Fill Out Your Kinship Tree Diagram Form
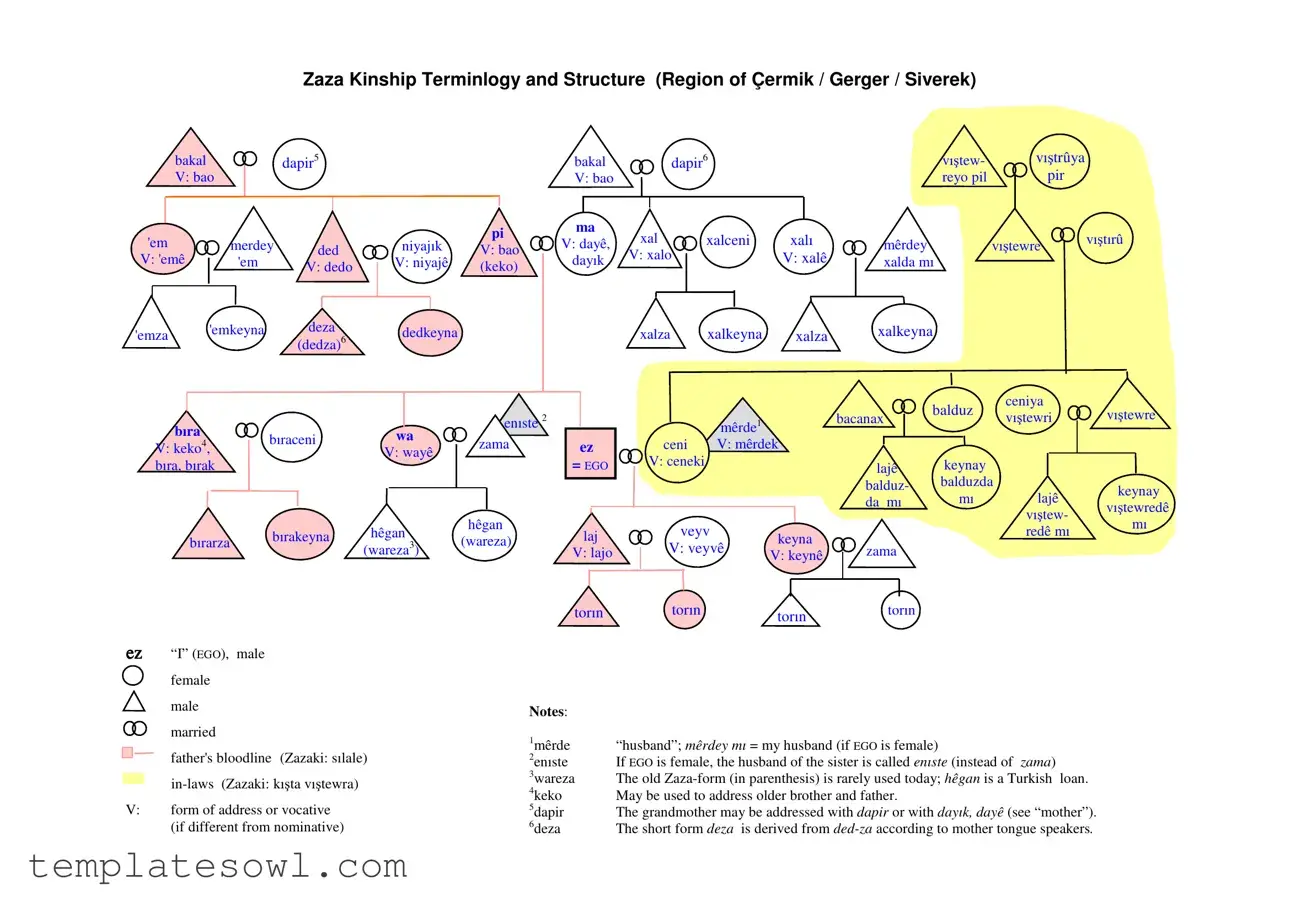
The Kinship Tree Diagram form serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complex relationships within Zaza society, specifically in the regions of Çermik, Gerger, and Siverek. It outlines unique terminologies that reflect how individuals relate to one another, both through bloodlines and marital connections. Central to this diagram is the concept of patrilineality, where lineage is traced exclusively through the father’s side, thus defining the familial structure and the role each member plays. Notably, the form highlights terms used to address specific relatives, such as 'dayê' for mother and 'mêrde' for husband. The relationships are distinctly marked by the inclusion of in-laws, referred to as “kıta vıtewra,” who are treated as non-blood relatives. Through this lens, the cultural significance of marriage emerges, particularly the preference for endogamous unions that reinforce clan ties, while also acknowledging the potential pitfalls of such arrangements. Additionally, the diagram reveals that children of a daughter are not recognized as part of their maternal lineage, highlighting the societal emphasis on male descendants as vital to perpetuating the clan. By examining the structure and terms depicted in the Kinship Tree Diagram, one gains insight into how lineage, marriage, and familial roles are understood and navigated in Zaza culture.
Kinship Tree Diagram Example
Zaza Kinship Terminlogy and Structure (Region of Çermik / Gerger / Siverek)
|
|
|
bakal |
|
|
|
dapir5 |
|
|
|
|
bakal |
|
|
|
|
|
dapir6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
V: bao |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V: bao |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pi |
ma |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
'em |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xalceni |
|
|
xalı |
||||||||||||||||
merdey |
|
|
|
niyajık |
V: dayê, |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
ded |
V: bao |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
V: 'emê |
|
'em |
|
|
dayık |
V: xalo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
V: xalê |
|||||||||||||||||
|
V: dedo V: niyajê |
(keko) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
'emkeyna |
deza |
dedkeyna |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
'emza |
|
|
|
|
|
xalza |
|
|
xalkeyna |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xalza |
|||||||||||||||||||||
(dedza)6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vıtew- |
|
vıtrûya |
|
|
reyo pil |
|
pir |
vıtırû |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mêrdey |
|
vıtewre |
||
|
|
|||
xalda mı |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xalkeyna
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
balduz |
ceniya |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
enıste 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
bacanax |
|
vıtewri |
|
vıtewre |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
bıra |
bıraceni |
wa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mêrde |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
V: keko4, |
zama |
|
ez |
|
ceni |
V: mêrdek |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
V: wayê |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
bıra, bırak |
|
|
|
= EGO |
|
V: ceneki |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lajê |
keynay |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
balduz- |
balduzda |
lajê |
|
keynay |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mı |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
da mı |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vıtewredê |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vıtew- |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
hêgan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mı |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
veyv |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
bırakeyna |
hêgan |
|
laj |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
redê mı |
|
|||||||||
|
bırarza |
(wareza) |
|
|
|
|
|
keyna |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
3 |
|
|
|
V: veyvê |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
(wareza ) |
|
|
V: lajo |
|
|
|
V: keynê |
|
|
zama |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
“I” (EGO), male
female
male
married
father's bloodline (Zazaki: sılale)
V:form of address or vocative (if different from nominative)
torın |
torın |
torın |
torın |
|
|
|
Notes: |
|
1mêrde |
“husband”; mêrdey mı = my husband (if EGO is female) |
2enıste |
If EGO is female, the husband of the sister is called enıste (instead of zama) |
3wareza |
The old |
4keko |
May be used to address older brother and father. |
5dapir |
The grandmother may be addressed with dapir or with dayık, dayê (see “mother”). |
6deza |
The short form deza is derived from |

Additions to kinship terms:
xalo, xalê, dedo “uncle, aunt” may be used to address elders respectfully who
|
are not family related. |
deza |
2nd or 3rd cousins of father's bloodline are also called deza. |
The following terms are not listed in the diagram: |
|
demari |
“step mother” |
weni |
how wifes call each other in polygamous marriages. |
gorım |
how wife of EGO calls sister of EGO. |
cêri |
how wife of EGO and wife of EGO’S brother call each |
|
other. |
Description of the kinship pattern
Zaza society1 is organized patrilinearly and patrilocally. This means that lineage depends exclusively on the father not the mother. Relatives on the mother's side including the mother herself are
Children of the daughter are not considered to be of one's blood line, they belong to the lineage of the daughter's husband (i.e. the son in law) instead. This explains the joy over the birth of a son. A male descendant guarantees the continuation of one's paternal lineage. It is noteworthy that this fact is not represented in the terminology. Both descendants of the son and of the daughter are called “torın” (turkish torun).
As an outward expression of this structure of the society, the bride moves into the house of the groom at the wedding (patrilocal residence). The relatives of the wife, the
1This summary is based on research among Sunni Zaza, living in the region of Çermik, Gerger and Siverek. The results are based on interviews with various Zaza families.
2If maternal and paternal relatives are considered equally in determining one's lineage, individuals have overlapping lineages to which they belong. This kind of pattern is called a bilateral descent, and is displayed in a typical modern Western European society.
If there are problems or dissent among the relatives of a blood line, all members are held responsible. Problems of the
Zaza society shows a pattern of unilineal descent, as each individual can be part of only one blood line.2
Marriage
When looking for a suitable marriage partner, Zaza society prefers partners of one's own blood line (endogamous marriage). The advantage of an endogamous marriage is that the descendants of the daughters will not be considered members of a different blood line, but will be considered relatives. This way, one's clan increases in number and gains more influence in society.
The disadvantage of an endogamous marriage is obvious when the marriage is not successful. Dissent and division within the clan cannot be avoided and hurt the group as a whole in the long run.
Exogamous marriages are frequent in Zaza culture as well. The advantage is seen in that disagreements between the spouses will not threaten the unity of one's clan, because the wife belongs to a different lineage.
Source:
Ember, Carol R. / Ember, Melvin. 1993. Cultural Anthropology.
Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
©Brigitte Werner, 2009. Kontakt:
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Patrilineal Structure | Zaza society organizes its lineage based exclusively on the father's side, meaning maternal relatives are considered in-laws, not blood relatives. |
| Patrilocal Residence | Upon marriage, the bride moves into her husband’s home, symbolizing the patrilocal tradition where the woman joins the man's family. |
| Bloodline Terminology | The father’s lineage is referred to as “sılaley mı” or “merdımê mı,” which translates to 'my people' in Zazaki. |
| Son Preference | The birth of a son is celebrated because male descendants ensure the continuity of the paternal lineage. This preference is embedded in cultural practices. |
| Kıta Vıtewra | The in-laws are collectively known as “kıta vıtewra,” reflecting their status outside the direct bloodline. |
| Endogamous Marriages | Zaza society often favors marriages within one's own bloodline to strengthen clan ties and maintain familial influence. |
| Exogamous Marriages | Marriages to partners outside one's lineage are also common, as they can help prevent conflicts that may arise from internal dissent. |
| Titles and Address | Zaza kinship terminology includes respectful forms of address for relatives, like “keko” for older brothers or fathers, enhancing social hierarchy and respect. |
| Unilineal Descent | Zaza culture exhibits a unilineal descent pattern, indicating that individuals belong to only one bloodline, simplifying familial relationships. |
| Interviews and Research | This analysis is derived from interviews conducted with various Zaza families, supporting a deeper understanding of their cultural framework. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Kinship Tree Diagram
Once you have the Kinship Tree Diagram form in front of you, gather any necessary information regarding your family. This may include names and relationships of each family member you wish to include. After you have all the details ready, follow the steps below to complete the form accurately.
- Identify EGO: Write your name in the designated spot. This indicates your position in the family tree.
- Label your immediate family: Fill in names of your parents, siblings, and children, ensuring you follow the correct kinship terms.
- Complete grandparent information: Enter the names of your grandparents. Use specific terminology as required.
- Add extended family: Include aunts, uncles, and cousins, using the right kinship descriptors.
- Note in-laws: Clearly indicate relationships to in-laws by labeling them properly within the diagram.
- Fill out marital status: If applicable, indicate your marital status and list your spouse's name.
- Review your entries: Go over the completed information to ensure accuracy. Correct any mistakes found.
- Submit the form: Once everything is filled out and checked, submit the form as instructed.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Kinship Tree Diagram form?
The Kinship Tree Diagram form helps document familial relationships within Zaza culture, particularly in regions like Çermik, Gerger, and Siverek. This diagram visually represents how relatives are connected through bloodlines and marriage, providing insight into the social structure and cultural practices of the Zaza people.
How is kinship defined in Zaza society?
In Zaza society, kinship is defined patrilineally. This means that lineage is traced exclusively through the father's side. Mothers and their relatives are considered in-laws rather than blood relatives. A child born to a daughter, for instance, is viewed as belonging to the lineage of the daughter's husband, not the mother’s family.
What does 'EGO' mean in the context of the Kinship Tree Diagram?
'EGO' represents the individual from whose perspective the family relationships are being viewed. In the diagram and terminology, this person is central, and relationships are defined in relation to EGO. The term helps clarify the connections between various relatives and their respective titles.
Why is having male descendants significant in Zaza culture?
The birth of a male descendant is significant due to the belief that males continue the paternal lineage. Sons are viewed as essential for ensuring the continuation of the family's bloodline. This cultural emphasis on male offspring illustrates the deep-rooted values placed on lineage continuity.
What are the implications of marriage choices in Zaza society?
Marriage choices often revolve around endogamous and exogamous practices. Endogamous marriages, which occur within the same bloodline, help strengthen clan ties and retain a sense of lineage. On the other hand, exogamous marriages bring in diverse perspectives and can reduce conflict, as spouses belong to separate lineages.
How do in-laws fit into Zaza kinship structures?
In-laws are categorized separately from blood relatives in Zaza kinship structures. Known collectively as 'kıta vıtewra,' these relatives play an important role but do not participate in the direct lineage. This distinction simplifies relationship dynamics, as issues regarding in-laws do not affect one's blood relatives.
What terms are used to describe relatives in the Zaza Kinship Tree?
The terminology includes various specific words for relatives, such as 'mêrde' for husband and 'enıste' for the husband of a sister if EGO is female. Each term carries cultural significance and reflects the social norms and values regarding family and respect within the community.
Are maternal relatives considered in Zaza lineage?
Maternal relatives do not figure into Zaza lineage; rather, they are regarded as in-laws. This creates a clear division in understanding family roles. Such structure minimizes potential conflicts and clarifies responsibilities among family members.
How does the structure of the Zaza Kinship Tree impact family gatherings?
The clear structure of the Zaza Kinship Tree facilitates gatherings, as roles and relationships are well understood. Events can be organized efficiently, knowing how to address each relative according to their specific titles. This organization fosters a sense of belonging and community among family members.
What cultural practices stem from Zaza kinship structures?
Cultural practices like patrilocal residence, where the bride moves into the groom's home, arise from the kinship structure. Such practices further entrench the concept of patrilineality and reflect the values of Zaza society, while also shaping the daily lives and interactions of the community.
Common mistakes
When filling out the Kinship Tree Diagram form, it’s easy to make mistakes that could lead to confusion and inaccuracies. One common mistake is overlooking the specific terminology used for family members. Each term holds particular significance, and using the wrong one can misrepresent relationships. For example, failing to differentiate between “mêrdek” (my husband) and “zama” (brother-in-law) can lead to misunderstandings.
Another mistake people often make is not including all relevant family members. Some individuals may focus solely on immediate relatives and exclude extended family, which could lead to incomplete representation. This oversight can have implications, especially in a culture where both immediate and extended families are important.
Not understanding the cultural context surrounding kin terms can also pose a challenge. Zaza society has specific customs regarding bloodlines and relationships. For instance, individuals may forget that maternal relatives are considered in-laws rather than blood relatives. This distinction is crucial in Zaza terminology and community structure.
Some users might also fail to clarify the relationships accurately. For instance, they might not explicitly indicate whether a relative is on the paternal or maternal side. This lack of precision can lead to an unclear understanding of family dynamics.
Additionally, people sometimes misinterpret the generational gaps in kinship. For example, understanding terms like “deza” for second or third cousins is essential. Misclassifying these relatives can result in incorrect lineage representation.
Lastly, neglecting to check for correct spelling or terminology variations can create errors. Phrases like “kıta vıtewra” may not be spelled consistently, leading to confusion. An accurate representation and understanding of these terms help ensure clarity and respect for cultural nuances.
Documents used along the form
The Kinship Tree Diagram form is an essential tool for mapping family relationships in Zaza society. Alongside this diagram, certain other forms and documents frequently support the understanding of familial ties and cultural norms. Below are some important documents that may be used in conjunction with the Kinship Tree Diagram form.
- Family Group Sheet: This document lists family members and their relationships to one another. It serves as a comprehensive overview of immediate family, including parents, siblings, and children. It can help to clarify roles within the family structure.
- Birth Certificate: This vital record provides official proof of an individual's birth. It includes details such as the person's name, date of birth, and parents’ names, which are key to establishing lineage and familial connections.
- Death Certificate: This document offers crucial information regarding a family member's passing. It includes the date and cause of death, which can affect family dynamics and inheritance issues within the Zaza community.
- Marriage Certificate: This official document records the union between two individuals. It indicates familial status changes and can significantly influence the kinship structure, especially through alliances formed via marriage.
Together, these documents provide a clearer understanding of personal histories and societal connections. They complement the Kinship Tree Diagram, helping families to articulate their relationships and navigate various cultural practices more effectively.
Similar forms
-
Family Tree Chart: Like the Kinship Tree Diagram, the Family Tree Chart visually represents relationships among relatives, showing how individuals are connected through generations.
-
Pedigree Chart: The Pedigree Chart focuses on biological lineage, similar to the Kinship Tree Diagram, but often emphasizes genetic relationships and hereditary traits.
-
Clan Genealogy Records: These records detail the lineage of clans, akin to the Kinship Tree Diagram. They outline relationships within a larger community rather than just a nuclear family.
-
Descendant Chart: This chart tracks the descendants of an ancestor, much like a Kinship Tree Diagram traces relationships over time and lines of descent.
-
Genealogical Report: This report provides a written record of family history that may accompany a Kinship Tree Diagram, emphasizing individual stories and family events over relationships.
-
Kinship Table: While the Kinship Tree Diagram is visual, a Kinship Table organizes the same information in a format that is often easier to read, displaying relationships in a clear, grid-like fashion.
-
Genogram: A genogram allows for the illustration of family dynamics across generations, just as the Kinship Tree Diagram does, but with additional details about relationships, health issues, and social structures.
-
Biographical Sketch: This is more of a narrative form that captures personal histories of family members. It complements the visual nature of the Kinship Tree Diagram by telling the stories behind the connections.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Kinship Tree Diagram form, it is important to follow some guidelines to ensure accuracy and clarity. Here is a list of things you should and shouldn't do:
- Do read through the form thoroughly before starting.
- Do use clear and legible handwriting or type your responses.
- Do label each family member accurately according to the kinship terms provided.
- Do double-check the relationships to avoid mistakes.
- Don't skip any sections, even if the information seems irrelevant.
- Don't use abbreviations that are not standard or widely recognized.
- Don't confuse maternal and paternal relations; keep them distinct.
- Don't leave any fields blank unless instructed to do so.
Misconceptions
- All family terms are the same across cultures: Many believe that kinship terms translate easily from one culture to another. However, the Kinship Tree Diagram illustrates that each society has unique terms that carry specific meanings, especially in Zaza culture.
- Only blood relatives are considered family: It's a common misconception that family only includes biological connections. The Zaza kinship system includes in-laws and non-relatives who are respected as elders, expanding the definition of family.
- Women are not part of the lineage: Some think that women hold no influence in family lineage. While Zaza culture is patrilineal, women still play vital roles within their families, especially through marriage and in how children are raised.
- The terms refer exclusively to direct family members: Many assume that kinship terms solely describe immediate family. However, the Zaza terminology encompasses uncles, aunts, and even friends addressed respectfully, showcasing a broad network of relationships.
- All marriages in Zaza culture are endogamous: It is a myth that Zaza society strictly practices endogamous marriage. In reality, exogamous marriages also occur frequently, allowing for diverse connections and reinforcing ties with other groups.
- The kinship diagram is static and unchangeable: There is a belief that the Kinship Tree Diagram is a permanent fixture. Yet, this representation can evolve as families grow, reflecting new relationships and social dynamics.
- Men have all the power in marriage: While it's widely thought that men dominate marital decisions, Zaza women bring significant influence, especially in choosing partners and managing family relations.
Understanding these misconceptions can enhance one’s comprehension of the Zaza kinship system and its nuanced social structure. Being aware of these distinctions fosters a deeper respect for cultural diversity and the ways in which societies structure their familial relationships.
Key takeaways
- Filling out the Kinship Tree Diagram requires accurate information about family relations, particularly through the father's bloodline.
- The diagram emphasizes the importance of patrilineal relationships, where lineage is traced through male descendants.
- Terms for relatives vary based on gender, lineage, and level of closeness, requiring attention to detail during completion.
- While completing the form, keep in mind that maternal relatives are generally considered in-laws rather than blood relatives.
- Take note that “EGO” is used to represent the individual filling out the diagram, making it easier to understand relationships.
- Identifying in-laws is essential, as they are an integral part of the family structure in Zaza society.
- The form includes terminology that reflects cultural practices, such as the preference for endogamous marriages.
- Be aware that children from daughters are not considered part of the paternal bloodline; they belong to the son-in-law’s lineage.
- Understanding these kinship terms can enhance communication and relationships within Zaza families.
- The Kinship Tree Diagram can serve as a helpful tool for recognizing family dynamics and heritage.
Browse Other Templates
Teacher Application - Understand your rights concerning any claims of unlawful disclosure or employment discrimination.
Welfare Documents - Providing Social Security Numbers is required for all applicants seeking assistance for themselves.
Fsis Form 7234-1 - A section is reserved for conditions that may apply to the use of the approved labels or devices.