Fill Out Your Monthly Budget Worksheet Form
Creating a solid financial plan requires careful tracking of income and expenses, and the Monthly Budget Worksheet provides an effective tool for achieving this clarity. By laying out your income sources such as paychecks, alimony, and other revenues, the worksheet allows you to see the big picture of your financial landscape. Moving to expenses, it categorizes essential spending—like housing, utilities, and food—while also accounting for irregular costs throughout the year. Notably, it prompts users to plan for expenses that may not fall on a traditional monthly billing cycle, such as medical bills and annual fees, helping ensure unanticipated costs don’t derail your budget. Additionally, this worksheet encourages individuals to document their financial performance by comparing what they budgeted against what was actually spent, identifying discrepancies that could lead to informed decisions for future months. In turn, documenting your financial journey can highlight areas for improvement and potentially guide you toward healthier spending habits. Furthermore, should anyone find themselves overwhelmed by their financial situation, the sheet reminds individuals of resources available, such as connecting with HUD-certified housing counselors for support and guidance. This comprehensive approach not only aids in budgeting but also fosters a proactive mindset toward financial well-being.
Monthly Budget Worksheet Example
Monthly Budget Worksheet
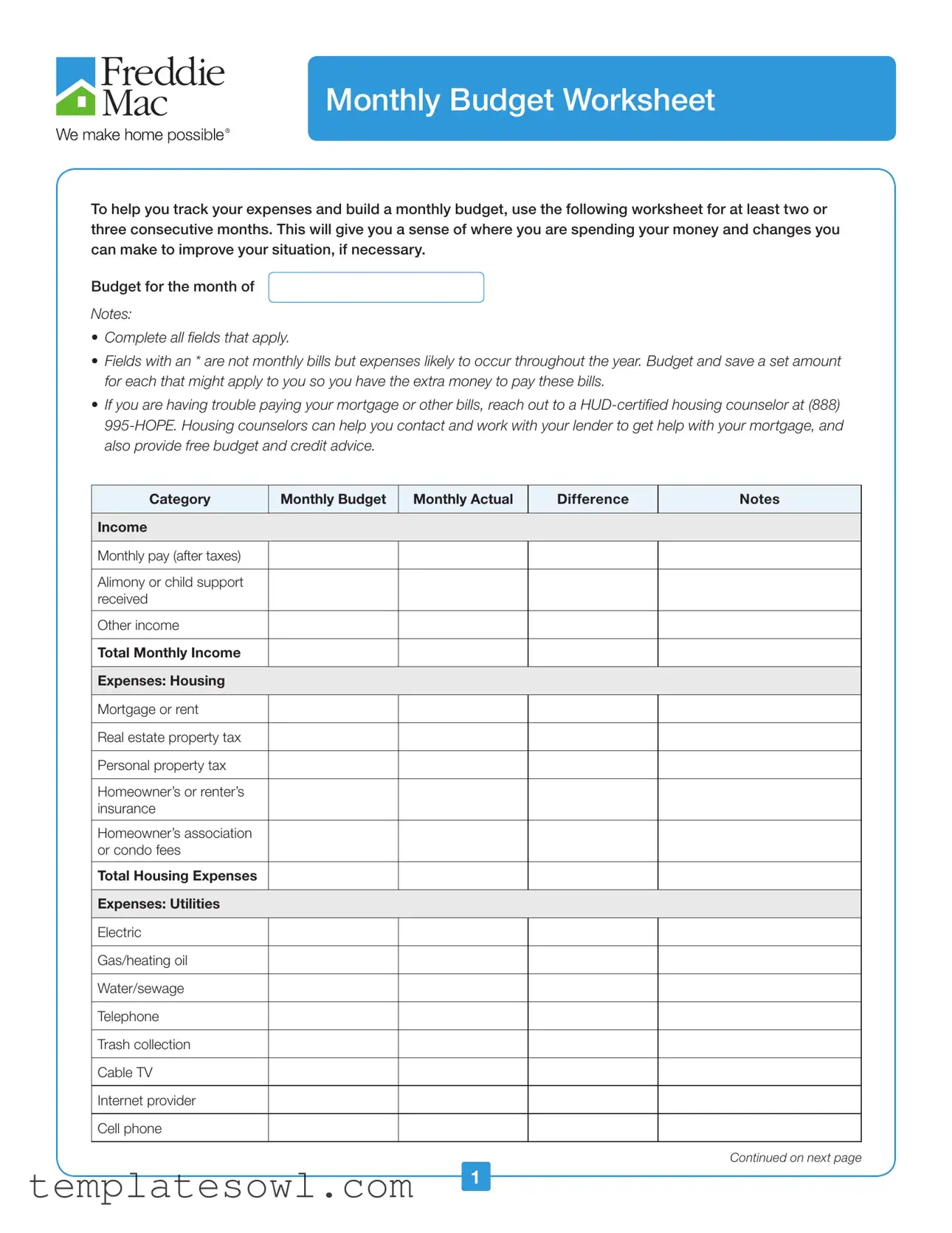
To help you track your expenses and build a monthly budget, use the following worksheet for at least two or three consecutive months. This will give you a sense of where you are spending your money and changes you can make to improve your situation, if necessary.
Budget for the month of
NOTES:
•Complete all ields that apply.
•Fields with an * are not monthly bills but expenses likely to occur throughout the year. Budget and save a set amount for each that might apply to you so you have the extra money to pay these bills.
•If you are having trouble paying your mortgage or other bills, reach out to a
Category
Monthly Budget
Monthly Actual
Difference
Notes
Income
Monthly pay (after taxes)
Alimony or child support received
Other income
Total Monthly Income
Expenses: Housing
Mortgage or rent
Real estate property tax
Personal property tax
Homeowner’s or renter’s insurance
Homeowner’s association or condo fees
Total Housing Expenses
Expenses: Utilities
Electric
Gas/heating oil
Water/sewage
Telephone
Trash collection
Cable TV
Internet provider
Cell phone
Continued on next page
1
Monthly Budget Worksheet
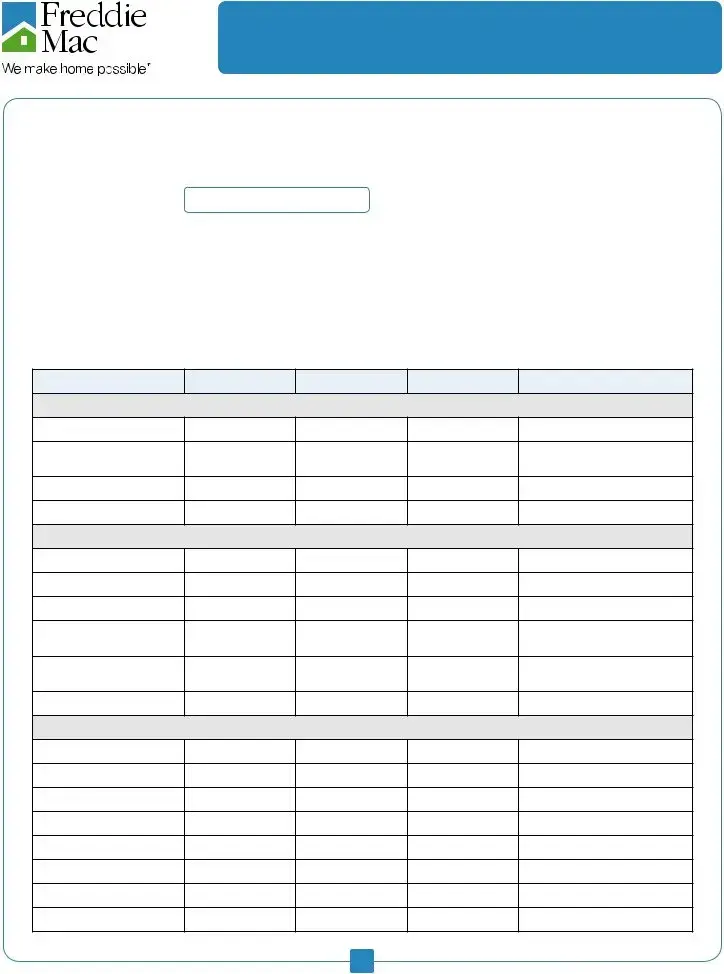
Category
Monthly Budget
Monthly Actual
Difference
Notes
Expenses: Health/Medical
*Expenses that you can budget for, so you have money saved to pay for unplanned or annual bills.
Medical insurance
Dental insurance
Doctor/lab*
Dentist*
Orthodontist*
Therapist*
Eyeglasses/ophthalmolo-
Hospital/emergency*
Medicines*
Other
Total Health/Medical
Expenses
Expenses: Transportation
*Expenses you can budget for, so you have money saved to pay for unplanned or annual bills.
Car payments
Car insurance
Car maintenance/repair*
Mass transit costs
Gas
Parking/tolls
Tags/inspection*
Total Transportation
Expenses
Expenses: Credit Cards, Loans, OE
*Expenses you can budget for, so you have money saved to pay for unplanned or annual bills.
Credit Card:
Balance:
Credit Card:
Balance:
Credit Card:
Balance:
Student Loans
Legal Fees
Alimony/child support paid
Total Credit Card/Loan/
Other Balances and Fees
Continued on next page
2
Monthly Budget Worksheet
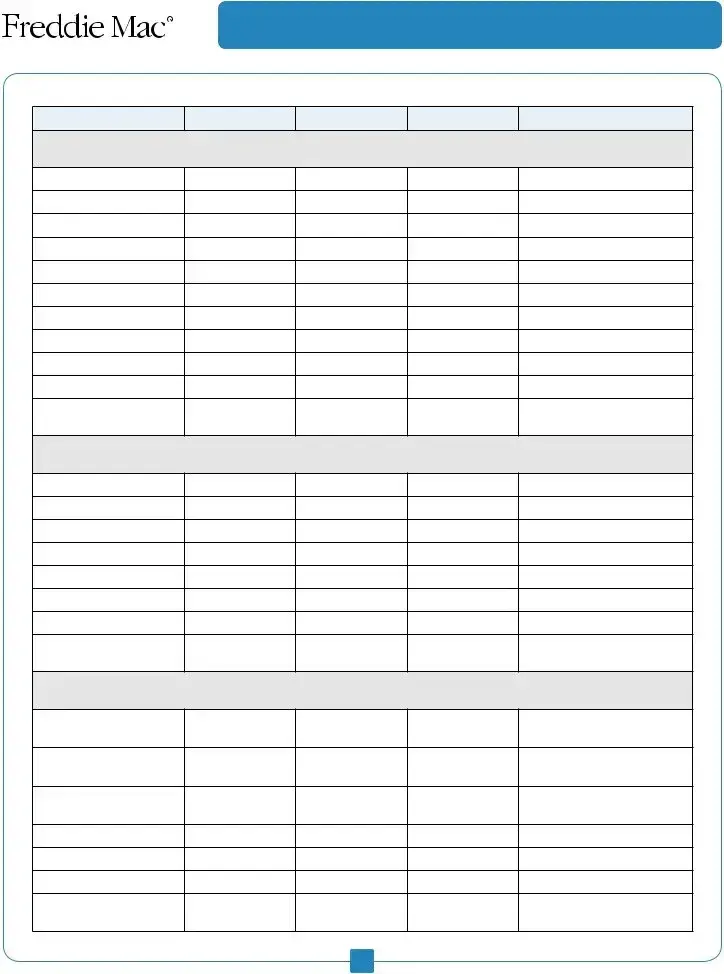
Category
Monthly Budget
Monthly Actual
Difference
Notes
Expenses: Food and Entertainment
Groceries
Meals out
Entertainment (movies, etc.)
Hobbies
Total Food and
Entertainment
Expenses: Children
Child care
School tuition
Lunch money
School supplies
Lessons/sports
New clothing
Personal grooming
Allowances
Other
Total Children Expenses
Expenses: Personal
Dry cleaning/laundry
Personal grooming
New clothing
Total Personal Expenses
Expenses: Savings/Large Expenses
*Expenses you can budget for, so you have money saved to pay for unplanned or annual bills.
Savings amount going into an account each month
Gifts (holiday, birthday)*
House maintenance/ repairs*
Furniture*
Church/charity*
Vacation*
Total Savings/Large
Expenses
Total Monthly Income
Total Monthly Expenses
Difference
3
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Monthly Budget Worksheet helps individuals track their expenses and manage their budget effectively. |
| Usage Duration | It is recommended to use the worksheet for at least two or three consecutive months. |
| Fields Included | Users should complete all applicable fields. Some fields marked with an asterisk (*) are for year-related expenses. |
| Support Resources | If you struggle with bills, it's suggested to contact a HUD-certified housing counselor at (888) 995-HOPE for assistance. |
| Expense Categories | The form includes categories like housing, utilities, transportation, and savings, helping to break down spending. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Monthly Budget Worksheet
Once you've gathered your income and expense sources, it’s time to tackle the Monthly Budget Worksheet. By tracking your finances, you can make informed decisions about spending and saving. Let’s break down the steps to fill it out clearly and effectively.
- Gather Your Financial Information: Collect all income statements, bills, and receipts for monthly expenses. This will ensure accurate budgeting.
- Fill in Your Income: Start with the income section. Write down your monthly pay (after taxes). Include any alimony or child support received, along with other income sources. Add these figures up to get your Total Monthly Income.
- Document Housing Expenses: List all housing-related costs like your mortgage or rent, property taxes, and insurance. Sum these to find the Total Housing Expenses.
- Calculate Utility Costs: In the Utilities section, record expenses for electricity, gas, water, telephone, and internet. Total these amounts for Total Utility Expenses.
- Account for Health/Medical Expenses: Fill in expected costs like medical and dental insurance, along with anticipated doctor visits. Do not forget to include any medicine costs. Add them up for Total Health/Medical Expenses.
- Track Transportation Expenses: Write down all transportation costs, including car payments and gas. Remember to consider maintenance and parking fees. Get a total for Total Transportation Expenses.
- List Credit Cards and Loans: Note your credit card balances, student loans, and any other debts. Total these for Total Credit Card/Loan/Others Balances and Fees.
- Record Food and Entertainment Expenses: Enter your groceries, dining out, and entertainment expenses. Summarize these for Total Food and Entertainment Expenses.
- Include Children-related Expenses: Add up costs related to child care, school supplies, and clothing. This will give you Total Children Expenses.
- Detail Personal Expenses: Write down expenses like dry cleaning and personal grooming. Total these for Total Personal Expenses.
- Log Savings/Large Expenses: List any savings contributions and planned large purchases such as gifts or vacations. Sum these for Total Savings/Large Expenses.
- Calculate Total Monthly Expenses: Add together all your expenses from the various categories to find your Total Monthly Expenses.
- Determine the Difference: Subtract your Total Monthly Expenses from Total Monthly Income to see what’s left. This difference can indicate how well you’re managing your budget.
When completed, this worksheet can serve as a valuable tool for tracking your finances and planning for future needs. With honest assessment and a bit of diligence, you can refine your budgeting strategies over time.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Monthly Budget Worksheet?
The Monthly Budget Worksheet is designed to help individuals track their expenses and establish a monthly budget. By using this worksheet over a period of two or three months, users can identify spending patterns and areas where adjustments may be necessary, thus improving their financial situation.
How do I fill out the Monthly Budget Worksheet?
To complete the worksheet, fill in all applicable fields for both income and expenses. Start by documenting your total monthly income. Next, list out each category of expenses, such as housing, utilities, and transportation. Be sure to note any expenses that occur less frequently by budgeting a set amount for those. This will facilitate easier payment when those expenses arise.
What types of income should be included in the worksheet?
Include all sources of income that you receive on a monthly basis, such as your pay after taxes, any alimony or child support, and additional income like freelance work or investments. Ensure that the total accurately reflects your financial situation.
What expenses should I categorize using the worksheet?
Expenses should be categorized into sections such as housing, utilities, health/medical, transportation, food, children, personal expenses, and savings. Each category should include line items that reflect your specific spending habits and needs, including both regular monthly bills and annual expenses.
What are the “*” fields mentioned in the worksheet?
Fields marked with an asterisk (*) indicate expenses that are not monthly bills but are likely to occur throughout the year. These could include medical expenses or car maintenance costs. It is advisable to budget and save a set amount for these expenses to ensure that you can cover them when they arise.
How can I track my actual spending against my budget?
Each month, record your actual spending in the designated area next to the budgeted amount. After documenting your expenses, calculate the difference to see how well you adhered to your budget. This will help you evaluate areas where you may need to adjust either your spending or your budget planning.
What should I do if I find it difficult to pay my mortgage or bills?
If you are experiencing trouble with mortgage payments or other bills, consider reaching out to a HUD-certified housing counselor at (888) 995-HOPE. Housing counselors can provide guidance, assist in negotiating with lenders, and offer free advice on budgeting and credit management.
How can I manage irregular or large expenses within my budget?
Managing irregular or large expenses starts with recognizing their potential impact on your finances. The worksheet allows you to set aside funds monthly for anticipated large expenses, such as home repairs or holiday gifts. By planning ahead, you can ensure that you have the necessary funds when those expenses arise.
What should I do if my actual expenses exceed my budgeted amounts?
If you find that your actual expenses exceed your budgeted amounts, it may be beneficial to review your spending habits. Analyze which categories are consistently exceeding budgets and determine if they are essential or if adjustments can be made. It may also be necessary to recalibrate your budget to reflect realistic spending practices.
How often should I review my budget?
Regularly reviewing your budget each month is essential. Consistent evaluations allow you to stay aware of your financial health and make informed decisions. As your income or expenses change, updating your budget will help you to remain on track toward achieving your financial goals.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Monthly Budget Worksheet can significantly aid in financial planning. However, many individuals make common mistakes that can compromise the effectiveness of the worksheet. One frequent error is failing to complete all applicable fields. Missing entries can lead to an inaccurate overall picture of one’s finances, making it hard to identify areas for improvement.
Another mistake occurs when expenses are underestimated. Individuals often provide lower figures for variable costs, mistakenly believing that they will spend less than they actually do. This practice can create a misleading budget, which does not reflect true spending habits. It is vital to review past statements to ensure that estimates are realistic.
Not including irregular or annual expenses is a third mistake. Certain expenses, such as property taxes or holiday gifts, are not monthly occurrences. Ignoring these costs can result in being unprepared when these payments arise. Instead, it is advisable to allocate funds for these expenditures in advance.
Inadequate tracking of actual spending is another common error. After establishing a budget, individuals often neglect to compare their planned expenses with actual spending. Regularly updating the worksheet with real expenses can provide valuable insights and help in maintaining accountability.
Failing to include all sources of income presents yet another issue. Some people only report their primary salary and overlook other income streams. To work towards financial goals effectively, it is essential to include all sources of income, such as freelance work or rental income.
Leaving out notes or comments is also a mistake. Using the notes section can offer explanations for budget variances. This practice helps in understanding spending patterns and provides context that can influence future budgeting decisions.
Ignoring the advice to contact a housing counselor in the event of financial distress reflects another oversight. It's important to seek help when facing difficulties in managing bills. Accessing resources for professional guidance can prove invaluable in creating a feasible budget and addressing financial obstacles.
Finally, not reviewing the budget on a regular basis can hinder progress. When individuals fail to revisit their budgets each month or quarter, they may overlook necessary adjustments based on changing circumstances. A budget should be a dynamic tool, adapting to evolving financial situations.
Documents used along the form
When managing your finances, several documents complement the Monthly Budget Worksheet to provide a complete picture of your financial health. These resources help track your spending, plan for the future, and ensure that you stay on top of your financial goals. Here is a list of common forms and documents often used alongside the Monthly Budget Worksheet.
- Income Statement: This document summarizes all your sources of income for a specific period. It helps you identify your total earnings and ensure that you are budgeting accurately.
- Expense Tracker: This ongoing record allows you to monitor spending on a day-to-day basis. By noting expenses immediately, you can easily adjust your budget in real-time.
- Savings Goal Planner: This form focuses on specific savings targets, like a vacation or emergency fund. It helps define how much to save and by when, making your goals more tangible.
- Debt Repayment Schedule: A detailed plan that outlines how and when you will pay off debts. It is essential for managing credit card balances, loans, or any other financial obligations.
- Financial Goals Worksheet: This document helps you set short-term and long-term financial objectives. Clearly defining these goals can lead to better budgeting and prioritization.
- Utility Comparison Sheet: Used to compare costs among different utility providers, this sheet helps identify potential savings on expenses like electricity, water, and internet.
- Monthly Expense Reports: A summary of your monthly spending, offering insights into where your money goes. Reviewing past reports can inform future budgeting decisions.
- Annual Budget Planner: This comprehensive form projects income and expenses for the entire year. It allows for seasonal variations in review and can help avoid overspending during high-expense months.
- Investment Tracking Sheet: A document that keeps tabs on any investments, including stocks or retirement funds. Tracking performance helps gauge financial health and adjust goals as necessary.
- Emergency Fund Calculator: A helpful tool for understanding how much you should save for unexpected expenses. This can be reassuring and help prepare for financial surprises.
Using these documents in conjunction with the Monthly Budget Worksheet will significantly improve your financial management. They provide clarity, foster accountability, and promote informed decision-making. With the right tools, you can successfully navigate your financial landscape.
Similar forms
Personal Finance Tracker: Similar to a Monthly Budget Worksheet, a personal finance tracker allows individuals to monitor their income and expenses. This tool provides a comprehensive view of financial health over time, helping users identify spending patterns and areas for improvement.
Expense Report: An expense report details an individual's expenditures during a specific period, much like the Monthly Budget Worksheet. This report typically records specific categories of spending, allowing users to compare expected costs with actual expenses.
Spending Plan: A spending plan outlines how an individual intends to allocate their income across various expenses, akin to a monthly budget. It encourages proactive financial management by promoting intentional spending habits and helping avoid overspending.
Financial Goals Worksheet: A financial goals worksheet focuses on setting and tracking personal financial objectives, similar to the Monthly Budget Worksheet which aids in understanding spending habits. Both documents foster mindful financial planning, although one is more about immediate budgeting while the other emphasizes future aspirations.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Monthly Budget Worksheet form, there are several important practices to follow, as well as some common pitfalls to avoid. Below are four key dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
- Do: Complete all fields that apply to your financial situation. This includes both sources of income and expenses.
- Do: Remember to budget for irregular expenses by setting aside money in advance. These might include annual bills such as property taxes or insurance premiums.
- Don't: Leave out any significant expense categories. Ensure you account for both regular and occasional expenses to get a comprehensive view of your finances.
- Don't: Rush through the process. Take your time to review and enter information accurately, as this worksheet serves as a critical tool for managing your finances effectively.
Misconceptions
Here are five common misconceptions about the Monthly Budget Worksheet form, along with clarifications for each:
- It's only for people with serious financial issues. Many believe that budgeting is reserved for those facing financial distress. In reality, anyone can benefit from using a budget to track spending and savings, regardless of their financial stability.
- You must input every single expense to make it useful. While tracking all expenses can provide a clearer picture of spending habits, the worksheet can still be effective even if you focus on major categories. It's about understanding trends, not micromanaging every penny.
- Using it is complicated. Some may think that budgeting involves complex calculations and detailed financial knowledge. However, the Monthly Budget Worksheet is designed to be straightforward and user-friendly, making it accessible for everyone.
- It's only necessary once a year. Many assume that they only need to create a budget during tax season or when preparing for a big purchase. In fact, consistently using the worksheet over several months provides valuable insights and allows for adjustments as circumstances change.
- The worksheet is only for tracking expenses. While its primary function is to log monthly income and expenses, it also encourages savings and helps plan for larger or less frequent costs throughout the year, making it a comprehensive financial tool.
Key takeaways
Filling out and utilizing the Monthly Budget Worksheet can significantly enhance your understanding of your financial situation. Here are some key takeaways to consider:
- Track for at least two months: Consistent tracking over two or three consecutive months will provide you with a clearer picture of your spending habits.
- Complete all applicable fields: Make sure to fill out all fields that apply to you. This will help gather comprehensive data on your income and expenses.
- Plan for irregular expenses: Keep in mind that some expenses, marked with an asterisk (*), are not monthly bills. Allocate funds for these to avoid financial surprises later on.
- Monitor differences: Review the difference between your budgeted amounts and actual spending. This can reveal trends that may need addressing.
- Don’t hesitate to seek help: If you struggle with bills or your budget, reach out to a HUD-certified housing counselor. They can offer valuable guidance and resources.
- Include all income sources: Make sure to account for every source of income, such as wages, alimony, or child support. This ensures your total income is accurate.
- Review regularly: Make it a habit to review your budget regularly. Regular check-ins will help you adjust spending and savings according to your financial goals.
Incorporating these strategies can promote better financial health and aid in making informed decisions regarding your spending and savings.
Browse Other Templates
Codicil to Will in Florida - This document must be carefully drafted to avoid potential legal disputes among beneficiaries.
Housing Authority Reno - Clear definitions of roles within the rental application process help streamline communication and expectations.
Heggstad Petition California - The petitioner must provide information about the deceased settlor and the trust in question.