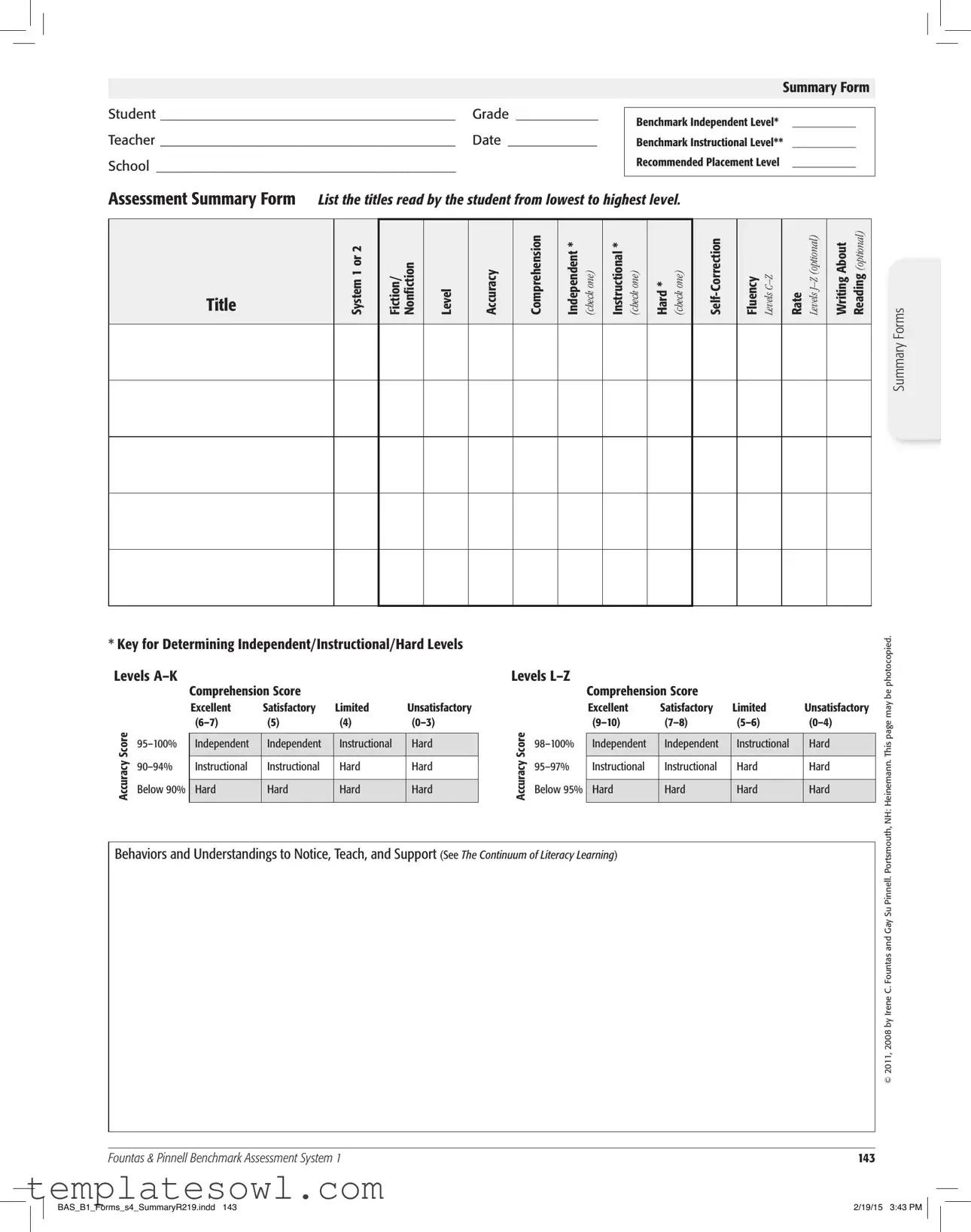
Fill Out Your Summary Sheet Form
The Summary Sheet form is a crucial tool in the educational assessment process. It helps teachers document a student's reading progress and place them at the appropriate instructional level. The form captures essential information about the student, including their name, grade, and the date, along with the benchmarks for their independent and instructional reading levels. Teachers can note titles read by the student, categorized from lowest to highest level, and classify them as either fiction or nonfiction. The form also includes areas for noting a student's accuracy and comprehension scores, with a clear rating system from excellent to unsatisfactory. There are specific checkboxes to identify whether the levels are independent, instructional, or hard, guiding educators in understanding where the student stands in their literacy journey. This systematic approach not only streamlines assessment but also provides insights into the teaching strategies that may need to be implemented moving forward.
Summary Sheet Example
Summary Form
Student ___________________________________________ |
Grade ____________ |
Benchmark Independent Level* |
___________ |
|
|
||
Teacher ___________________________________________ |
Date _____________ |
Benchmark Instructional Level** |
___________ |
School ____________________________________________ |
|
Recommended Placement Level |
___________ |
Assessment Summary Form
Title
List the titles read by the student from lowest to highest level.
System 1 or 2 |
Fiction/ Nonfiction |
Level |
Accuracy |
Comprehension |
Independent * (check one) |
Instructional * (check one) |
Hard * (check one) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Levels
Fluency
Levels
Rate
Reading (optional)
Writing About
Summary Forms
*Key for Determining Independent/Instructional/Hard Levels
Comprehension Score
|
|
Excellent |
Satisfactory |
Limited |
Unsatisfactory |
|
Score |
|
(5) |
(4) |
|||
Independent |
Independent |
Instructional |
Hard |
|||
|
||||||
Accuracy |
Instructional |
Instructional |
Hard |
Hard |
||
Below 90% |
Hard |
Hard |
Hard |
Hard |
||
|
Comprehension Score
|
|
|
Excellent |
|
Satisfactory |
|
|
|
|
||
Score |
|
Independent |
|
Independent |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Accuracy |
|
Instructional |
|
Instructional |
|
Below 95% |
|
Hard |
|
Hard |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limited |
|
Unsatisfactory |
|
||
Instructional |
|
Hard |
|
||
Hard |
|
Hard |
Hard |
|
Hard |
|
|
|
NH: Heinemann. This page may be photocopied.
Behaviors and Understandings to Notice, Teach, and Support (See The Continuum of Literacy Learning)
© 2011, 2008 by Irene C. Fountas and Gay Su Pinnell. Portsmouth,
Fountas & Pinnell Benchmark Assessment System 1 |
143 |
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Summary Sheet is used to assess a student's reading level and comprehension skills. |
| Student Information | This form requires the student's name, grade, and teacher's name. |
| Assessment Levels | It distinguishes between Independent, Instructional, and Hard reading levels. |
| Comprehension Scoring | Scores for comprehension range from Excellent to Unsatisfactory, guiding future instructional decisions. |
| Fiction vs Nonfiction | Readers can practice with both fiction and nonfiction materials, which reflects their comprehensive skills. |
| Optional Sections | Sections for Fluency Levels and Rate Reading are available, but not mandatory to complete. |
| Copyright Information | Materials can be photocopied as stated in the copyright notices from Heinemann and Fountas & Pinnell. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Summary Sheet
Filling out the Summary Sheet is a straightforward process that captures key information regarding a student's reading abilities. This data will help educators assess and plan for the student’s instructional needs. Here are the steps to complete the form effectively.
- Write the student’s name in the designated space.
- Indicate the student’s grade level.
- Fill in the Benchmark Independent Level by selecting the appropriate option.
- Record the teacher's name and the date on which the assessment is conducted.
- Fill in the Benchmark Instructional Level using the corresponding selection.
- Write the name of the school where the assessment takes place.
- Provide the Recommended Placement Level based on the assessment results.
- List the titles read by the student in order from lowest to highest level in the Assessment Summary section.
- For each title, specify whether it is from System 1 or 2 and indicate if it is fiction or nonfiction.
- Record the assessed level along with the accuracy and comprehension for the student’s reading.
- Check the type of level—Independent, Instructional, or Hard—as appropriate for each title.
- Note the Self-Correction Levels for levels C–Z, if applicable.
- If desired, include the fluency levels for J–Z.
- Provide a reading rate if this information is available.
- Summarize any writing about the assessed materials in the designated area.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Summary Sheet form?
The Summary Sheet form serves as a tool for educators to assess and document a student's reading level and comprehension skills. It provides critical information needed for instructional planning and helps identify the student's independent and instructional levels of reading proficiency.
What information do I need to fill out in the Summary Sheet form?
Key details to complete include the student’s name, grade, and the teacher's name. Additionally, it requires the date, the school's name, and the assessment summary that lists reading titles from lowest to highest level, along with levels of accuracy and comprehension.
How do I determine a student's Independent, Instructional, and Hard levels?
These levels are determined using a scoring system based on students’ comprehension and accuracy during assessments. For levels A-K, the scores for comprehension and accuracy range from excellent to unsatisfactory, with specific percentage thresholds outlined in the key provided. For levels L-Z, similar criteria apply, focusing on both comprehension scores and accuracy percentages.
What do the levels A-K indicate?
Levels A-K focus on early reading skills. An independent level means the student can read with high accuracy and comprehension. Instructional levels indicate that the student needs some support while reading, whereas hard levels denote that the text is too challenging for the student, requiring substantial assistance.
What about levels L-Z?
Levels L-Z are designed for more advanced readers. As with levels A-K, independent levels indicate effective reading without assistance, whereas instructional and hard levels highlight the need for more support. The criteria for scoring remains the same, with emphasis on comprehension and accuracy.
What types of reading materials should be included in the assessment summary?
Both fiction and nonfiction titles should be listed. It is important to arrange these titles in order from the lowest level the student can read to the highest. This organization allows for a clear understanding of the student's reading progression and strengths.
Is it necessary to document fluency and reading rate on the Summary Sheet form?
While documenting fluency and reading rate is optional, it can provide additional insight into a student’s reading abilities. This information can inform instructional strategies tailored to the specific needs of the student.
How can the data on the Summary Sheet benefit the student’s learning?
The data collected on the Summary Sheet helps educators tailor their teaching approaches to fit individual reading levels. By understanding a student's strengths and weaknesses, teachers can provide targeted support, enhancing the overall learning experience.
Can the Summary Sheet form be duplicated for use?
Yes, the Summary Sheet form can be photocopied for ease of use. This allows educators to efficiently assess multiple students or keep a record of assessments over time.
Where can additional resources or guidance on assessment be found?
Further information and resources are often available through educational institutions or literacy programs. Specifically, the referenced "Continuum of Literacy Learning" offers strategies for behaviors and understandings to notice, teach, and support in literacy development.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Summary Sheet form accurately is essential for documenting a student's reading levels and making appropriate educational recommendations. However, there are common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate information and hinder a student's learning process.
One prevalent error involves leaving out critical student information, such as the student’s name or grade. This can create confusion when retrieving the form later, especially if there are multiple students being assessed. Ensuring that all personal details are complete and clear is fundamental.
Another mistake is failing to properly identify the benchmark independent level and benchmark instructional level. Selecting the wrong levels can affect a student's placement and subsequent instruction. This can lead to students being placed inappropriately, either too easily or too challenging reading materials.
Many individuals also overlook the importance of listing the titles the student has read in the correct order from lowest to highest level. This oversight can complicate the assessment of the student’s reading progression. Properly documenting these titles is vital for tracking growth over time.
Inaccurate choice of the fiction/nonfiction category is another common mistake. Classifying a book incorrectly not only skews data but also misrepresents a student’s reading preferences and competencies. It’s crucial to carefully assess the content type when completing this section.
Additionally, failing to check the appropriate levels for independent, instructional, and hard can create significant inaccuracies. Incorrect checks can lead to a misunderstanding of a student's ability and needs, making it essential to review each definition before making a selection.
Another significant issue arises from skipping or rushing through the accuracy and comprehension scores. Not taking the time to assess these elements can result in incomplete or misleading evaluations, ultimately affecting the educational strategy tailored for the student.
Moreover, many people forget to rate reading fluency, which is listed as optional. While it may not seem critical, fluency provides additional context for a student’s reading ability. Neglecting this information can leave gaps in understanding a student’s overall progress.
Improperly completing the behaviors and understandings section can also be detrimental. Users must notice, teach, and support students correctly. Failing to do so might lead to incomplete insights into a student's reading behaviors.
Lastly, not reviewing the Summary Sheet for overall clarity can hinder effective communication. A messy or unclear form can lead to misunderstandings among educators and may impact the support the student receives. Thorough reviews and attention to detail are key in ensuring all information conveyed in the form is precise and useful.
Documents used along the form
The Summary Sheet form plays a crucial role in compiling important information regarding a student’s reading assessment. Educators often use additional documents to provide comprehensive insights into a student's performance and progress. Below are several forms that complement the Summary Sheet.
- Assessment Summary Form: This document provides a detailed overview of a student's reading abilities. It includes data such as titles read, levels of comprehension, and accuracy scores. This form helps to categorize the student's performance in terms of independent, instructional, and hard levels.
- Benchmark Instructional Level Form: This form is designed to establish the appropriate instructional level for a student based on their assessment scores. It helps educators identify the best reading materials and strategies that will foster improvement and growth.
- Behavioral Checklist: This checklist captures the student's literacy behaviors and tendencies during reading activities. It assists teachers in identifying areas of strength and those needing further support, enabling targeted interventions.
- Reading Progress Report: This form documents a student's reading journey over a set period. It highlights improvements and any persistent challenges, providing a clear picture of their literacy development for both educators and parents.
Utilizing these additional forms alongside the Summary Sheet can enhance the understanding of a student's reading skills, guiding personalized instruction and fostering educational growth.
Similar forms
- Report Card: A report card summarizes a student's performance over a grading period, similar to how the Summary Sheet provides a snapshot of a student's reading levels and assessments.
- Progress Report: Like the Summary Sheet, a progress report tracks a student's growth in certain areas, including literacy, focusing on skills such as accuracy and comprehension.
- IEP (Individualized Education Program): An IEP outlines specific educational goals for a student with disabilities and can include assessments like those found in the Summary Sheet to determine instructional needs.
- Benchmark Assessment: This document compares a student's performance against predetermined benchmarks, similar to how the Summary Sheet assesses reading levels and comprehension.
- Assessment Rubric: An assessment rubric breaks down evaluation criteria, mirroring the Summary Sheet's criteria for determining reading levels and comprehension scores.
- Behavioral Assessment: A behavioral assessment evaluates a student's social skills and behaviors, which can supplement academic assessments like the Summary Sheet to provide a more holistic view.
- Reading Log: A reading log records the titles a student has read, resembling the Summary Sheet's section for listing books read at various reading levels.
- Evaluation Summary: This document consolidates findings from various assessments, similar to how the Summary Sheet condenses a student's reading abilities and progress into concise evaluations.
- Learning Plan: A learning plan outlines specific instructional strategies and goals for a student, akin to the recommendations provided in the Summary Sheet regarding placement levels.
- Curriculum Map: A curriculum map details what students are expected to learn over time, paralleling how the Summary Sheet indicates where a student stands on their literacy journey.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Summary Sheet form, it helps to keep some simple do's and don'ts in mind. Here’s a handy list to guide you.
- Do fill in all required fields completely.
- Do list the titles read by the student in order from lowest to highest level.
- Do double-check comprehension scores for accuracy.
- Do ensure that you specify the correct level (Independent, Instructional, Hard) for each section.
- Do include the assessment date and teacher’s name for reference.
- Don't leave any fields blank unless the information is truly not applicable.
- Don't guess the scores; always base them on the student's performance.
- Don't forget to check the appropriate boxes for the reading levels.
- Don't use shorthand or abbreviations that others may not understand.
Follow these tips, and you'll fill out the Summary Sheet form with confidence and clarity.
Misconceptions
-
Misconception 1: The Summary Sheet is only for teachers.
This form is designed for multiple users, including students, parents, and administrators. Teachers fill it out, but everyone involved in a student's education can benefit from understanding the data it contains.
-
Misconception 2: The Summary Sheet only reflects reading skills.
While reading levels are significant, the form also includes important information about comprehension and fluency. These additional elements provide a fuller picture of a student’s literacy abilities.
-
Misconception 3: The levels indicated on the Summary Sheet are fixed.
In reality, these levels can change. Students might progress or regress in their skills, which means the information on the form should be updated regularly to reflect their current abilities.
-
Misconception 4: The data is too complex for parents to understand.
Although the Summary Sheet includes various scores and classifications, it is straightforward. Parents can easily grasp the meanings of independent, instructional, and hard levels, allowing them to better support their child’s learning.
Key takeaways
When completing and utilizing the Summary Sheet form, keep the following key takeaways in mind:
- Make sure to fill in the student’s name and grade clearly at the top of the form.
- Record the teacher's name and the date accurately to maintain proper documentation.
- Evaluate and indicate the Benchmark Independent Level and Benchmark Instructional Level for the student.
- List all titles read by the student in an organized manner, from lowest to highest level.
- Choose the appropriate category for each title as either System 1 or 2, and state whether it is fiction or nonfiction.
- Assess the student’s comprehension and accuracy levels based on the provided scoring keys.
- Note the self-correction levels, fluency rates, and writing summaries if applicable.
- Understanding the scoring range for independent, instructional, and hard levels is crucial for accurate assessment.
- The form may be photocopied for additional use, ensuring easy access and reference in the future.
Browse Other Templates
Icici Bank Letter Head - Make sure to include all required documents if necessary.
What Is a Form 945 - Employers should verify all reported figures for accuracy before submitting to minimize discrepancies.