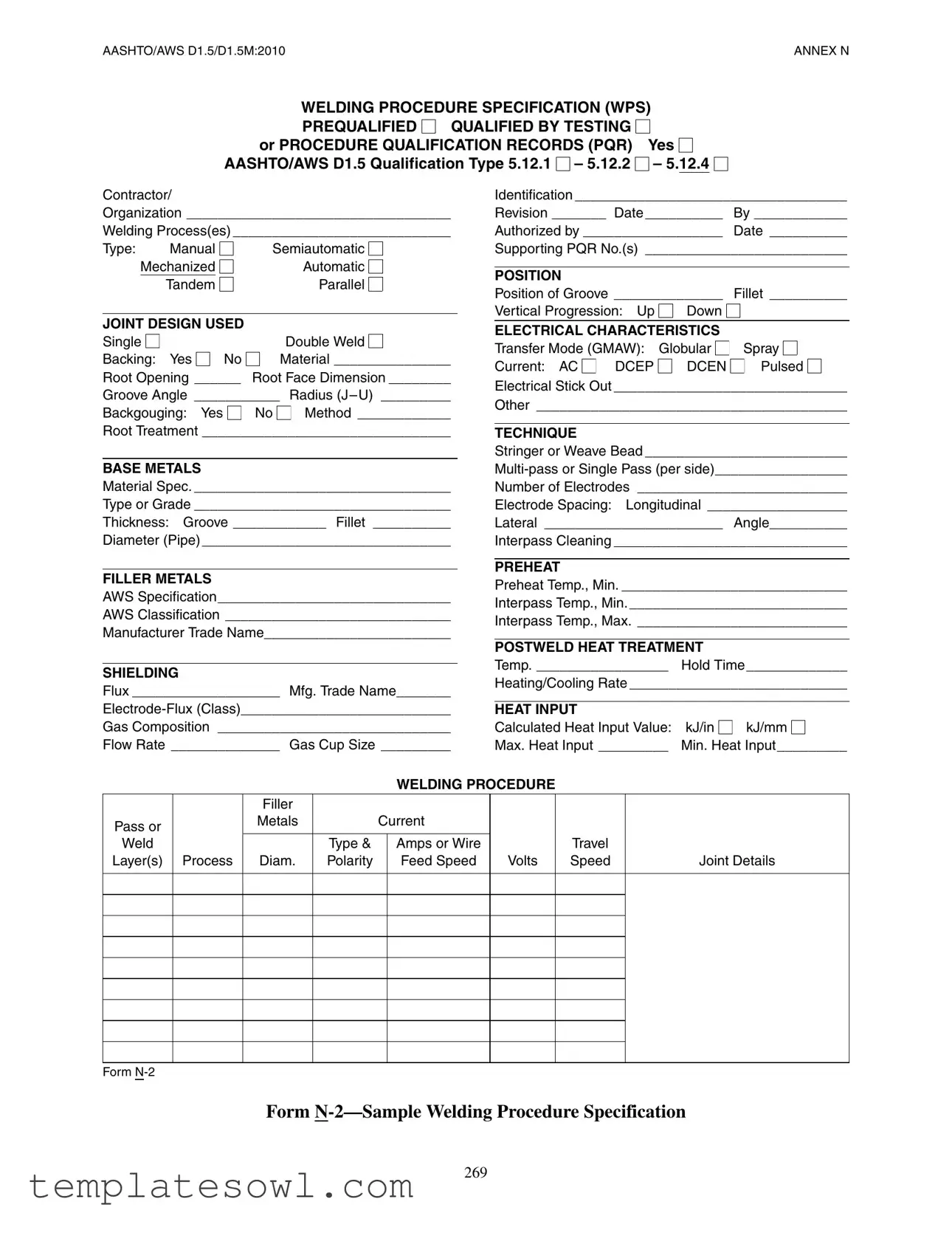
Fill Out Your N 2 Form
The N 2 form is a crucial document in the field of welding, specifically designed to ensure that welding procedures meet the necessary qualifications and standards set forth by AASHTO/AWS D1.5. This form serves as a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) and provides a structured means for contractors and organizations to describe their welding processes in detail. Key components of the N 2 form include sections on joint design, base metals, and filler metals, enabling users to specify important aspects like material specifications, electrode classifications, and dimensional parameters. It also requires information on welding techniques, electrical characteristics, and preheat/post-weld heat treatment processes. Each of these elements plays a significant role in establishing the consistency and quality of the welds, while also promoting safety and compliance with industry standards. Importantly, the N 2 form addresses both qualified procedures and those prequalified by testing or using Procedure Qualification Records (PQR), thereby accommodating various levels of welding expertise and project requirements. By outlining these specifications systematically, the N 2 form not only facilitates clear communication among welding professionals but also enhances the overall reliability of welded structures.
N 2 Example
AASHTO/AWS D1.5/D1.5M:2010ANNEX N
WELDING PROCEDURE SPECIFICATION (WPS)
PREQUALIFIED |
QUALIFIED BY TESTING |
|
|
or PROCEDURE QUALIFICATION RECORDS (PQR) |
Yes |
||
AASHTO/AWS D1.5 Qualification Type 5.12.1 – 5.12.2 |
– 5.12.4 |
||
|
|
|
|
Contractor/
Organization __________________________________
Welding Process(es) ____________________________
Type: |
Manual |
Semiautomatic |
||
Mechanized |
|
Automatic |
||
|
Tandem |
|
Parallel |
|
|
|
|
||
JOINT DESIGN USED |
|
|
||
Single |
|
|
|
Double Weld |
Backing: |
Yes |
No |
|
Material _______________ |
Root Opening ______ |
Root Face Dimension ________ |
|||
Groove Angle ___________ |
Radius (J – U) _________ |
|||
Backgouging: |
Yes |
No |
Method ____________ |
|
Root Treatment ________________________________
BASE METALS
Material Spec. _________________________________
Type or Grade _________________________________
Thickness: Groove ____________ Fillet __________
Diameter (Pipe) ________________________________
FILLER METALS
AWS Specification______________________________
AWS Classification _____________________________
Manufacturer Trade Name________________________
SHIELDING
Flux ___________________ Mfg. Trade Name_______
Gas Composition ______________________________
Flow Rate ______________ Gas Cup Size _________
Identification ___________________________________
Revision _______ Date __________ By ____________
Authorized by __________________ Date __________
Supporting PQR No.(s) __________________________
POSITION |
|
|
|
Position of Groove ______________ |
Fillet __________ |
||
Vertical Progression: Up |
Down |
|
|
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
||
Transfer Mode (GMAW): |
Globular |
Spray |
|
Current: AC |
DCEP |
DCEN |
Pulsed |
Electrical Stick Out ______________________________
Other ________________________________________
TECHNIQUE
Stringer or Weave Bead __________________________
Number of Electrodes ___________________________
Electrode Spacing: Longitudinal __________________
Lateral _______________________ Angle__________
Interpass Cleaning ______________________________
PREHEAT
Preheat Temp., Min. _____________________________
Interpass Temp., Min. ____________________________
Interpass Temp., Max. ___________________________
POSTWELD HEAT TREATMENT
Temp. _________________ Hold Time _____________
Heating/Cooling Rate ____________________________
HEAT INPUT |
|
|
Calculated Heat Input Value: |
kJ/in |
kJ/mm |
Max. Heat Input _________ |
Min. Heat Input _________ |
|
WELDING PROCEDURE
|
|
Filler |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pass or |
|
Metals |
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weld |
|
|
Type & |
|
Amps or Wire |
|
Travel |
|
Layer(s) |
Process |
Diam. |
Polarity |
|
Feed Speed |
Volts |
Speed |
Joint Details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form
Form
269
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Governing Standards | The N2 form adheres to AASHTO/AWS D1.5/D1.5M:2010 requirements. |
| Qualification Types | It involves prequalification through testing or Procedure Qualification Records (PQR). |
| Welding Processes | The form covers various welding processes: Manual, Semiautomatic, Mechanized, Automatic. |
| Joint Design | Single and double joint designs can be used, with options for backing. |
| Base Metals Specification | Requires specification for material type, grade, and thickness for groove and fillet welds. |
| Filler Metal Requirements | Documentation of AWS specifications and classifications for filler metals is necessary. |
| Electrical Characteristics | Details on transfer modes, currents (AC, DCEP, DCEN), and stick-out lengths are included. |
| Preheat Requirements | Minimum preheat and interpass temperatures must be documented for the welding process. |
| Heat Input Calculation | Calculates both maximum and minimum heat input values, measured in kJ/in and kJ/mm. |
| Post-Weld Treatment | Specifies temperature, hold time, and cooling rates for any post-weld heat treatment required. |
Guidelines on Utilizing N 2
Filling out the N 2 form requires attention to detail and accurate information to create a complete Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). It is essential to gather all necessary documentation and information regarding the welding process, materials, and qualifications before starting. Following a clear set of steps ensures that all relevant data is included properly.
- Contractor/Organization: Enter the name of your organization in the designated space.
- Welding Process: Specify the type of welding processes you will use. Check all that apply: Manual, Semiautomatic, Mechanized, Automatic, Tandem, or Parallel.
- Joint Design: Indicate whether it is a Single or Double joint design. State if backing is used with "Yes" or "No." Fill in the material type, root opening, root face dimension, groove angle, and radius details.
- Backgouging: Indicate if this is performed, then provide the method and root treatment if applicable.
- Base Metals: Specify material specifications, type or grade of base metals, and their thickness for both groove and fillet. Include the diameter for pipe materials as well.
- Filler Metals: Enter the AWS specification and classification, along with the manufacturer's trade name for the filler metals used.
- Shielding: List the type of shielding, including flux and gas composition, along with the flow rate and gas cup size.
- Identification: Fill in revision details, date, and your name along with the authorized name and date.
- Supporting PQR No(s): Include any relevant procedure qualification record numbers.
- Position: Indicate the position of the groove or fillet and describe the progression (up or down).
- Electrical Characteristics: State the transfer mode and electrical parameters like current type, stick out length, and any additional details.
- Technique: Describe the welding technique, number of pass(es), and details about electrode spacing.
- Interpass Cleaning: Specify any interpass cleaning methods used.
- Preheat: Document preheat and interpass temperatures, both minimum and maximum.
- Post-weld Heat Treatment: Note the temperature, hold time, and heating/cooling rates for post-weld treatment.
- Heat Input: Calculate and enter the heat input values, including maximum and minimum heat input.
- Welding Procedure: Fill in details such as filler pass/type of metal, current type, amps, wire diameter, polarity, travel speed, volts consumed, and joint details.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the N 2 form?
The N 2 form is a detailed document used in the field of welding, specifically in reference to the Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) as per the AASHTO/AWS D1.5 standard. This form outlines the specifications and qualifications required for different welding procedures, which are crucial for ensuring safety and quality in welding projects.
Who needs to fill out the N 2 form?
This form must be completed by contractors or organizations that conduct welding operations. It is typically filled out by welding engineers, inspectors, or qualified personnel responsible for developing and documenting welding procedures. This way, all applicable parameters and qualifications of the welding process are properly addressed.
What information is required on the N 2 form?
The N 2 form requests various details about the welding procedure, including contractor information, joint design and dimensions, base and filler metals specifications, shielding gases, electrical characteristics, and preheat and post-weld heat treatment parameters. Additionally, it asks for the positions of the weld and any required qualifications or supporting documentation.
How does the N 2 form relate to quality control?
The N 2 form serves as a critical component of quality control in welding. By documenting the exact procedures, materials, and techniques, it provides a reference for inspectors and engineers. This ensures that the welding process adheres to established standards and reduces the likelihood of defects, which in turn enhances the overall safety and integrity of the welded structure.
Is the N 2 form mandatory?
The use of the N 2 form is mandated by various codes and standards in the welding industry. Depending on the project and jurisdiction, failing to use the correct documentation may result in penalties or disqualification for contractors. Therefore, it is often a requirement for compliance on governmental and structural projects.
What types of welding processes can the N 2 form accommodate?
The N 2 form is designed to accommodate various welding processes, including manual, semiautomatic, mechanized, automatic, and tandem parallel welding. This flexibility allows it to be used for a wide range of applications, tailored to the specific needs and technologies being employed in a construction project.
How can one ensure that the N 2 form is correctly completed?
To correctly complete the N 2 form, it is essential to refer to the applicable standards, such as AASHTO and AWS. Collaboration with experienced welding engineers or inspectors can help clarify any questions and ensure that incorrect or incomplete information does not compromise the submission. Additionally, the use of a checklist can assist in capturing all necessary data.
What happens after submitting the N 2 form?
Once the N 2 form is completed and submitted, it often undergoes review by relevant oversight bodies or quality control personnel. They will verify the information, assess it against the required standards, and determine if the welding procedure is acceptable. Subsequent approvals may allow the project to proceed while maintaining compliance with safety regulations.
Where can one find the N 2 form?
The N 2 form can typically be found through associations related to welding standards, such as AASHTO or AWS. It may also be available from welding equipment suppliers or as part of training materials for welding professionals. Furthermore, some companies may have their own templates or guidelines for filling out the form correctly.
Common mistakes
When filling out the N 2 form, individuals often make several common mistakes that can lead to delays or complications in the approval process. A particularly frequent error is providing incomplete or inaccurate information in the sections reserved for contractor or organization details. Ensure that the organization’s name is clearly stated, as missing this can create confusion.
Another common mistake is failing to select the appropriate welding process. The form allows for several different types, including manual, semiautomatic, mechanized, and automatic. Not specifying the correct process can lead to significant issues, as the specifications differ based on the welding method.
People frequently overlook the importance of accurately defining joint design. This includes specifying whether a single or double joint design is used and providing details about backing configurations. Errors in this section can affect the structural integrity of the weld and must be corrected for regulatory compliance.
In the section related to base metals, a common oversight is not including the correct material specifications and thickness. Ensure that both groove and fillet thicknesses are accurately represented. Failing to specify these details can result in an invalid application.
When it comes to filler metals, individuals often forget to provide the AWS specification and classification. These details are crucial for determining the compatibility of materials being welded together. Without them, the form may be deemed incomplete, leading to processing delays.
Another area that sees mistakes is the identification of shielding gas composition and flow rate. Incorrect entries or omission of this data can lead to improper welding conditions, which can jeopardize the quality of the weld. Always double-check this information.
Progression settings are also frequently misrepresented. The vertical progression should accurately state whether the weld is moving up or down. An error in this selection could mislead those reviewing the specification, resulting in misunderstanding of the welding approach being utilized.
Finally, applicants often neglect to verify the calculated heat input values. Incorrect values, whether too high or too low, may affect the overall integrity of the weld. Double-checking these calculations can prevent potential issues down the line.
Documents used along the form
The N 2 form, often used in welding procedures, is accompanied by several other important documents that provide essential details for compliance and quality assurance. Keeping in mind the complexities involved in welding specifications, these supporting documents add clarity and structure, ensuring safe and effective practices. Below are a few key forms frequently utilized with the N 2 form.
- Welding Procedure Qualification Record (PQR): This document records the testing results that validate a specific welding procedure. It includes detailed information about the weld's characteristics, materials used, and the testing methods applied. By providing evidence of compliance, it ensures that the procedure is capable of producing welds meeting required standards.
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS): This is a formalized document that details how specific welding tasks should be accomplished. It outlines the conditions under which welding is to take place, including the materials, processes, and techniques involved. Adherence to the WPS helps to achieve consistent and high-quality welds.
- Joint Design Specification: This document specifies the design and configuration of the welded joint. It includes critical details such as joint geometry, dimensions, and the type of weld to be used. A well-defined joint design is crucial to the structural integrity of the welded assembly.
- Material Specifications: This document outlines the types and grades of materials used in the welding process. It ensures that all materials meet the required standards, which is vital for achieving desired performance and safety in the final product.
Understanding and utilizing these documents alongside the N 2 form greatly enhances the reliability and safety of welding practices. By maintaining thorough documentation, organizations can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also foster a culture of quality control and improvement in their operations.
Similar forms
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS): The N 2 form closely resembles a Welding Procedure Specification, which outlines how welding should be performed. Both documents provide detailed parameters regarding materials, welding processes, and techniques to ensure consistent and quality welds.
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR): Similar to the N 2 form, a PQR documents the actual welding performed during qualification testing. It includes information on the weld properties and helps verify that the WPS is effective in producing a sound weld.
- Welding Inspection Report: This document is akin to the N 2 form as it records the results of inspections conducted on welds. It ensures that welding processes align with the documented WPS, ensuring compliance and quality assurance.
- Material Test Report (MTR): An MTR provides evidence of the material properties used in the welding process. Like the N 2 form, it includes specifications and compliance data that verify the quality of the base and filler metals used.
- Certificates of Compliance: These certifications, similar to the N 2, affirm that the materials and processes adhere to regulatory or industry standards. They provide assurance of quality and safety in welding procedures.
- Weld Procedure Approval Form: This form is related to the N 2 as it is used for seeking approval of a welding procedure. It summarizes the essential data similar to the N 2, which is part of the approval process for specific welding techniques.
- Welding Sequence Plan: This document outlines the specific order and method of welding operations, much like the N 2 form, which provides critical guidance for carrying out the welding tasks effectively and efficiently.
- Welding Quality Control Plan: Much like the N 2 form, this plan specifies the measures required to control welding quality. It outlines procedures, inspections, and tests to verify that the welding process follows the established standards.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the N 2 form, careful attention to detail is essential. Here are five recommendations and precautions to ensure an accurate submission.
- Double-check all entries: Verify that all information is accurate and complete before submitting the form.
- Use clear and legible handwriting: If filling out the form by hand, ensure that your writing is neat to avoid misinterpretation.
- Follow all formatting guidelines: Adhere to any specific requirements regarding font size, spacing, and section titles.
- Consult applicable references: Utilize the AASHTO/AWS D1.5 documentation to ensure compliance with all technical requirements.
- Keep a copy: Always make a copy of the completed form for your records before submission.
- Avoid leaving fields blank: Fill in all required fields to prevent delays in processing your application.
- Refrain from using abbreviations: Write out terms fully to reduce confusion.
- Do not ignore instructions: Carefully read through all instructions provided in the form.
- Do not submit without review: Have another individual review the form for completeness and errors.
- Avoid using unofficial sources: Rely only on official guidelines and documents related to the N 2 form.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The N 2 form is only for large construction projects.
- Misconception 2: Completing the N 2 form guarantees a pass on all welding inspections.
- Misconception 3: The N 2 form is primarily concerned with the materials used in welding.
- Misconception 4: There is no need for updates once the N 2 form is completed.
- Misconception 5: Only certified welders can fill out the N 2 form.
- Misconception 6: The N 2 form is not required for small welds or repairs.
- Misconception 7: The N 2 form is too complex to understand.
This form is applicable to a variety of welding applications, not just large-scale projects. It addresses welding procedures in many industries, ensuring quality and safety across different types of jobs.
While the N 2 form provides crucial details about the welding process, it does not guarantee that inspections will pass. Quality of execution is equally important in meeting inspection standards.
Although material specifications are part of the N 2 form, it covers much more. The form outlines welding techniques, positions, preheat temperatures, and post-weld treatments, all critical for successful welding processes.
Welding procedures can change based on various factors, such as new materials or techniques. Thus, it is important to regularly review and, if necessary, update the N 2 form to reflect the most current practices.
While certified personnel should ideally oversee the welding process, anyone knowledgeable about the welding procedures and materials can assist in completing the N 2 form. However, authorized personnel should finalize and sign it.
The N 2 form is beneficial even for small welds or repairs. It helps ensure that even less significant applications meet industry standards and maintains consistency in quality.
Though it contains technical information, the N 2 form is designed to provide clear guidance. Individuals involved in the welding process should be able to comprehend and use the form effectively with appropriate training and knowledge.
Key takeaways
The N 2 form is an essential document related to the Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) utilized in various welding projects.
- Purpose: The N 2 form evaluates and records the qualifications of welding procedures based on specific standards.
- Qualification Types: Ensure to select the appropriate qualification type as outlined in sections 5.12.1, 5.12.2, and 5.12.4.
- Contractor Information: Accurately enter the contractor or organization’s name, as it is critical for identification and accountability.
- Welding Processes: Choose the correct welding process. Options include manual, semiautomatic, mechanized, automatic, tandem, and parallel.
- Joint Design: Provide detailed specifications for joint design, including root opening, face dimensions, and groove angles.
- Base Metals: Clearly state the base metal specifications like type, grade, and thickness. This information is crucial for safety and compliance.
- Filler Metals: Specify the AWS specification and classification, as well as the manufacturer’s trade name of the filler metal used.
- Electrical Characteristics: Include details such as transfer mode, current type, and other electrical settings to ensure proper welding conditions.
- Post-Weld Treatment: Document any post-weld heat treatment, holding times, and heating/cooling rates, as these factors significantly influence the weld's integrity.
Completing the N 2 form with due diligence helps maintain adherence to safety standards and contributes to the overall quality of the welding work performed.
Browse Other Templates
Family Support Information Sheet,Army Reserve Family Data Form,Servicemember Family Contact Worksheet,Reserve Component Family Registration,Military Family Program Contact Form,Dependent Information Data Collection,Family Programs Participation Works - Compliance with the Privacy Act of 1974 protects the data provided in this form.
Medicaid Application Louisiana - This form is used to apply for healthcare coverage for disabled individuals who are working.
Surety Bond for Vehicle Title Colorado - All out-of-state vehicles require a title and lien record search from their respective states.