Fill Out Your Mcps 335 37 Form
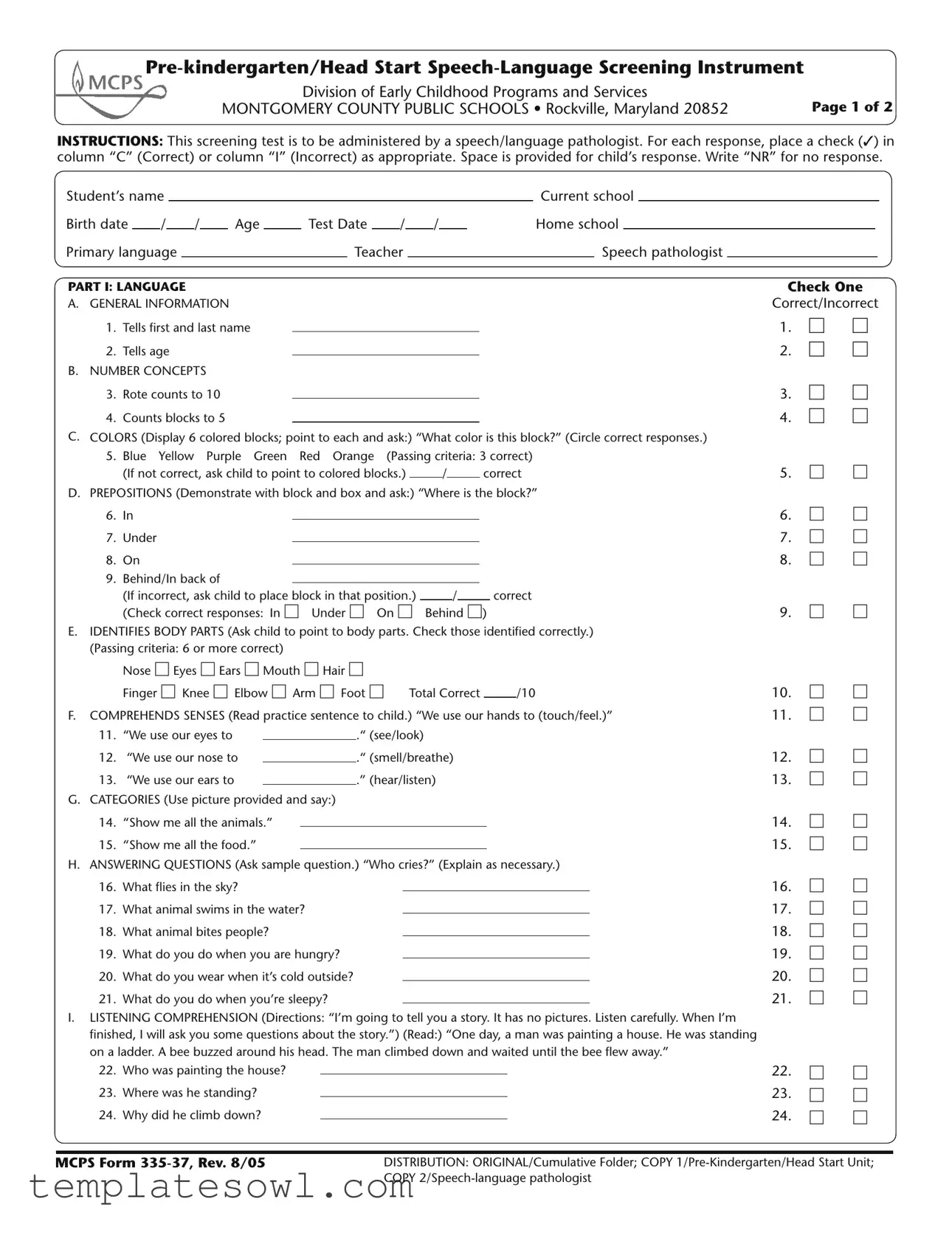
The MCPS 335-37 form plays a crucial role in early childhood education by providing a structured means for speech-language screening, specifically designed for pre-kindergarten and Head Start students within Montgomery County Public Schools. This form, utilized by qualified speech-language pathologists, offers a comprehensive evaluation across various domains of language and speech development. Major components include assessments for general information, number concepts, color identification, prepositions, body part recognition, listening comprehension, and expressive language. Each section assesses a child's capabilities through a series of targeted questions and tasks, allowing evaluators to record responses systematically. For example, the child may be asked to identify colors or demonstrate understanding of body parts. The screening also examines auditory memory and the ability to follow multi-step directions. Furthermore, it includes evaluations of articulation, fluency, and voice to provide a holistic view of the child's communication skills. The results gleaned from this form are vital, serving not only to identify areas needing support but also to guide decisions about intervention strategies and resources necessary for fostering optimal language development in young learners.
Mcps 335 37 Example
Division of Early Childhood Programs and Services |
|
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS • Rockville, Maryland 20852 |
Page 1 of 2 |
INSTRUCTIONS: This screening test is to be administered by a speech/language pathologist. For each response, place a check ( ) in column “C” (Correct) or column “I” (Incorrect) as appropriate. Space is provided for child’s response. Write “NR” for no response.
Student’s name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current school |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Birth date |
|
|
/ |
|
|
/ |
|
|
Age |
|
|
|
Test Date |
|
|
/ |
|
|
|
/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Home school |
|
|
|
|
||
Primary language |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Teacher |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speech pathologist |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
PART I: LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check One |
|||||||||
A. GENERAL INFORMATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct/Incorrect |
||||||||||||||
1. |
Tells first and last name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
|
||||||||||||||
2. |
Tells age |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
|||||||||
B. NUMBER CONCEPTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
3. |
Rote counts to 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
||||||||||||||
4. |
Counts blocks to 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
C. COLORS (Display 6 colored blocks; point to each and ask:) “What color is this block?” (Circle correct responses.) |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5. |
Blue |
Yellow |
|
|
Purple Green |
|
Red Orange |
(Passing criteria: 3 correct) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
(If not correct, ask child to point to colored blocks.) |
|
|
|
|
/ |
|
|
|
|
correct |
5. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
D. PREPOSITIONS (Demonstrate with block and box and ask:) “Where is the block?” |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6. |
In |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
|
|||||
7. |
Under |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
|
|||||
8. |
On |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
|
|||||
9. |
Behind/In back of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
(If incorrect, ask child to place block in that position.) |
|
|
|
/ |
|
|
|
correct |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
(Check correct responses: In Under On Behind ) |
9. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
E.IDENTIFIES BODY PARTS (Ask child to point to body parts. Check those identified correctly.) (Passing criteria: 6 or more correct)
|
Nose Eyes Ears Mouth Hair |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Finger Knee Elbow Arm Foot |
Total Correct |
|
|
/10 |
|
10. |
|||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
F. COMPREHENDS SENSES (Read practice sentence to child.) “We use our hands to (touch/feel.)” |
11. |
|||||||||||
11. |
“We use our eyes to |
|
|
.“ (see/look) |
|
|
|
|
12. |
|||
12. |
“We use our nose to |
|
|
.“ (smell/breathe) |
|
|
|
|
||||
13. |
“We use our ears to |
|
|
.” (hear/listen) |
|
|
|
|
13. |
|||
G. CATEGORIES (Use picture provided and say:) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
14. |
“Show me all the animals.” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. |
|||
15. |
“Show me all the food.” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
|||
H. ANSWERING QUESTIONS (Ask sample question.) “Who cries?” (Explain as necessary.) |
|
|
|
|||||||||
16. |
What flies in the sky? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16. |
||||
17. |
What animal swims in the water? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17. |
||||
18. |
What animal bites people? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
18. |
||||
19. |
What do you do when you are hungry? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19. |
||||
20. |
What do you wear when it’s cold outside? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
20. |
||||
21. |
What do you do when you’re sleepy? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21. |
||||
I.LISTENING COMPREHENSION (Directions: “I’m going to tell you a story. It has no pictures. Listen carefully. When I’m finished, I will ask you some questions about the story.”) (Read:) “One day, a man was painting a house. He was standing on a ladder. A bee buzzed around his head. The man climbed down and waited until the bee flew away.”
22. |
Who was painting the house? |
|
22. |
||
|
|||||
23. |
Where was he standing? |
|
23. |
||
|
|||||
24. |
Why did he climb down? |
|
24. |
||
|
|||||
|
|
||||
MCPS Form |
DISTRIBUTION: ORIGINAL/Cumulative Folder; COPY |
||||
|
|
COPY |
|
|
|
Student’s name
|
Signature, |
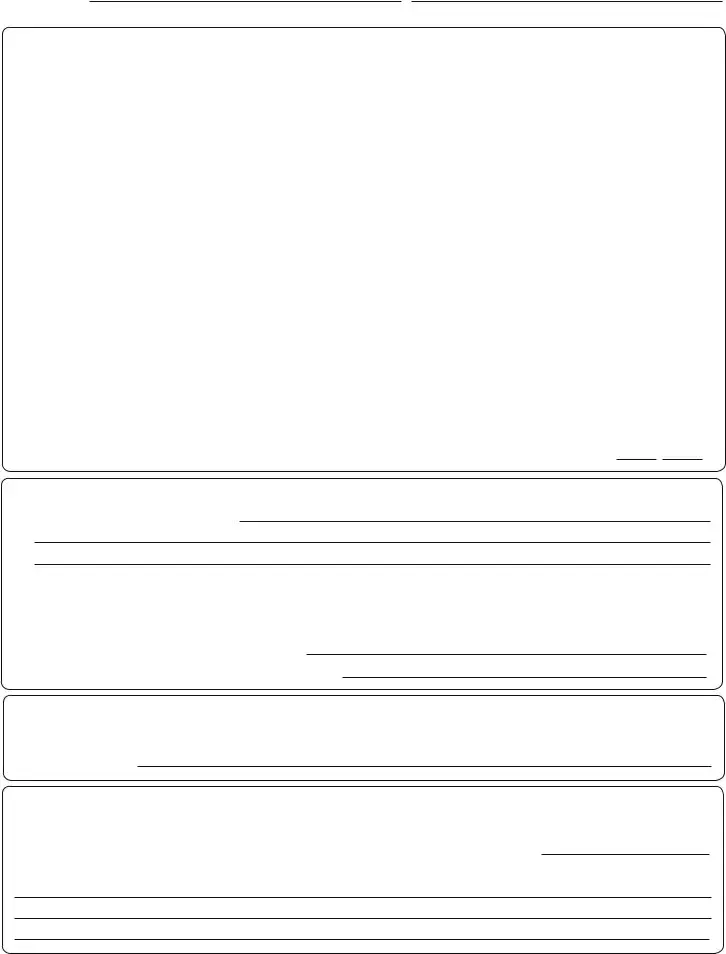
PART I: LANGUAGE (continued) |
Check One |
|
Correct/Incorrect |
J.AUDITORY MEMORY FOR SENTENCES
25. |
“Toy...Chair...Light” |
|
25. |
||
|
|||||
26. |
“Cars are big.” |
|
26. |
||
|
|||||
27. |
“He sleeps in a bed.” |
|
27. |
||
|
|||||
28. |
“The boy played ball with his dog.” |
|
28. |
||
|
K.EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE SAMPLE (Use sequence picture provided. Point to each picture and say: “Tell me a story about these pictures.” Record responses on lines provided, including articulation errors. Give credit if the child uses a minimum of three phrases or sentences that include action words.)
29. |
|
29. |
|
||
|
|
|
L. SYNTAX (Record any grammatical differences or errors on lines provided.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M. FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS (Say: “Listen carefully. I want you to do three things.”) |
|
|
|
|
30. “Clap your hands. Put your hands on your head. Touch your nose.” |
30. |
|
|
(Passing criteria: Child performs all 3 directions.) |
|
|
|
If incorrect, say: “Close your eyes. Clap your hands.” |
|
|
|
TOTAL |
Correct/Incorrect |
|
PART II: SPEECH
A. ARTICULATION (Record sound errors.)
Spontaneous speech: Intelligible Not intelligible Intelligible with careful listening Not enough said to judge
If multiple errors, administer
Adequate Recheck
B. FLUENCY: Fluent Dysfluent Comments
C. VOICE: Adequate If not adequate, describe quality.
PART III: HEARING
No known problem Suspect problem
History of Problem
PART IV: |
|
||
1. |
Speech and language is within normal limits. |
||
3. |
English Language Learner (ELL) |
||
COMMENTS
2.Confer with team/observe further.
4.Administered in (language)
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The MCPS 335-37 form is designed for speech-language screening for pre-kindergarten and Head Start students. |
| Administration | The screening must be administered by a certified speech/language pathologist. |
| Completion Criteria | Specific passing criteria exist for various sections, such as identifying body parts and color recognition, ensuring a standardized assessment. |
| Governing Laws | The form operates under Maryland law and guidelines from the Division of Early Childhood Programs and Services. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Mcps 335 37
After completing the MCPS Form 335-37, the data collected will assist in evaluating the child's speech and language abilities. It's crucial to ensure accurate responses and thorough documentation to aid in any recommended follow-ups or interventions.
- Obtain the form, ensuring it's the latest version (MCPS Form 335-37).
- Fill in the child's information at the top: Student’s name, Current school, Birth date, Age, Test Date, Home school, Primary language, Teacher, and Speech pathologist.
- Proceed to Part I: LANGUAGE. For each statement listed, observe the child and mark Correct (C) or Incorrect (I) accordingly.
- In the COLORS section, show the child six colored blocks and ask for their names. Circle the correct responses, ensuring at least three are correct for passing.
- For the PREPOSITIONS, demonstrate with a block and box, then ask the questions. Check the correct responses and document them.
- Ask the child to identify BODY PARTS. Ensure they identify at least six parts correctly for passing.
- In the COMPREHENDS SENSES section, read each sentence and assess the child’s understanding. Mark responses as correct or incorrect.
- Using a picture, assess CATEGORIES by asking the child to identify animals and food.
- Pose sample questions in the ANSWERING QUESTIONS section, recording each response accurately.
- Read the story in the LISTENING COMPREHENSION section and ask the questions afterwards, noting how many they answer correctly.
- For AUDITORY MEMORY, read the phrases and record the child's recall of those phrases.
- Utilize the EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE SAMPLE to evaluate storytelling, recording responses including any articulation errors.
- Evaluate SYNTAX, noting any grammatical differences or errors.
- Conduct the FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS task, ensuring the child completes all three directions for passing.
- Transition to Part II: SPEECH. Record any articulation errors, fluency, and voice quality assessments.
- In Part III: HEARING, note any existing issues.
- Complete Part IV: FOLLOW-UP AND COMMENTS based on observations and findings, choosing the appropriate options.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the MCPS 335 37 Form?
The MCPS 335 37 Form is a Speech-Language Screening Instrument designed for pre-kindergarten and Head Start programs. It is administered by a speech or language pathologist to assess a child's communication skills in several areas, including language comprehension, speech articulation, and auditory memory.
Who administers the MCPS 335 37 Form?
The screening test must be administered by a certified speech-language pathologist. Their expertise ensures that the assessment is conducted effectively and that results are interpreted accurately for each child.
What areas does the screening evaluate?
The form evaluates various aspects of a child's communication abilities, including general information, number concepts, color identification, understanding of prepositions, identification of body parts, comprehension of senses, answering questions, listening comprehension, auditory memory, expressive language, articulation, fluency, voice quality, and hearing capability.
What are the passing criteria for the different sections?
Each section of the screening has specific passing criteria. For example, a child must answer at least three color identification questions correctly and correctly identify six or more body parts. Additionally, the child must follow a set of three directions accurately in the directions following section.
What should be done if a child does not meet the criteria?
If a child does not meet the passing criteria in certain areas, the speech-language pathologist may recommend further observation, additional assessments, or interventions to address any identified concerns, ensuring that appropriate support is provided.
How is the child's progress documented on the form?
The form includes spaces where the pathologist can mark whether each response was correct or incorrect. For sections that require a narrative, such as the expressive language sample, specific responses can be recorded, allowing for a comprehensive view of the child's abilities.
Is there a component for parents or guardians on this form?
The MCPS 335 37 Form primarily focuses on the child's assessment; however, parents or guardians may be involved in discussions about the results and any necessary follow-up actions based on the findings of the screening.
What is the purpose of auditory memory exercises within the screening?
Auditory memory exercises assess a child's ability to remember and recall information presented verbally. This skill is vital for effective communication and language development, as it affects how children follow directions and engage in conversations.
What happens after the screening is completed?
Upon completion of the screening, results are compiled and shared with relevant parties, including teachers and parents. Based on the findings, recommendations for follow-up actions, further assessments, or interventions may be provided to support the child's language and speech development.
How often should the MCPS 335 37 Form be administered?
The frequency of administering the MCPS 335 37 Form can vary based on the individual needs of the child and the policies of the educational institution. It is typically conducted at the beginning of a program and may be repeated as necessary to monitor progress.
Common mistakes
Filling out the MCPS 335-37 form is crucial for assessing a child's speech and language skills. However, there are several common mistakes individuals make when completing this form.
One significant error is failing to provide complete and accurate demographic information. Omitting details like the child’s full name, current school, and birth date can lead to confusion later on. Ensuring this data is accurate is essential for proper tracking and reporting.
Another mistake is not following the instructions as they are laid out. Each section requires specific actions, such as checking boxes in the "Correct" or "Incorrect" columns. Skipping this step, or marking responses inconsistently, can compromise the overall assessment quality. Attention to detail plays a vital role in the effectiveness of this screening.
Equally important is the neglect of the passing criteria. Each section has specific requirements, such as the need for a child to provide a certain number of correct responses for categories like colors or categories. Ignoring these benchmarks can lead to misinterpretation of the child’s abilities. Clarity in identifying whether a child meets the required number is essential for accurate results.
Another common pitfall is a lack of engagement with the child during the assessment. The screening is designed to be interactive, requiring the child’s participation. When assessors do not actively engage, they risk missing important responses that demonstrate the child’s skills. Evaluators should create a supportive environment to help the child perform at their best.
Inconsistent recording of responses presents yet another challenge. It is vital to maintain a uniform approach when documenting answers. This includes ensuring notes about articulation errors or expressive language samples are clearly recorded. If records are incoherent or incomplete, it becomes challenging to analyze the findings accurately.
Forgetting to seek clarification or provide examples can also hinder the assessment process. If a child seems unsure about a question, the assessor should provide additional context or prompts. This can lead to a more accurate understanding of what the child knows, and a deeper insight into their language abilities.
Lastly, not following up after the screening can be a major oversight. The MCPS form contains a section for follow-up comments and recommendations. Failing to provide this information limits the potential for ongoing support and growth for the child. Each assessment should culminate in a clear plan for next steps, benefitting the child's development.
Documents used along the form
The MCPS 335 37 form is often used in conjunction with several other forms and documents to ensure a comprehensive assessment of a child's speech and language development. Below is a list of related documents commonly used in this process.
- Pre-Kindergarten/Head Start Articulation Screening: This document is used to identify articulation errors in a child's speech. It allows speech pathologists to assess how clearly a child pronounces sounds, providing essential information for planning intervention.
- Progress Monitoring Report: This report tracks a child's progress over time regarding speech and language goals. It offers insights into improvements and areas needing additional focus, facilitating more tailored support and intervention.
- Speech-Language Evaluation Report: This in-depth report summarizes the results of various assessments administered to the child. It provides a comprehensive overview of the child’s communication skills, challenges, and recommendations for further action.
- Individualized Education Program (IEP): For children who qualify, the IEP outlines specific educational goals and services tailored to their individual needs. This document is crucial for ensuring that students receive the necessary support to succeed academically.
These documents complement the MCPS 335 37 form, providing a fuller picture of a child's speech and language capabilities, guiding intervention strategies, and supporting educational success.
Similar forms
The MCPS Form 335-37 is a comprehensive tool designed for assessing speech and language skills in young children. Several documents serve similar purposes in evaluating a child's developmental progress or special education needs. Below is a list of forms that share characteristics with the MCPS 335-37:
- Childhood Developmental Screening Form: This document assesses various developmental milestones in areas such as cognitive, language, and motor skills, much like the MCPS 335-37 focuses on language skills.
- Speech and Language Evaluation Report: This report provides an in-depth assessment of a child’s speech and language abilities. Similar to the MCPS 335-37, it includes specific areas of assessment and observations by professionals.
- Kindergarten Readiness Assessment: This tool evaluates a child's readiness for school, incorporating language skills and social interactions, akin to the language focus of the MCPS 335-37.
- Individualized Education Program (IEP): Created for students with identified disabilities, it outlines specific goals and assessments, paralleling the detailed observations used in the MCPS 335-37.
- Behavioral Observation Form: Used by educators to track behavioral and social skills, this form emphasizes observational data similar to the language observations made in the MCPS 335-37.
- Early Childhood Assessment System: This is a broader evaluation that looks at multiple areas of development, including language and communication, reflecting the MCPS 335-37's focus on speech and language.
- Language Proficiency Assessment: This document assesses a child's proficiency in their primary language, sharing a goal with the MCPS 335-37 to ensure children have appropriate language skills.
- Cognitive Assessment Tool: Evaluating cognitive abilities and strengths, this tool complements the language focus of the MCPS 335-37 by addressing overall cognitive development in children.
- Parent Interview Form: Used to gather insight from parents regarding their child’s language use at home, this form seeks to inform assessments like the MCPS 335-37.
- Screening for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): This document looks for specific signs of autism in early language and communication skills, paralleling the early speech assessments found in the MCPS 335-37.
Each of these documents plays an essential role in determining a child's developmental status, offering valuable insights for educators and speech-language pathologists alike. Understanding these similarities can help in recognizing the importance of comprehensive assessments in fostering a child’s growth.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the MCPS 335 37 form, there are essential dos and don’ts that can enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of the screening process. Adhering to these guidelines will help ensure that the form serves its intended purpose.
- Do clearly print the child's name and other details to avoid any confusion.
- Do administer the screening test in a quiet environment to limit distractions.
- Do ensure that you have the necessary materials, such as colored blocks and pictures, ready before starting the assessment.
- Do provide clear instructions to the child for each section of the screening.
- Do place checks in the appropriate columns (Correct/Incorrect) accurately for each response.
- Don’t rush through the assessment; take the time needed for each question and activity.
- Don’t influence the child's answers by providing hints or leading questions.
- Don’t disregard any responses; even “no response” should be noted properly as “NR.”
- Don’t hesitate to repeat questions if necessary to ensure understanding.
Following these pointers can facilitate a more accurate assessment and provide valuable insights into the child’s language abilities.
Misconceptions
Understanding the MCPS Form 335-37 can be challenging due to various misconceptions that often arise. Here are seven common misunderstandings regarding this screening instrument:
- It can be completed by anyone. Many believe that anyone can administer the form. However, it is designed to be administered by a qualified speech-language pathologist to ensure accurate results.
- It is only for children with known speech issues. Some think this form is only for children who already have identified speech or language problems. In reality, it is a screening tool intended to assess any child's language skills, regardless of prior diagnosis.
- Results are definitive. There is a misconception that the results of this screening provide a conclusive diagnosis. This is not true; results should be interpreted as indicators that guide further evaluation if necessary.
- Only English speakers need to complete it. Some assume that the form applies solely to English-speaking children. However, it is applicable to children who speak other primary languages, as indicated in the follow-up section.
- All questions must be answered correctly. Many believe that children must get every question right to pass the screening. This is incorrect; specific passing criteria exist for various sections, not requiring perfection.
- The form is lengthy and overly complex. While the form appears detailed, it is structured to gather necessary information efficiently. Many users find it manageable when approached step by step.
- It can replace comprehensive assessments. Some think that completing this form eliminates the need for a full speech and language assessment. This form serves as a preliminary screening, not a substitute for a detailed evaluation by a professional.
Clarifying these misconceptions ensures that the MCPS Form 335-37 is used correctly and effectively in evaluating children's speech and language skills.
Key takeaways
When using the MCPS 335-37 form for speech-language screening, consider the following key points:
- Use Proper Administration. The screening should only be conducted by a certified speech-language pathologist to ensure accurate results.
- Check Responses Carefully. For each item on the form, you must indicate whether the child’s response is correct or incorrect. This will help in evaluating their language skills.
- Record Details Thoroughly. Ensure you write all necessary information, such as the child's name, birth date, and relevant responses, to maintain comprehensive records.
- Follow the Passing Criteria. The form outlines specific passing standards for different sections, such as needing 3 correct answers in the colors section. Keep these criteria in mind while assessing.
- Provide Feedback and Follow-Up. After completing the screening, document any observations or recommendations. Consider further evaluations if issues are identified.
Browse Other Templates
Tourist Visa Australia - Each applicant, including children, must submit separate forms.
Braden Scale Score Interpretation - The Braden Scale assesses the risk of developing pressure sores in patients.