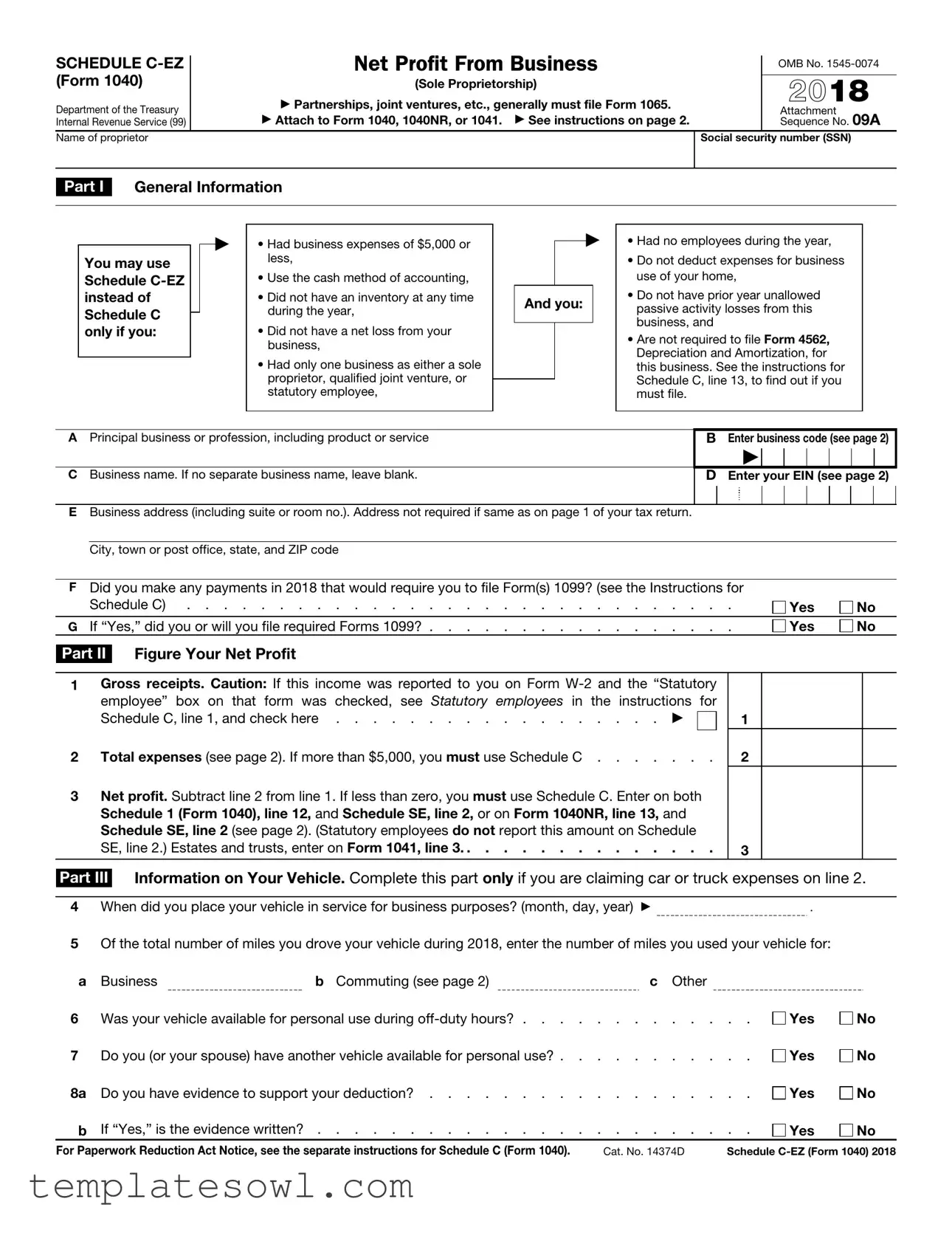
Fill Out Your Irs Schedule C Ez Form
The IRS Schedule C-EZ form serves as a simplified tool for sole proprietors, allowing them to report their business income and expenses with ease. Tailored for individuals with straightforward business activities, this form provides a streamlined approach to documenting net profit from a trade or profession. Eligibility requirements stipulate that individuals can utilize this form if their business expenses do not exceed $5,000, they operated without employees, and they maintained a cash accounting method. Moreover, the absence of inventory or prior year losses further qualifies potential filers. Importantly, the form requires reporting gross receipts, total expenses, and ultimately calculating net profit, which determines tax obligations. Vehicle expenses may also be included if appropriately documented. In cases of more intricate financial scenarios, such as exceeding expense limitations or utilizing depreciation, standard Schedule C would instead apply. Understanding the nuances of Schedule C-EZ can help business owners navigate their tax filings with greater confidence and efficiency.
Irs Schedule C Ez Example
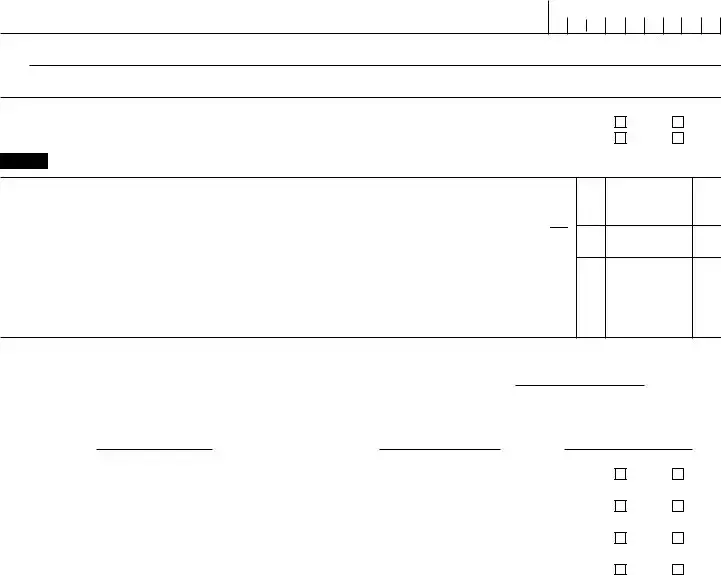
SCHEDULE |
|
|
|
|
Net Profit From Business |
|
|
OMB No. |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
(Form 1040) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
(Sole Proprietorship) |
|
|
2018 |
|
||||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
▶ Partnerships, joint ventures, etc., generally must file Form 1065. |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
▶ Attach to Form 1040, 1040NR, or 1041. |
▶ See instructions on page 2. |
|
Attachment |
|||||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
|
|
|
|
Sequence No. 09A |
||||||||||||||||
Name of proprietor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social security number (SSN) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General Information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Part I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
▶ |
• Had business expenses of $5,000 or |
|
|
|
• Had no employees during the year, |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
You may use |
|
|
|
less, |
|
|
|
|
|
• Do not deduct expenses for business |
|
|
|||||||||
|
Schedule |
|
|
|
• Use the cash method of accounting, |
|
|
|
|
|
use of your home, |
|
|
|||||||||
|
instead of |
|
|
|
• Did not have an inventory at any time |
|
And you: |
|
• Do not have prior year unallowed |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Schedule C |
|
|
|
during the year, |
|
|
passive activity losses from this |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
only if you: |
|
|
|
• Did not have a net loss from your |
|
|
|
|
|
business, and |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Are not required to file Form 4562, |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
business, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and Amortization, for |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Had only one business as either a sole |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
this business. See the instructions for |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
proprietor, qualified joint venture, or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule C, line 13, to find out if you |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
statutory employee, |
|
|
|
|
|
must file. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
A Principal business or profession, including product or service |
|
|
|
|
|
B Enter business code (see page 2) |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C Business name. If no separate business name, leave blank. |
|
|
|
|
|
D Enter your EIN (see page 2) |
||||||||||||||||
EBusiness address (including suite or room no.). Address not required if same as on page 1 of your tax return. City, town or post office, state, and ZIP code
FDid you make any payments in 2018 that would require you to file Form(s) 1099? (see the Instructions for
Schedule C) |
Yes |
No |
G If “Yes,” did you or will you file required Forms 1099? |
Yes |
No |
Part II Figure Your Net Profit
1Gross receipts. Caution: If this income was reported to you on Form
Schedule C, line 1, and check here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶  2 Total expenses (see page 2). If more than $5,000, you must use Schedule C . . . . . . .
2 Total expenses (see page 2). If more than $5,000, you must use Schedule C . . . . . . .
3Net profit. Subtract line 2 from line 1. If less than zero, you must use Schedule C. Enter on both Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 12, and Schedule SE, line 2, or on Form 1040NR, line 13, and Schedule SE, line 2 (see page 2). (Statutory employees do not report this amount on Schedule SE, line 2.) Estates and trusts, enter on Form 1041, line 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
2
3
Part III Information on Your Vehicle. Complete this part only if you are claiming car or truck expenses on line 2.
4 When did you place your vehicle in service for business purposes? (month, day, year) ▶ |
. |
5Of the total number of miles you drove your vehicle during 2018, enter the number of miles you used your vehicle for:
a |
Business |
b Commuting (see page 2) |
c |
Other |
|
|
6 |
Was your vehicle available for personal use during |
. |
. . . . . |
Yes |
No |
|
7 |
Do you (or your spouse) have another vehicle available for personal use? |
. |
. . . . . |
Yes |
No |
|
8a |
Do you have evidence to support your deduction? |
. |
. . . . . |
Yes |
No |
|
b |
If “Yes,” is the evidence written? |
. |
. . . . . |
Yes |
No |
|
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the separate instructions for Schedule C (Form 1040). |
Cat. No. 14374D |
Schedule |
Schedule |
Page 2 |
Instructions
Future developments. For the latest information about developments related to Schedule
! |
Before you begin, see General Instructions in the 2018 |
▲ |
Instructions for Schedule C. |
CAUTION |
|
You can use Schedule
•You operated a business or practiced a profession as a sole proprietorship or qualified joint venture, or you were a statutory employee, and
•You have met all the requirements listed in Schedule
For more information on electing to be taxed as a qualified joint venture (including the possible social security benefits of this election), see Qualified Joint Venture in the Instructions for Schedule C. You can also go to www.irs.gov/QJV.
Line A
Describe the business or professional activity that provided your principal source of income reported on line 1. Give the general field or activity and the type of product or service.
Line B
Enter the
Line D
Enter on line D the employer identification number (EIN) that was issued to you and in your name as a sole proprietor. If you are filing Form 1041, enter the EIN issued to the estate or trust. Do not enter your SSN. Do not enter another taxpayer’s EIN (for example, from any Forms
EIN, leave line D blank.
You need an EIN only if you have a qualified retirement plan or are required to file an employment, excise, alcohol, tobacco, or firearms tax return, are a payer of gambling winnings, or are filing Form 1041 for an estate or trust. If you need an EIN, see the Instructions for Form
Line E
Enter your business address. Show a street address instead of a box number. Include the suite or room number, if any.
Line F
See the instructions for Schedule C, line I, to help determine if you are required to file any Forms 1099.
Line 1
Enter gross receipts from your trade or business. Include amounts you received in your trade or business that were properly shown on Form
Line 2
Enter the total amount of all deductible business expenses you actually paid during the year. Examples of these expenses include advertising, car and truck expenses, commissions and fees, insurance, interest, legal and professional services, office expenses, rent or lease expenses, repairs and maintenance, supplies, taxes, travel, the allowable percentage of business meals and entertainment, and utilities (including telephone). For details, see the instructions for Schedule C, Parts II and V. You can use the optional worksheet below to record your expenses. Enter on lines b through f the type and amount of expenses not included on line a.
If you claim car or truck expenses, be sure to complete Schedule
Line 3
Nonresident aliens using Form 1040NR should also enter the total on Schedule SE, line 2, if you are covered under the U.S. social security system due to an international social security agreement currently in effect. See the Instructions for Schedule SE for information on international social security agreements.
Line 5b
Generally, commuting is travel between your home and a work location. If you converted your vehicle during the year from personal to business use (or vice versa), enter your commuting miles only for the period you drove your vehicle for business. For information on certain travel that is considered a business expense rather than commuting, see the instructions for Schedule C, line 44b.
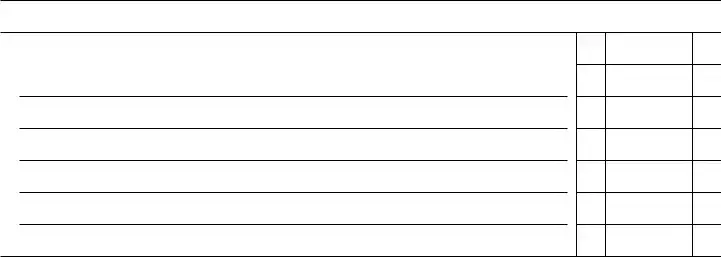
Optional Worksheet for Line 2 (keep a copy for your records)
a Deductible meals (see the instructions for Schedule C, line 24b) . . . . . . . . . . . . .
b
c
d
e
f
g Total. Add lines a through f. Enter here and on line 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
Schedule
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Fact Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Schedule C-EZ form is designed for sole proprietors to report income and expenses from a business. |
| Eligibility | Taxpayers can use Schedule C-EZ if they had no employees and business expenses were $5,000 or less. |
| Cash Method Requirement | Eligible taxpayers must use the cash method of accounting when filing Schedule C-EZ. |
| Inventory Status | If a business holds an inventory, it cannot use Schedule C-EZ and must use Schedule C instead. |
| Net Income Limit | Those with a net loss from their business cannot file Schedule C-EZ; they must use Schedule C. |
| Form Attachment | Schedule C-EZ must be attached to Form 1040, 1040NR, or 1041 when filed. |
| Statutory Employees | Individuals designated as statutory employees may still need to attach different forms despite using Schedule C-EZ. |
| Business Name Requirement | A separate business name is not required; leaving that field blank is acceptable if there's no specific name. |
| Vehicle Expenses | Taxpayers can claim vehicle expenses on Schedule C-EZ if they complete the corresponding section accurately. |
| Future Updates | Updates and changes to Schedule C-EZ can be found on the IRS website to reflect the most current regulations. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Irs Schedule C Ez
Filling out the IRS Schedule C-EZ form is an essential part of reporting the income from a sole proprietorship. This form allows sole proprietors to simplify their tax filing when their business expenses are limited and meet specific criteria. Follow the detailed steps below to accurately complete the form.
- General Information: Start by entering your personal information, including your name and Social Security Number (SSN), at the top of the form.
- Basic Eligibility: Confirm that you meet the eligibility requirements to use Schedule C-EZ, including having no more than $5,000 in expenses and not having inventory or previous year unallowed passive activity losses.
- Part I: Provide details regarding your business:
- A: Describe the main business activity or profession.
- B: Enter the corresponding six-digit business code.
- C: Fill in the business name, or leave blank if none exists.
- D: Enter your Employer Identification Number (EIN), if applicable; leave blank if not.
- E: Enter your business address or leave it blank if it matches page 1 of your tax return.
- F: Indicate whether payments were made that would require filing Forms 1099.
- G: If "Yes" to F, state whether you have filed the required Forms 1099.
- Part II: Calculate your net profit:
- 1: Enter total gross receipts made from your business.
- 2: Total all your deductible business expenses incurred during the year. Ensure this amount does not exceed $5,000 to maintain eligibility.
- 3: Subtract total expenses from gross receipts to find your net profit. Report this net profit accurately on the designated lines of other forms as required.
- Part III: If applicable, provide vehicle information:
- 4: Indicate when you placed the vehicle in service for business.
- 5: Record the total number of miles driven for business, commuting, and other purposes.
- 6: State whether the vehicle was available for personal use during off-duty hours.
- 7: Confirm if you or your spouse has another vehicle available for personal use.
- 8: Answer whether you have evidence to support your vehicle deduction and if that evidence is documented.
Review the form for any errors or omissions, ensuring all relevant information has been accurately reported. After completion, Schedule C-EZ should be attached to your Form 1040, 1040NR, or 1041 prior to submission.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the IRS Schedule C-EZ form?
The IRS Schedule C-EZ form allows sole proprietors and certain qualified joint ventures to report their net profit from business activities. It simplifies the reporting process for individuals with straightforward business expenses, generally those who do not exceed $5,000 in expenses or who did not have employees during the year.
Who can use Schedule C-EZ instead of Schedule C?
Individuals can use Schedule C-EZ if they operated a business or practiced a profession as a sole proprietorship, are a statutory employee, and meet specific criteria. Key requirements include having no more than $5,000 in business expenses, not having any employees, and not needing to report certain types of losses or deductions.
What are the qualification criteria for using Schedule C-EZ?
To qualify for Schedule C-EZ, a taxpayer must not deduct business use of home expenses, must not have end-of-year inventory, and cannot report a net loss. Additionally, they must not be required to file Form 4562 for depreciation and amortization, and must use the cash method of accounting.
What type of income should I report on Schedule C-EZ?
Gross receipts from your business activities should be reported on Schedule C-EZ. This includes all income received from sales, services, and any other receipts. The income must be taxable and can include amounts shown on Form 1099-MISC if applicable.
How do I report expenses on Schedule C-EZ?
Business expenses that are allowable can be reported directly on line 2 of Schedule C-EZ. Total deductible expenses include categories such as advertising, legal fees, and office supplies. However, if expenses exceed $5,000, one must use Schedule C instead of Schedule C-EZ.
What if I use my vehicle for business?
If claiming vehicle expenses, you must complete Part III of Schedule C-EZ. This includes reporting the date your vehicle was placed in service, the total miles driven, and how many of those miles were for business purposes. Documentation for these deductions should be kept for tax records.
What is the purpose of the business code on Schedule C-EZ?
The six-digit business code classifies the primary type of business activity. It helps the IRS categorize and analyze business income reported on your tax returns. Specific codes can be found in the instructions for Schedule C.
Do I need an employer identification number (EIN)?
An EIN is only required if a business has a qualified retirement plan, needs to file employment or excise taxes, or operates as a partnership or corporation. Sole proprietors without these requirements can leave the EIN field blank if they do not have one.
Where can I get more information about Schedule C-EZ?
For the most current information and instructions regarding Schedule C-EZ, individuals should visit the IRS website at www.irs.gov/ScheduleCEZ. This site provides updates on any legislative changes and detailed filing instructions.
Common mistakes
Filling out IRS Schedule C-EZ can be straightforward, but many individuals overlook critical details that could lead to costly errors. One common mistake is incorrectly reporting business income. Schedule C-EZ requires accurate reporting of gross receipts from your business activities. If you received payments reported on Forms 1099-MISC, you must ensure those amounts align with what you enter. Discrepancies may raise flags during processing and result in an audit or adjustments.
Another frequent oversight is failing to provide a complete business description. The form requests a brief overview of your primary business activity, yet some individuals either leave this section blank or write vague descriptions. A clear and specific description helps the IRS understand the nature of your business, which is essential for proper categorization and processing.
Many people also mistakenly miscalculate their allowable expenses. Schedule C-EZ has very strict guidelines regarding what can be included as business expenses. For instance, the total must not exceed $5,000; otherwise, one must use Schedule C. This limitation is often overlooked, causing individuals to claim too many deductions and forcing them to amend their returns later. It's important to keep diligent records of expenses to avoid this issue.
In addition, the business code section on the form often poses challenges. Entering an incorrect six-digit business code can lead to misclassification of your business type. This misstep could affect your eligibility for specific tax deductions or credits. Make sure to consult the list of codes provided in the instructions to ensure proper classification.
Finally, individuals frequently fail to understand the implications of marking the "Statutory employee" box if it applies to their situation. This designation carries specific tax responsibilities and could change how income is reported. Carefully read the instructions related to this box to avoid accidental misreporting, which can complicate your tax situation.
Documents used along the form
When filing your taxes as a sole proprietor, using Form Schedule C-EZ is often just the beginning. There are several other important documents that may accompany this form to ensure accurate reporting of your business income and expenses. Understanding these forms can help you file your taxes effectively and avoid complications with the IRS.
- Form 1040: This is the standard individual income tax return form. Whether you are filing as a sole proprietor or reporting other income, Form 1040 captures your total income, claiming deductions, and calculating your tax liability. Schedule C-EZ is attached to this form to report your business profits.
- Schedule SE: If you earn income from a business, you also need to file Schedule SE to calculate your self-employment tax. This form helps determine how much you owe in Social Security and Medicare taxes based on your self-employment income.
- Form 1099-MISC: Received for various types of income, including freelance work or contract pay. If you paid independent contractors $600 or more in a year, you would need to file separate forms to report those payments, ensuring compliance with IRS reporting requirements.
- Form 4562: This form is used to claim depreciation on property or assets used in your business. Although not always necessary for Schedule C-EZ, you may need this form if your business has significant assets that depreciate over time.
Be proactive about gathering these documents. Missing any of them can delay your tax filing or result in adjustments from the IRS. Staying organized and prepared gives you peace of mind as tax season approaches.
Similar forms
- IRS Form 1040: Schedule C-EZ is typically attached to Form 1040, like the standard Form 1040 which is used to report individual income tax. Both forms capture income and deductions but Schedule C-EZ specifically focuses on self-employment income.
- Schedule C: This form is similar to Schedule C-EZ as both document income from a business. However, Schedule C is for individuals with more complex situations, such as higher expenses or multiple businesses, whereas Schedule C-EZ is for those with simpler business activities.
- Form 1065: Partnerships file this form. Similarly, it reports income, deductions, and profits. However, Schedule C-EZ is for sole proprietors, while Form 1065 is for partnerships.
- Schedule SE: This form is related as it calculates the self-employment tax based on the net profit reported on Schedule C-EZ. If you file Schedule C-EZ and have net profit, you will usually also complete Schedule SE.
- Form 1099-MISC: Individuals report their income received on this form. It can be used in conjunction with Schedule C-EZ to account for income from self-employment reported on 1099 forms.
- Form 4562: This form is used for depreciation and amortization. While Schedule C-EZ does not allow for complex expense reporting like depreciation, both forms deal with business expenses.
- Form 1041: Used by estates and trusts to report income, similar to how Schedule C-EZ is used by sole proprietorships for business income. Both aim to capture income, but for different entities.
- Schedule A: This form is for itemizing deductions on individual returns. If a taxpayer uses Schedule C-EZ for business deductions, they cannot also use Schedule A for personal business expenses.
- Form W-2: Employers use this to report wages paid and taxes withheld. Sole proprietors who receive wages can report this income but also need to complete Schedule C-EZ for self-employment income.
- Form 941: Employers file this form to report payroll taxes. If a business has employees, it usually files Form 941 instead of using Schedule C-EZ, which is meant for sole proprietors without employees.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS Schedule C-EZ form, it’s important to keep certain best practices in mind. Here are six do’s and don’ts to help ensure a smooth process:
- Do: Make sure your business qualifies for Schedule C-EZ by meeting the income and expense thresholds.
- Do: Complete all sections accurately, including your business name and EIN if applicable.
- Do: Keep good records of your income and expenses throughout the year for accurate reporting.
- Do: Use the cash method of accounting, as required by the form.
- Don't: Deduct home office expenses on this form, as they are not allowed with Schedule C-EZ.
- Don't: Forget to check off whether you need to file any Forms 1099 if applicable.
Adhering to these guidelines will help you navigate the process more easily and can minimize potential issues with the IRS. Always refer to the instructions accompanying the form for the most current information.
Misconceptions
When it comes to filing taxes, specifically using the IRS Schedule C-EZ form, there are quite a few misconceptions that can lead to confusion. Here are seven of those misconceptions, along with clarifications to help set the record straight.
- Only large businesses can use Schedule C-EZ. Many people think that only businesses with significant revenue can use this simpler form. In fact, Schedule C-EZ is specifically designed for small businesses and sole proprietors with straightforward income and expenses.
- You must have multiple businesses to use Schedule C-EZ. Some believe that if they run only one business, they must use the standard Schedule C. That's not true! Single-business owners are eligible for Schedule C-EZ, provided they meet other requirements.
- All business expenses can be deducted on Schedule C-EZ. It's a common assumption that any and all expenses are deductible. However, this form limits the deductions primarily to cash basis expenses and does not allow certain deductions, like those related to home offices.
- You cannot use Schedule C-EZ if your business has employees. Many have the misconception that having any employees disqualifies them from using Schedule C-EZ. In reality, if you did not have employees during the tax year, you can still file this simpler form.
- Schedule C-EZ is the same as Schedule C. While both forms deal with business income and expenses, they differ in complexity. Schedule C-EZ is a simplified version and has fewer requirements, making it quicker and easier to fill out.
- Having any inventory means you cannot use Schedule C-EZ. Some individuals mistakenly think that holding inventory automatically disqualifies them from this form. Schedule C-EZ can only be used if you did not have any inventory at any point during the year.
- Filing Schedule C-EZ does not require supporting documents. Lastly, it's important to note that although Schedule C-EZ is simpler, it doesn’t free you from keeping documentation. You must maintain evidence to support your deductions in case of an audit.
Understanding these misconceptions can save you time, effort, and even money when navigating through your tax obligations. Always make sure to review the requirements carefully and consider seeking advice if you're unsure.
Key takeaways
1. Schedule C-EZ is designed for sole proprietors with simpler business situations. It streamlines the process of reporting income and expenses for your business.
2. To qualify for Schedule C-EZ, your total business expenses must not exceed $5,000, and you should not have had employees during the year.
3. You are required to report all business income accurately. This includes any amounts reported on Form 1099-MISC and any other taxable income you received as cash, property, or services.
4. Any expenses should be documented and directly related to your business activities. This includes costs related to advertising, supplies, and travel.
5. It's crucial to maintain good records. Keep all receipts and documents that support your claimed deductions to protect against potential audits.
6. If you are using your vehicle for business, you will need to record the miles driven and the date the vehicle was first used for business purposes.
7. Remember to check off if you have made any payments that require you to file Form 1099. This ensures compliance with IRS rules.
8. Schedule C-EZ helps in determining your net profit. Always subtract your total expenses from your gross receipts to find this amount.
9. Finally, upon completion, ensure to include Schedule C-EZ with your primary tax form, which is typically Form 1040, to avoid filing issues.
Browse Other Templates
Medicare Cgm Form - Any discrepancies or omissions can lead to serious repercussions for both the provider and the patient.
Participant Information Form,Vocational Rehabilitation Application,Ohio VR Service Application,Commission Rehabilitation Request Form,Disability Services Application,Employment Support Form,VR Client Intake Form,Rehabilitation Services Participant Fo - Consumers are encouraged to share insights during the application process, cultivating collaborative relationships with staff.
Jdf 1000 Colorado - Eligibility for filling out the form applies to both married and civil union partners.