Fill Out Your Medication Administration Record Sheet Form
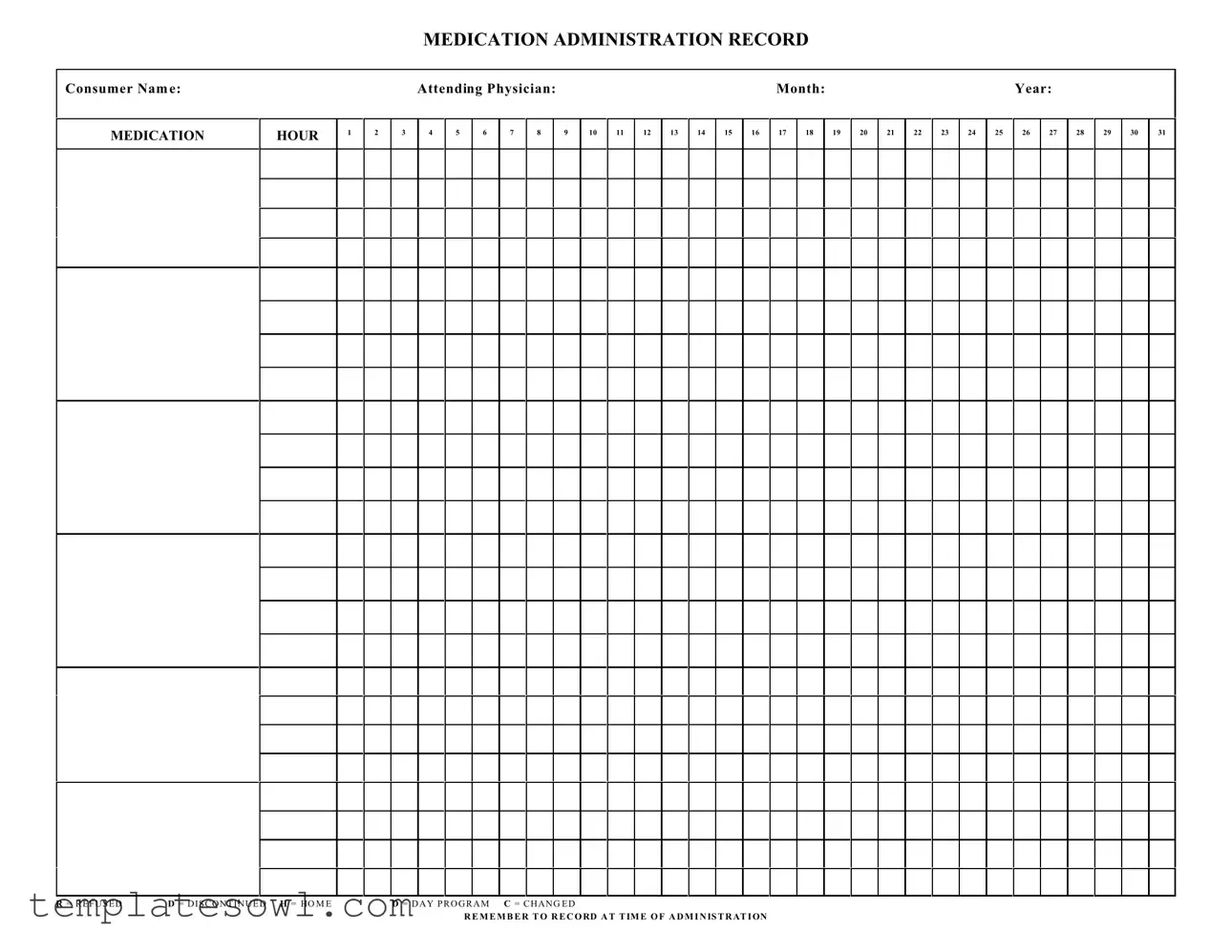
The Medication Administration Record (MAR) Sheet is a vital tool used in healthcare settings to ensure accurate and efficient medication management for consumers. It facilitates the orderly documentation of medication administration, allowing healthcare providers to track when each medication is given. Each entry includes essential information such as the consumer's name, the attending physician, and the specific month and year. The form is organized by hour, providing designated spaces to note the administration of medications throughout the day. Each day of the month is represented with clear boxes for recording medication given at specific times. Additionally, different codes such as R for Refused, D for Discontinued, H for Home, D for Day Program, and C for Changed provide quick reference options to indicate particular circumstances. This structured approach not only enhances accountability but also ensures that all changes and refusals are documented promptly, fostering better communication among caregivers. By following the prescribed guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure that they record the administration at the correct time, which is critical for maintaining medication safety and efficacy.
Medication Administration Record Sheet Example
MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION RECORD
Consumer Nam e:
MEDICATION
HOUR
1
2
|
Attending Physician: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Month: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year: |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R = R E F U S E D |
D = D I S C O N T I N U E D H = HO M E |
D = D A Y P R O G R A M C = C H A N G E D |
R E M E M B E R T O R E C O RD A T T IM E O F A D M I N IS T R AT I ON
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Medication Administration Record Sheet is used to document the administration of medications to consumers in a structured manner, ensuring compliance and safety in medication management. |
| Format Requirements | Typically, the form includes spaces for consumer names, medication hours, and notations concerning refusals, discontinuations, and changes to medication. |
| Time of Recording | It is critical to record medication administration at the exact time it occurs. This helps maintain important records for healthcare oversight. |
| Legal Compliance | States may have specific laws governing the use of Medication Administration Records, making compliance essential. In California, for instance, the Health and Safety Code outlines requirements for medication administration documentation. |
| Standardized Codes | The form often includes standardized codes such as R for Refused, D for Discontinued, and H for Home. These codes help in quickly conveying the status of medication administration. |
| Attending Physician’s Role | Information regarding the attending physician is critical, as it connects the medication administration directly with medical oversight and accountability. |
| Monthly and Yearly Tracking | The inclusion of month and year allows for effective tracking over time, enabling healthcare providers to assess patterns in medication adherence and effectiveness for each consumer. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Medication Administration Record Sheet
Completing the Medication Administration Record Sheet is a vital task in healthcare settings. This form helps ensure that patients receive their medications correctly and on time. Properly filling out this form is essential for maintaining accurate medical records. Here’s how to do it step by step.
- Enter the Consumer Name: Write the full name of the patient at the top of the form in the designated space.
- Fill in the Attending Physician's Name: Specify the name of the physician overseeing the patient’s care.
- Indicate the Month and Year: Write the current month and year in the specified areas for easy reference.
- Select the Medication Hours: In the boxes labeled 1 to 12, record the appropriate time the medication is to be administered.
- Document the Date: For each date of the month, fill in the boxes numbered 1 to 31 with the date the medication was administered.
- Record Medication Details: For each administration, enter details such as the name of the medication, dosage, and route of administration.
- Note Refused or Discontinued Medications: Use the letters R (Refused), D (Discontinued), H (Home), D (Day Program), and C (Changed) in the appropriate boxes to denote any discrepancies.
- Ensure Timely Documentation: Remember to record each medication administration at the time it occurs. This step is crucial for accuracy and accountability.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Medication Administration Record Sheet?
The Medication Administration Record Sheet (MARS) serves as a crucial tool for tracking the administration of medications to consumers. It is designed to ensure that all medication doses are administered correctly and documented in a timely manner. This form helps healthcare providers maintain an accurate record of what medications have been given, when they were given, and whether any doses were refused or discontinued. By using this sheet, it supports safe medication practices and enhances patient care.
How should I fill out the Medication Administration Record Sheet?
Filling out the MARS requires careful attention to detail. Start by entering the consumer's name and the attending physician's name at the top of the form. Next, you’ll need to indicate the month and year. For each hour of medication administration, mark the corresponding boxes for the days of the month. Use specific codes: “R” for refused, “D” for discontinued, “H” for home, “D” for day program, and “C” for changed. It is critical to record this information at the time the medication is administered, ensuring accuracy and minimizing the risk of errors.
What do I do if a medication was refused?
If a consumer refuses a medication, you should mark the corresponding box with an “R” at the appropriate hour on the MARS. It’s also important to document the reason for the refusal in the consumer's medical record, if applicable. This information helps healthcare providers understand the consumer's preferences and monitor their overall adherence to the medication plan. Consistent patterns of refusal may indicate a need for further assessment or a change in the medication regimen.
Can I use the Medication Administration Record Sheet for multiple consumers?
No, the MARS is designed to be used for one consumer at a time. Each sheet contains specific information pertinent to an individual, including their unique medication regimen. Using one sheet for several consumers would not only create confusion but also compromise the integrity of the medication records. It is essential to maintain separate records for each consumer to ensure clear and accurate documentation.
What should I do if I make a mistake on the Medication Administration Record Sheet?
If an error occurs while filling out the MARS, it is important to correct it appropriately to avoid any misunderstandings. Do not use whiteout or erasers, as these can obscure the original entry. Instead, you should cross out the mistake with a single line and initial it. Then, neatly write the correct information adjacent to the error. This practice ensures transparency in documentation and maintains the integrity of the record.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet form is crucial for ensuring accurate medication management. Mistakes in this form can have serious consequences for patient safety and care. One common error is failing to include the consumer's name. Omitting this vital information can lead to misadministration or confusion about which patient the record belongs to, causing further complications in their treatment.
Another mistake often made is neglecting to document the attending physician. Including the physician's name helps clarify responsibility for the medication prescribed and can be essential if there are questions or issues about the treatment plan later on. Always ensure this section is accurately filled out to maintain clear lines of communication.
People frequently forget to record the correct month and year when filling out the Medication Administration Record. This oversight might seem minor, but without accurate dates, tracking medication history becomes nearly impossible. Ensure you double-check these fields to avoid confusion.
A significant number of individuals also make the mistake of not clearly marking the appropriate medication hours. Each medication should have its assigned time, and failing to record this accurately can lead to administration discrepancies. Accuracy in this area is vital for each dose's timing and effectiveness.
Some users overlook the importance of noting if the medication was refused or discontinued. Marking "R" for refused or "D" for discontinued helps keep an accurate account of a patient's treatment and response to medication. Skipping this step can lead to misunderstanding the patient's needs and may result in unnecessary medication being offered thereafter.
The lack of timely recordings during administration is another common issue. It is crucial to document at the time of administration rather than guessing later. This practice ensures that the information is fresh and accurate, contributing to a reliable treatment history.
Lastly, failing to check for changes in medication requirements can pose risks. If medications change, the record must reflect these updates immediately. Utilizing the “C” notation in the designated place can help mark those alterations efficiently, keeping the entire medical team informed and aligned on the patient’s current needs.
Documents used along the form
The Medication Administration Record (MAR) Sheet is a crucial document in health care settings, primarily used to track the administration of medications to patients. Alongside the MAR, several other forms and documents support medical staff in providing effective and safe care to consumers. Below, you'll find a list of related documentation that plays a vital role in medication management and patient safety.
- Patient Information Sheet: This document provides essential details about the patient's demographics, medical history, and current medications. It ensures that all medical staff are informed about the individual's background, which is crucial for safe medication administration.
- Prescription Order: A formal directive from a physician indicating the specific medication the patient should receive. This document is the foundation for the MAR, as it details the dosage, frequency, and type of medication required.
- Medication Reconciliation Form: Used during patient transitions—such as admissions or discharges—this form compares the patient's current medication list against new prescriptions. It aims to avoid medication errors and ensure the continuity of care.
- Incident Report Form: This document is filled out if there is a medication error or an adverse drug reaction. It includes details about what occurred and actions taken to address the situation, serving as an important tool for quality improvement.
- Consent Form: Often required before a new medication is administered, this document captures the patient's or guardian's agreement to receive specific treatments or medications, ensuring that they are informed and consenting.
- Allergy Record: This form lists any known allergies a patient has, especially to medications. It’s crucial that this information is readily available to prevent allergic reactions during medication administration.
- Vital Signs Record: A log that tracks a patient’s vital signs, such as pulse, blood pressure, and temperature. These readings are often monitored before and after administering certain medications to assess the patient's response to treatments.
- Physician's Progress Notes: These notes provide ongoing updates about a patient's condition and treatment progress. They are essential for ensuring that every member of the health care team is aware of the current status and any changes in the patient's care plan.
- Discharge Summary: This document summarizes a patient's hospital stay and outlines any medications to continue after leaving the facility. It plays a crucial role in ensuring safe medication management after discharge.
These forms and documents, when used together with the Medication Administration Record, create a comprehensive approach to patient care, promoting safety, clarity, and communication among healthcare providers. Understanding each of these documents is essential for medical staff to enhance the quality of patient treatment and minimize errors.
Similar forms
- Patient Intake Form: This document collects essential information about a patient's medical history, allergies, and medications. Similar to the Medication Administration Record Sheet, it captures data crucial for effective treatment and medication management.
- Medication Reconciliation Form: This form addresses the need to compare a patient's current medication list against their prescribed medications. Like the Medication Administration Record Sheet, it ensures accuracy in medication administration and reduces the risk of errors.
- Patient Care Plan: A care plan outlines the overall treatment strategy for a patient, including medication schedules. It parallels the Medication Administration Record Sheet by coordinating therapeutic goals and specific medication instructions.
- Incident Report Form: This form documents any adverse events related to medication administration. While it serves a different purpose, both forms aim to enhance safety and improve the quality of care by tracking medication management.
- Progress Notes: Healthcare providers use progress notes to record observations and patient responses during treatment. These notes can reference the Medication Administration Record Sheet to monitor medication effectiveness and address any issues that arise.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet, attention to detail is crucial for ensuring the accurate administration of medications. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind.
- Do ensure that you fill in the consumer's name clearly at the top of the sheet.
- Don't leave any sections blank. Every field must be completed to maintain comprehensive records.
- Do record the date, month, and year accurately for each entry.
- Don't use abbreviations or unclear language when indicating medication status (e.g., refused, discontinued).
- Do make timely entries at the exact time of administration or refusal.
- Don't overwrite or use correction fluid on the sheet; this can lead to confusion or disputes.
- Do sign and date the form if required, ensuring accountability for the administration process.
- Don't forget to inform the attending physician if there are any changes or issues with medication administration.
- Do store the completed sheets in a secure location to protect the consumer's confidential information.
By adhering to these guidelines, you contribute to the safety and well-being of individuals receiving medication. Each entry is an important part of their care journey.
Misconceptions
Understanding the Medication Administration Record (MAR) Sheet is important for anyone involved in medication management. However, several misconceptions surround its use. Here are seven common misunderstandings:
- It's only for nurses to fill out. The MAR sheet can be used by any qualified staff member responsible for medication administration, not just nurses.
- All medications must be recorded at once. Medications should be recorded at the time of administration, allowing for accurate tracking. It's okay to document medications as they are given.
- It's unnecessary if medications are administered daily. Even if medications are given daily, each administration must be documented to ensure proper tracking and safety.
- Using abbreviations is always acceptable. While some abbreviations are commonly used, it's essential to use clear language to avoid misunderstandings, especially in critical situations.
- The MAR sheet is only important for prescribed medications. Any medication administered, including over-the-counter drugs, should be recorded on the MAR sheet.
- One error can always be corrected later. It's crucial to double-check entries in real-time, as corrections may lead to further complications or errors in patient care.
- It's not necessary to document refusals. Recording refused medications is vital. It helps to understand a patient’s compliance and can impact their treatment plan.
Clearing these misconceptions can help ensure safe and effective medication management. Proper use of the MAR sheet is vital for patient care and safety.
Key takeaways
The Medication Administration Record (MAR) Sheet is a crucial tool for managing medication. Understanding how to effectively fill it out and use it can enhance patient safety and care quality.
- Consumer Name: Always include the full name of the consumer receiving medication to avoid any confusion.
- Attending Physician: Document the name of the attending physician. This provides a point of contact for any medication-related questions.
- Month and Year: Clearly indicate the month and year. This aids in tracking and organizing records over time.
- Medication Hours: The form allows for medication entries throughout the day. Each hour should be accurately noted to ensure timely administration.
- Medication Codes: Familiarize yourself with the coding system for refusals, discontinued medications, and other statuses. This includes letters such as R for refused and D for discontinued.
- Record Time: It is essential to record the actual time of administration. Accurate timestamps help maintain a clear history of medication intake.
- Changes: If there are changes in medication, make sure to note this on the record. Keeping track of medication adjustments is vital for continuity of care.
- To Avoid Errors: Double-check entries before finalizing them. Mistakes in the MAR can lead to incorrect medication administration.
- Training: Ensure all staff responsible for completing the MAR are trained in how to fill it out properly. This promotes consistency and accuracy in the records.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular reviews of the MAR sheets. Audits can help identify trends or issues that need addressing.
Adhering to these practices can lead to improved medication management and better health outcomes for consumers.
Browse Other Templates
Pa Tint Exemption Form - There is a fee associated with each temporary registration plate, which is $17.
Proof of Income Letter Self-employed - Both the owner's signature and the notary's signature are required on the document.
Electrician Certification Texas - Submit a Certificate of Insurance post-examination to meet licensing requirements.