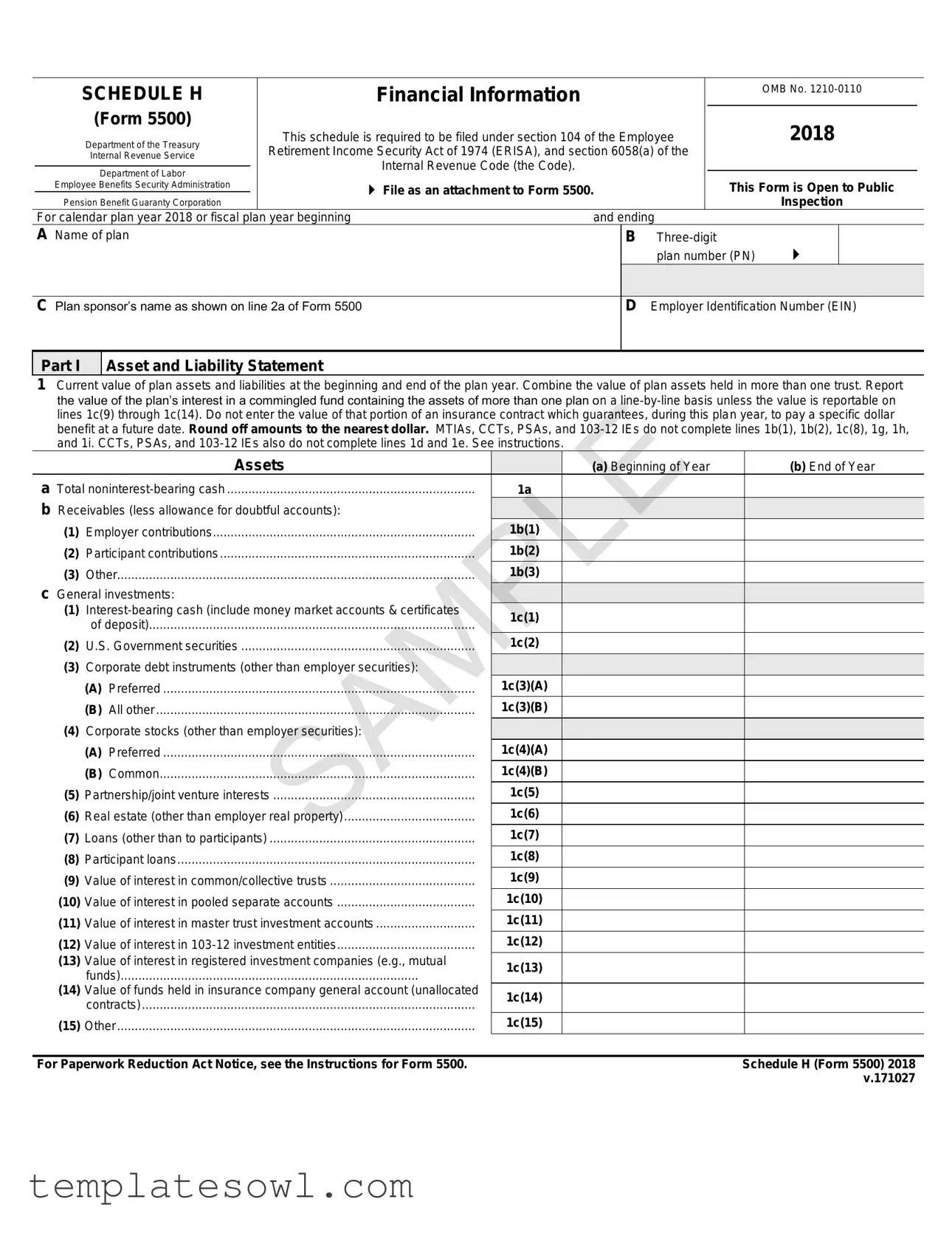
Fill Out Your H 5500 Form
The H 5500 form plays a pivotal role for retirement plans in the United States, serving as a comprehensive reporting document governed by various regulatory frameworks. It is essential for plan sponsors to file this form under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) and the Internal Revenue Code, ensuring compliance with federal regulations. The form comprises several schedules, including Schedule H, which presents detailed financial information regarding plan assets and liabilities. This schedule captures data on the plan's financial health through a thorough asset and liability statement along with an income and expense statement. Tasks such as aggregating contributions from employers and participants, detailing investment earnings, and summarizing total expenditures are crucial for an accurate representation of the plan's financial activities over the specified plan year. Furthermore, the form includes sections for an accountant’s opinion, compliance questions, and important disclosures, which enhance transparency and accountability. Overall, meticulous completion of the H 5500 form and its associated schedules is critical for fulfilling compliance requirements, maintaining the integrity of retirement plans, and safeguarding participants' benefits.
H 5500 Example
|
SCHEDULE H |
|
|
Financial Information |
|
|
OMB No. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
(Form 5500) |
|
|
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Department of the Treasury |
|
This schedule is required to be filed under section 104 of the Employee |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA), and section 6058(a) of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Internal Revenue Code (the Code). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Department of Labor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Employee Benefits Security Administration |
|
|
File as an attachment to Form 5500. |
|
This Form is Open to Public |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation |
|
|
|
|
|
Inspection |
|
|
|||
|
For calendar plan year 2018 or fiscal plan year beginning |
and ending |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
A Name of plan |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
plan number (PN) |
|
|
001 |
|
||||||
|
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
C Plan sponsor’s name as shown on line 2a of Form 5500 |
|
D Employer Identification Number (EIN) |
|
|
|||||||
|
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
012345678 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Part I |
|
Asset and Liability Statement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1Current value of plan assets and liabilities at the beginning and end of the plan year. Combine the value of plan assets held in more than one trust. Report the value of the plan’s interest in a commingled fund containing the assets of more than one plan on a
|
|
Assets |
|
(a) Beginning of Year |
|
(b) End of Year |
a Total |
1a |
|
||||
b Receivables (less allowance for doubtful accounts): |
|
|
|
|
||
(1) |
Employer contributions |
1b(1) |
|
|||
(2) |
Participant contributions |
1b(2) |
|
|||
(3) |
Other |
1b(3) |
|
|||
c General investments: |
|
|
|
|
||
(1) |
1c(1) |
|
||||
|
of deposit) |
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
(2) |
U.S. Government securities |
1c(2) |
|
|||
(3) |
Corporate debt instruments (other than employer securities): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(A) |
Preferred |
1c(3)(A) |
|
||
|
(B) |
All other |
1c(3)(B) |
|
||
(4) |
Corporate stocks (other than employer securities): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(A) |
Preferred |
1c(4)(A) |
|
||
|
(B) |
Common |
1c(4)(B) |
|
||
(5) |
Partnership/joint venture interests |
1c(5) |
|
|||
(6) |
Real estate (other than employer real property) |
1c(6) |
|
|||
(7) |
Loans (other than to participants) |
1c(7) |
|
|||
(8) |
Participant loans |
1c(8) |
|
|||
(9) |
Value of interest in common/collective trusts |
1c(9) |
|
|||
(10) |
Value of interest in pooled separate accounts |
1c(10) |
|
|||
(11) |
Value of interest in master trust investment accounts |
1c(11) |
|
|||
(12) |
Value of interest in |
1c(12) |
|
|||
(13) |
Value of interest in registered investment companies (e.g., mutual |
1c(13) |
|
|||
|
funds) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
(14) |
Value of funds held in insurance company general account (unallocated |
1c(14) |
|
|||
|
contracts) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
(15) |
Other |
1c(15) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the Instructions for Form 5500. |
|
|
Schedule H (Form 5500) 2018 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
v.171027 |

Schedule H (Form 5500) 2018 |
Page 2 |
1d
(1)Employer securities .................................................................................
(2)Employer real property ............................................................................
1e Buildings and other property used in plan operation ......................................
1f Total assets (add all amounts in lines 1a through 1e) ....................................
Liabilities
1g Benefit claims payable...................................................................................
1h Operating payables .......................................................................................
1i Acquisition indebtedness ...............................................................................
1j Other liabilities ...............................................................................................
1k Total liabilities (add all amounts in lines 1g through1j) ...................................
Net Assets
1l Net assets (subtract line 1k from line 1f) ........................................................
|
(a) Beginning of Year |
(b) End of Year |
|
|
|
1d(1) |
||
|
|
|
1d(2) |
||
|
|
|
1e |
||
|
|
|
1f |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1g |
||
|
|
|
1h |
||
|
|
|
1i |
||
|
|
|
1j |
||
|
|
|
1k |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1l |
Part II Income and Expense Statement
2Plan income, expenses, and changes in net assets for the year. Include all income and expenses of the plan, including any trust(s) or separately maintained fund(s) and any payments/receipts to/from insurance carriers. Round off amounts to the nearest dollar. MTIAs, CCTs, PSAs, and
Income
aContributions:
(1)Received or receivable in cash from: (A) Employers................................
(B)Participants......................................................................................
(C)Others (including rollovers) ..............................................................
(2)Noncash contributions .............................................................................
(3)Total contributions. Add lines 2a(1)(A), (B), (C), and line 2a(2)................
bEarnings on investments:
(1)Interest:
(A)
(B)U.S. Government securities .............................................................
(C)Corporate debt instruments..............................................................
(D)Loans (other than to participants).....................................................
(E)Participant loans ..............................................................................
(F)Other ...............................................................................................
(G)Total interest. Add lines 2b(1)(A) through (F) ...................................
(2)Dividends: (A) Preferred stock .................................................................
(B)Common stock.................................................................................
(C)Registered investment company shares (e.g. mutual funds) ............
(D)Total dividends. Add lines 2b(2)(A), (B), and (C)
(3)Rents.......................................................................................................
(4)Net gain (loss) on sale of assets: (A) Aggregate proceeds......................
(B)Aggregate carrying amount (see instructions) ..................................
(C)Subtract line 2b(4)(B) from line 2b(4)(A) and enter result ................
(5)Unrealized appreciation (depreciation) of assets: (A) Real estate.......................
(B)Other ...............................................................................................
(C)Total unrealized appreciation of assets.
Add lines 2b(5)(A) and (B)...............................................................
|
(a) Amount |
(b) Total |
|
|
|
2a(1)(A) |
|
|
|
|
|
2a(1)(B) |
|
|
|
|
|
2a(1)(C) |
|
|
|
|
|
2a(2) |
|
|
2a(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(1)(A) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(1)(B) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(1)(C) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(1)(D) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(1)(E) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(1)(F) |
|
|
2b(1)(G) |
|
|
2b(2)(A) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(2)(B) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(2)(C) |
|
|
2b(2)(D) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(3) |
|
|
2b(4)(A) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(4)(B) |
|
|
2b(4)(C) |
|
|
|
|
|
2b(5)(A) |
|
|
2b(5)(B) |
|
|
2b(5)(C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule H (Form 5500) 2018 |
Page 3 |
(6)Net investment gain (loss) from common/collective trusts .........................
(7)Net investment gain (loss) from pooled separate accounts .......................
(8)Net investment gain (loss) from master trust investment accounts............
(9) Net investment gain (loss) from
(10)Net investment gain (loss) from registered investment
companies (e.g., mutual funds).................................................................
cOther income..................................................................................................
dTotal income. Add all income amounts in column (b) and enter total.....................
Expenses
eBenefit payment and payments to provide benefits:
(1)Directly to participants or beneficiaries, including direct rollovers ..............
(2)To insurance carriers for the provision of benefits.....................................
(3)Other ........................................................................................................
(4)Total benefit payments. Add lines 2e(1) through (3)..................................
fCorrective distributions (see instructions) .......................................................
gCertain deemed distributions of participant loans (see instructions) ................
hInterest expense .............................................................................................
iAdministrative expenses: (1) Professional fees..............................................
(2)Contract administrator fees.......................................................................
(3)Investment advisory and management fees..............................................
(4)Other ........................................................................................................
(5)Total administrative expenses. Add lines 2i(1) through (4)........................
jTotal expenses. Add all expense amounts in column (b) and enter total ........
Net Income and Reconciliation
|
(a) Amount |
|
(b) Total |
2b(6) |
|
|
|
2b(7) |
|
|
|
2b(8) |
|
|
|
2b(9) |
|
|
|
2b(10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2c |
|
|
|
2d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2e(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2e(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2e(3) |
|
|
|
2e(4) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
2f |
|
||
|
|
|
|
2g |
|
||
|
|
|
|
2h |
|
||
2i(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2i(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2i(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2i(4) |
|
|
|
2i(5) |
|
||
2j |
|
||
kNet income (loss). Subtract line 2j from line 2d ...........................................................
lTransfers of assets:
(1)To this plan...............................................................................................
(2)From this plan...........................................................................................
2k
2l(1)
2l(2)
Part III Accountant’s Opinion
3Complete lines 3a through 3c if the opinion of an independent qualified public accountant is attached to this Form 5500. Complete line 3d if an opinion is not attached.
aThe attached opinion of an independent qualified public accountant for this plan is (see instructions):
(1)X
Unqualified |
(2) |
X |
Qualified |
(3) |
X |
Disclaimer |
(4) |
X |
Adverse
b Did the accountant perform a limited scope audit pursuant to 29 CFR |
X Yes |
X No |
|
|
|
|
|
c Enter the name and EIN of the accountant (or accounting firm) below: |
|
|
|
(1) Name: ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCD |
(2) EIN: 123456789 |
|
|
dThe opinion of an independent qualified public accountant is not attached because:
(1) X This form is filed for a CCT, PSA, or MTIA. (2) X It will be attached to the next Form 5500 pursuant to 29 CFR
Part IV Compliance Questions
4CCTs and PSAs do not complete Part IV. MTIAs,
During the plan year:
aWas there a failure to transmit to the plan any participant contributions within the time
period described in 29 CFR
bWere any loans by the plan or fixed income obligations due the plan in default as of the
close of the plan year or classified during the year as uncollectible? Disregard participant loans secured by participant’s account balance. (Attach Schedule G (Form 5500) Part I if “Yes” is checked.) ........................................................................................................................................
|
Yes No |
Amount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4a
4b
|
Schedule H (Form 5500) 2018 |
Page 4- |
1 |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yes No |
Amount |
|
c |
Were any leases to which the plan was a party in default or classified during the year as |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
uncollectible? (Attach Schedule G (Form 5500) Part II if “Yes” is checked.) |
|
|
4c |
|
||||
d |
Were there any nonexempt transactions with any |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
reported on line 4a. Attach Schedule G (Form 5500) Part III if “Yes” is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
checked.) |
|
|
4d |
|
||||
e |
Was this plan covered by a fidelity bond? |
|
|
4e |
|
||||
f |
Did the plan have a loss, whether or not reimbursed by the plan’s fidelity bond, that was caused by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
fraud or dishonesty? |
|
|
4f |
|
||||
g |
Did the plan hold any assets whose current value was neither readily determinable on an |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
established market nor set by an independent third party appraiser? |
|
|
4g |
|
||||
h |
Did the plan receive any noncash contributions whose value was neither readily |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
..................determinable on an established market nor set by an independent third party appraiser? |
4h |
|
||||||
iDid the plan have assets held for investment? (Attach schedule(s) of assets if “Yes” is checked, and
see instructions for format requirements.) |
4i |
jWere any plan transactions or series of transactions in excess of 5% of the current value of plan assets? (Attach schedule of transactions if “Yes” is checked, and
|
see instructions for format requirements.) |
|
4j |
|
|
|||||||
k |
Were all the plan assets either distributed to participants or beneficiaries, transferred to another |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
plan, or brought under the control of the PBGC? |
|
4k |
|
|
|||||||
l |
Has the plan failed to provide any benefit when due under the plan? |
4l |
|
|||||||||
m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
If this is an individual account plan, was there a blackout period? (See instructions and 29 CFR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
n |
...................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
4m |
|
|
|||||
If 4m was answered “Yes,” check the “Yes” box if you either provided the required notice or one of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
. .........................................the exceptions to providing the notice applied under 29 CFR |
4n |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5a Has a resolution to terminate the plan been adopted during the plan year or any prior plan year? |
X Yes X No |
If “Yes,” enter the amount of any plan assets that reverted to the employer this year ____________________________________.
5b If, during this plan year, any assets or liabilities were transferred from this plan to another plan(s), identify the plan(s) to which assets or liabilities were
transferred. (See instructions.)
5b(1) Name of plan(s) |
|
|
5b(2) EIN(s) |
5b(3) PN(s) |
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
123456789 |
123 |
||
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
123456789 |
123 |
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
123456789 |
123 |
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI |
BCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
|
|
|
||
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
123456789 |
123 |
||
ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI ABCDEFGHI |
|
|
||
5c If the plan is a defined benefit plan, is it covered under the PBGC insurance program ( ee ERISA section 4021.)? ...... X Yes X No |
X Not determined |
If “Yes” is checked, enter the My PAA confirmation number from the PBGC premium filing for this plan year________________________. (See instructions.)
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Fact Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The H 5500 Form is required under ERISA and the Internal Revenue Code to provide a comprehensive overview of a pension plan's financial conditions for the year. |
| Filing Frequency | This form must be filed annually, typically by the last day of the seventh month after the end of the plan year. |
| Included Information | It includes detailed financial information regarding assets, liabilities, income, and expenses of the pension plan. |
| Governing Laws | This form operates under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA) and the Internal Revenue Code. |
Guidelines on Utilizing H 5500
Filling out the H 5500 form is essential for pension plans to provide financial information required by federal regulations. Following the steps outlined below will help ensure that all necessary sections of the form are completed accurately. Take your time and gather all relevant financial data before starting.
- Start with the header section. Enter the name of the plan in line A and its three-digit plan number in line B.
- Fill in the plan sponsor's name on line C and the Employer Identification Number (EIN) on line D.
- Move on to Part I, the Asset and Liability Statement. Complete the current value of plan assets and liabilities at the beginning and end of the plan year.
- Detail assets in the specified categories. For each item, round off amounts to the nearest dollar. Remember to report any combined values appropriately.
- Calculate the total assets by adding all values from lines 1a through 1e in Part I.
- Complete the liabilities section by listing benefit claims payable, operating payables, acquisition indebtedness, and any other liabilities. Add these amounts to get a total liability on line 1k.
- Find the net assets by subtracting total liabilities (line 1k) from total assets (line 1f) on line 1l.
- Proceed to Part II, the Income and Expense Statement. Report all income sources and expenses, rounding to the nearest dollar, including contributions and any earnings on investments.
- For income, sum total contributions and earnings on investments to find the overall income for the plan.
- List all expenses, including benefit payments, administrative costs, and interest expenses. Add these to get the total expenses on line 2j.
- Calculate net income by subtracting total expenses (line 2j) from total income (line 2d) and record the result on line 2k.
- If applicable, complete Part III regarding the accountant's opinion. Indicate whether an opinion is attached and provide necessary details.
- Finally, address the compliance questions in Part IV, ensuring that every applicable question is answered correctly.
- Once all sections are filled out and reviewed, attach the completed Schedule H to the Form 5500 and submit as required.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the H 5500 form?
The H 5500 form, specifically Schedule H, is a financial report that must be filed in compliance with the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA). This form provides details about a pension plan’s financial condition, including its assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. It serves as an essential tool for regulating private pension plans and is designed to protect the interests of participants and beneficiaries.
Who is required to file the H 5500 form?
Generally, any employee benefit plan that qualifies as a defined benefit plan or a defined contribution plan must file this form. Typically, plans with over 100 participants are required to submit Schedule H as part of Form 5500. This requirement helps to ensure compliance with federal regulations and provides transparency regarding the plan’s financial operations.
What information does the H 5500 form collect?
Schedule H gathers various financial data about the retirement plan. This includes the total assets and liabilities at the beginning and end of the plan year, income from employee and employer contributions, investment earnings, and expenses related to benefit payments, administrative costs, and more. It aims to provide a comprehensive financial picture of the pension plan.
How is the data on the H 5500 form used?
The information collected helps federal agencies, such as the Department of Labor and the Internal Revenue Service, monitor and evaluate pension plans’ compliance with ERISA regulations. Analyzing this data can identify any financial issues within the plans and ensure that funds are being used appropriately to benefit participants and beneficiaries.
What are the consequences of failing to file the H 5500 form?
Failing to file Schedule H can lead to significant penalties. Plans may incur monetary fines that vary based on the circumstances and duration of the failure to comply. Moreover, the failure to provide accurate and timely information can raise red flags, potentially resulting in further scrutiny from regulatory bodies.
How can a plan sponsor complete the H 5500 form?
Completing the H 5500 form requires an understanding of the plan's financial situation. Plan sponsors generally gather documents detailing assets, liabilities, income, and expenses before filling out the form. For more complex plans, seeking the assistance of financial professionals or accountants can ensure accuracy. It’s essential to follow the detailed instructions provided with the form, as each section must be filled out carefully.
Is the H 5500 form publicly accessible?
Yes, the H 5500 form is accessible to the public. Once filed, the information becomes part of a public database, allowing transparency for interested parties, including participants, beneficiaries, and researchers. This accessibility helps promote accountability in employee benefit plans.
What should be done if there are corrections needed after filing the H 5500?
If a plan sponsor discovers discrepancies after submitting the H 5500 form, they should take steps to correct the errors promptly. This involves filing an amended return with the appropriate adjustments. Transparency about the corrections made is critical, and the sponsor should keep detailed records of both the original submission and any amendments.
Where can I find additional resources or help regarding the H 5500 form?
Additional resources for the H 5500 form can be found on the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employee Benefits Security Administration (EBSA) website. They provide extensive guidelines and support for plan sponsors. Consulting with legal or financial professionals can also provide valuable insights into specific situations related to the H 5500 form.
Common mistakes
Completing the H 5500 form can be a challenging task, and many individuals make common mistakes that can lead to delays or inaccuracies. One prevalent error is failing to carefully round off amounts to the nearest dollar. The instructions clearly state this requirement, yet minor rounding miscalculations can create significant discrepancies in financial reporting.
Another frequent mistake involves incorrect reporting of assets. Individuals may combine values from multiple trusts improperly or neglect to report interests in commingled funds on the required line-by-line basis. It's essential to follow the specific instructions regarding asset valuation to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Inadequate attention to detail in filling out employer identification numbers (EINs) can also lead to errors. An incorrect EIN can disrupt the filing process and potentially cause serious compliance issues. It is critical to verify that this information accurately reflects what is recorded by the IRS to prevent complications.
People often overlook the necessity of completing all requested sections of the Income and Expense Statement. Missing entries, especially for income or expenses, can result in incomplete records that do not accurately portray the plan's financial position. This insight demonstrates the importance of thoroughness when detailing income sources and expenses incurred during the plan year.
Another common pitfall is misunderstanding the specific lines that need to be filled for different types of plans. Many individuals fail to recognize that certain categories of plans, such as Master Trust Investment Accounts (MTIAs), are exempt from completing specific lines. Consult the instructions to understand which requirements apply to your particular plan to avoid unnecessary confusion.
Administrative expenses often receive insufficient emphasis. Some individuals neglect to provide detailed information on fees incurred for professional services. Understanding and disclosing these fees is crucial for maintaining transparency and ensuring the plan's financial health is appropriately represented.
Additionally, many people do not attach the necessary opinions from independent qualified public accountants when required. This oversight can lead to a form being deemed incomplete or inaccurate, prompting further scrutiny from regulatory bodies.
Finally, ignorance of compliance questions can prove detrimental. Responding to these inquiries accurately is vital for regulatory compliance. Neglecting to address questions about fidelity bonds or potential uncollectible transactions can trigger audits or result in penalties. Each question is designed to provide a full picture of the plan's administration and adherence to regulations.
Documents used along the form
Filing Form H 5500 is an important part of managing employee benefit plans. Accompanying documents can provide more context and details necessary for compliance and transparency. Here are five forms commonly filed alongside the H 5500 form.
- Schedule A: This form reports information about insurance contracts held by the plan. It includes details such as premiums paid and benefits provided through these contracts. Schedule A allows regulators and other interested parties to assess the coverage and financial standing of the insurance arrangements.
- Schedule C: Schedule C discloses information about service providers and their compensation. It provides insights into who is managing the plan and how they are compensated, which can address any potential conflicts of interest.
- Schedule D: This schedule is used to present information regarding the plan’s assets, particularly those that are not liquid. It helps to ensure transparency around investments that may not be easily sold or assessed.
- Schedule G: This form outlines financial transactions between the plan and parties in interest. It captures crucial data about transactions that may affect the plan's financial integrity and help prevent any improprieties.
- Schedule H: While it is part of the H 5500 form itself, this detailed financial schedule offers comprehensive financial information about the employee benefit plan, covering assets, liabilities, income, and expenses.
Completing these forms accurately is critical for maintaining trust and compliance with federal regulations. Each document serves its own purpose but contributes to a holistic understanding of the plan’s operations and financial health.
Similar forms
- Form 5500: The H 5500 form is a part of the larger Form 5500 series. Like the H 5500, it collects information about employee benefit plans to comply with regulations and reporting requirements.
- Form 5500-SF: This simplified version of Form 5500 is designed for certain small plans. Similar to H 5500, it gathers essential information about plan finances and operations but has fewer reporting requirements.
- Schedule A: This schedule is attached to Form 5500 and details insurance information related to employee benefit plans. It is similar in that it requires financial data about the plan.
- Schedule C: It provides details on service provider fees and is attached to Form 5500. This schedule aims to disclose financial transactions that may affect the plan, making it similar to Schedule H in scope.
- Schedule D: This schedule reports on the investment information of employee benefit plans. Like the H 5500, it focuses on financial data crucial for assessing the plan’s performance.
- Schedule G: It deals with financial transactions and compliance issues regarding the plan. Like the H 5500, this document addresses the financial health and regulation adherence of the plan.
- Form 5330: This form is used to report certain excise taxes related to employee benefit plans. Both forms are important for maintaining compliance with regulations and tax obligations.
- IRS Form 990: Nonprofits must file this form to report their financial activities. Like the H 5500, it aims to provide transparency regarding financial matters.
- PBGC Premium Filing: While specific to plans insured by the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation, this filing includes financial details similar to those sought in H 5500 to ensure ongoing compliance with federal regulations.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the H 5500 form, it’s essential to approach the task with care to ensure compliance and accuracy. Below is a list of practices to follow and avoid, aimed at simplifying the process.
- Do ensure accuracy in all amounts: Misreporting figures can lead to compliance issues or penalties.
- Do include all required attachments: Missing documents can delay processing or result in rejection of the form.
- Do round off amounts: Round your figures to the nearest dollar to avoid complications or scrutiny.
- Do double-check your EIN: Ensure that the Employer Identification Number provided is correct to prevent complications.
- Do familiarize yourself with the instructions: Read through the guidelines thoroughly before completing the form.
- Don't forget to report noncash contributions: These are important aspects of your plan’s financial picture.
- Don't overlook deadlines: Late filings can incur significant penalties.
- Don't leave any sections blank: Each required section must be addressed, even if the answer is zero.
- Don't ignore compliance questions: Answer them truthfully to avoid issues with regulatory bodies.
- Don't hesitate to seek assistance: If unsure, consulting a professional can provide necessary guidance.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The H 5500 form is optional for all retirement plans.
- Misconception 2: Only large plans need to complete Schedule H.
- Misconception 3: Schedule H only focuses on fund performance.
- Misconception 4: Completing Schedule H is a one-time task.
- Misconception 5: There are no penalties for failing to file Schedule H accurately.
- Misconception 6: Only the plan administrator is responsible for Schedule H.
In fact, the H 5500 form is a required attachment for plans subject to the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). It must be filed each year.
All ERISA-covered plans must file Schedule H, regardless of size. The amount of information required may vary, but the obligation stands for all plans.
Schedule H includes not only fund performance but also detailed financial information about the plan's assets, liabilities, income, and expenses.
Schedule H must be completed annually as part of the Form 5500 filing. Ongoing record-keeping is essential to ensure accuracy from year to year.
Failure to file Schedule H correctly can result in penalties imposed by the Department of Labor. It is imperative to ensure compliance to avoid these repercussions.
While the plan administrator typically prepares the form, all parties involved in the plan's management share responsibility for ensuring accuracy in the filing.
Key takeaways
When filling out and using the H 5500 form, there are several important considerations to keep in mind. Here are the key takeaways:
- File Timely: This form is required to be filed on time to comply with ERISA and IRS regulations.
- Accurate Information: Ensure that the information provided, including plan assets and liabilities, is accurate and reflects the correct values.
- Attachment Requirements: Remember to file Schedule H as an attachment to the main Form 5500.
- Complete All Sections: Fill out all required sections carefully, paying special attention to the Income and Expense Statement.
- Use Round Numbers: Round all amounts to the nearest dollar to maintain consistency and accuracy.
- Review Compliance Questions: Answer compliance questions thoroughly, as failures can have significant implications.
- Consult Guidance: Refer to the IRS instructions if there is any uncertainty about how to complete specific sections of the form.
By keeping these takeaways in mind, you can help ensure that the process of completing the H 5500 form is both efficient and compliant.
Browse Other Templates
Oklahoma Ui Tax Account Number - Encouragement to maintain detailed employee records aids in smooth submission processes.
Nurse Aide Employment Confirmation,Texas Nurse Aide Verification Form,CNA Employment Record,Texas Nurse Aide Certification Validation,Certified Nurse Aide Employment Affidavit,Nurse Aide Job History Form,CNA Registration Employment Verification,Texas - The form is a mechanism for ensuring that nursing professionals meet state-defined standards.