Fill Out Your Nonconformity Report Form
The Nonconformity Report (NCR) form serves as a crucial tool in the quality management and compliance process, designed to document and address deviations from established standards or procedures. This form is structured with several key sections, each tailored to ensure thorough communication and resolution of nonconformities identified during audits. In the first section, specific details about the non-conformity are captured, including a concise description, the auditor's name, and relevant standards being violated. The second section is dedicated to the auditee's proposed action plan, where root cause analysis is performed to unpack how and why the issue occurred. It highlights necessary corrections to be implemented promptly, alongside corrective actions aimed at preventing future occurrences. The third section emphasizes the auditor's verification of the auditee's efforts to enact the action plan, ensuring accountability and proper follow-through. Finally, the form concludes with a confirmation from the auditor that the NCR has been effectively resolved, signaling a collaborative effort towards compliance and improvement. By capturing these elements, the NCR form facilitates structured problem resolution and enhances an organization’s adherence to regulatory and quality standards.
Nonconformity Report Example
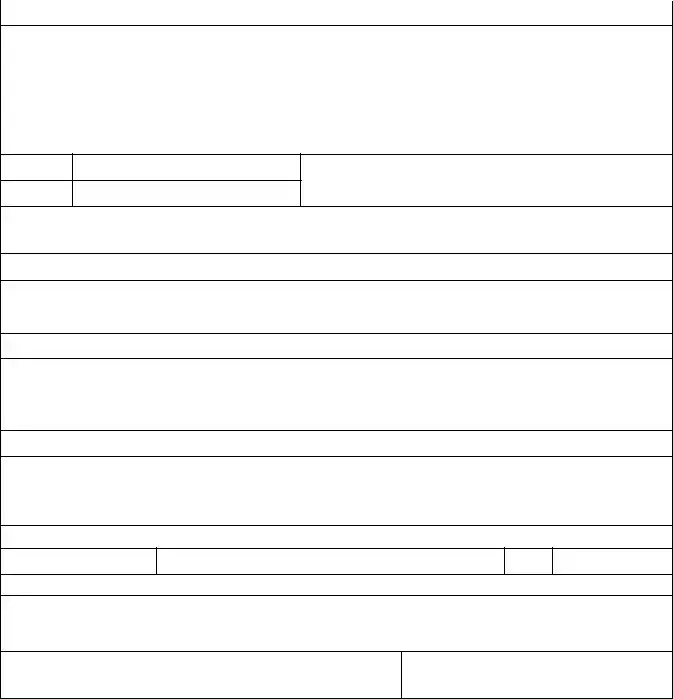
Annex A – Example of a Nonconformity Report (NCR) form
NCR # |
Client: |
|
File No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function/Area/Process: |
|
|
Site: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Std. and Clause No(s): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Section 1- Details of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Description |
|
|
Auditor :
Date:
Auditee representative acknowledgement: |
Category: |
|
|
Section 2- Auditee Proposed Action Plan
(Attach separate sheet if required)
Root Cause analysis (how/why did this happen?):
Correction (fix now) with completion dates:
Corrective Action (to prevent recurrence) with completion dates:
“Auditor” review and acceptance of Corrective Action Plan:
Auditee representative:
Date:
Section 3- Details of “Auditor” verification of Auditee implementation of action plan
Section 4- NCR closed out by “Auditor” on (date):
“Auditor” Team Leader name:
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Fact Description |
|---|---|
| NCR Purpose | The Nonconformity Report (NCR) form is used to document any deviations from established standards during an audit. It ensures accountability and fosters engagement in corrective processes. |
| Auditor Involvement | An auditor is responsible for reviewing the non-conformity and accepting the proposed corrective action plan to ensure proper resolution. The auditor’s acceptance is vital to closing the NCR. |
| Root Cause Analysis | Section 2 of the NCR form includes a root cause analysis, which helps identify the reasons behind the non-conformity. Understanding the root cause is essential for effective corrective measures. |
| Category Importance | The NCR form categorizes the non-conformity. Categorization aids in prioritizing which issues require immediate attention and assists in tracking recurring problems over time. |
| Closure Documentation | Closure of the NCR is documented by the auditor in Section 4. This documentation provides a formal confirmation that the issues have been addressed, allowing for accountability. |
| State-Specific Compliance | In some states, compliance with industry regulations requires the use of specific NCR forms and adherence to governing laws. It is crucial to verify local regulations applicable to the NCR. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Nonconformity Report
Completing the Nonconformity Report (NCR) form accurately is crucial for tracking and addressing issues that arise in processes. After filling out the form, it will be submitted for review and action based on the proposed plans for corrective measures.
- Begin by entering the NCR # at the top of the form.
- Specify the Client name and the File No.
- Identify the Function/Area/Process related to the non-conformity.
- Indicate the Site where the non-conformity was observed.
- List the applicable Standard and Clause No(s).
- In Section 1, provide a detailed Description of the non-conformity.
- Input the Auditor name and the Date of the report.
- Obtain and note the Auditee representative acknowledgement.
- Classify the non-conformity by selecting an appropriate Category.
- Proceed to Section 2, where the Auditee Proposed Action Plan is documented. If necessary, attach a separate sheet for more detailed information.
- Conduct a Root Cause analysis to determine how and why the issue occurred.
- Detail the Correction measures that will be taken immediately along with their completion dates.
- Outline the Corrective Action plans to prevent recurrence, including projected completion dates.
- Have the Auditor review and accept the Corrective Action Plan, then have the Auditee representative sign and date the section.
- In Section 3, provide details of the Auditor’s verification of the Auditee’s implementation of the action plan.
- Complete Section 4 by indicating when the NCR was closed out by the Auditor and providing the Auditor Team Leader name.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is a Nonconformity Report (NCR) form?
A Nonconformity Report (NCR) form is a document used to record instances where a product, service, or process does not meet specified standards. It captures essential information about the issue, including its description, root causes, and the proposed action plan for resolution. The form serves as a formal record to ensure accountability and facilitate improvement.
What information is required to complete the NCR form?
Completing the NCR form requires various details. Initially, it identifies the nonconformity with a clear description, along with associated factors like the auditor's name, the date, and the client's information. Furthermore, sections outlining the root cause analysis, corrective actions, and action plan implementation must be filled in to allow for thorough follow-up and resolution.
Who is responsible for filling out the NCR?
The responsibility of filling out the NCR typically lies with the auditor who identifies the nonconformity. However, collaboration with the auditee is essential. The auditee must provide details about the corrective actions taken and their effectiveness in rectifying the issues highlighted.
What is the purpose of the root cause analysis section?
The root cause analysis section is critical. It seeks to uncover the underlying reasons that led to the nonconformity. By analyzing how and why the issue occurred, organizations can prevent similar issues from arising in the future. This section serves as the foundation for developing an effective corrective action plan.
What should be included in the corrective action plan?
The corrective action plan should detail the specific actions to be taken to rectify the nonconformity. This includes immediate corrections to fix the identified problem and longer-term corrective actions aimed at preventing recurrence. Each action should also specify completion dates and responsible parties to ensure accountability.
How is the auditor involved in the NCR process?
The auditor plays a critical role throughout the NCR process. Initially, they identify and document the nonconformity. After the auditee submits their action plan, the auditor reviews and accepts that plan to ensure its adequacy. Verification of the implementation of the action plan and the closure of the NCR is also overseen by the auditor.
What are the potential outcomes after submitting the NCR form?
After submitting the NCR form, several outcomes may arise. If the auditor finds the corrective action adequate, the NCR can be marked as closed. Alternatively, if the actions are insufficient, further clarification or additional steps may be necessary. The outcome is a vital part of maintaining quality and compliance within an organization.
Is there a deadline for resolving issues highlighted in an NCR?
Typically, there is a designated time frame for resolving nonconformities outlined in the NCR form. This deadline varies based on the nature of the issue, its severity, and organizational policies. Adhering to these deadlines is essential to preserving quality standards and promoting continuous improvement.
How can organizations benefit from using NCR forms?
Utilizing NCR forms fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within organizations. By documenting issues systematically, organizations can track patterns, enhance decision-making, and ultimately improve their processes. This results in higher quality products and services, bolstering customer satisfaction and trust.
What happens if nonconformities are not addressed?
Failure to address nonconformities can lead to serious consequences. Over time, unresolved issues may cause recurring problems, decrease product or service quality, and harm the organization’s reputation. Additionally, it may result in regulatory penalties or liability concerns in certain industries. Hence, addressing NCRs promptly is crucial for overall business health and compliance.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Nonconformity Report (NCR) form requires attention to detail. One common mistake is leaving fields incomplete. Sections such as the "Description" in Section 1 must contain a clear and thorough explanation of the non-conformity. Omitting information can lead to confusion and potential miscommunication later in the process.
Another frequent error is failing to clearly identify the root cause of the issue in the proposed action plan. Without a comprehensive analysis of what led to the non-conformity, corrective actions may not effectively address the underlying problem. This oversight can result in repeated issues.
Some individuals neglect to provide specific completion dates for both the correction and corrective action sections. Vague timelines can prevent accountability and hinder effective follow-up. Clear deadlines are essential for ensuring that actions are taken promptly.
It is also a mistake to provide insufficient detail in the proposed corrective actions. A well-defined plan is crucial for prevention of recurrence. Simply stating "we will fix it" lacks the necessary information on how such a fix will be implemented.
Another error is neglecting to obtain proper acknowledgment from the auditee representative on the form. Without this acknowledgment, there may be a lack of agreement on obligations, which can lead to misunderstandings regarding the implementation of the action plan.
It can also be problematic to skip the "Auditor" review section. This part is essential for verifying that the proposed actions are adequate. An oversight here can signify that an important checkpoint has been missed, leading to continued issues.
Many individuals forget to close out the NCR properly. The form requires the auditor’s signature and the date of closure. Without this final step, it remains unclear whether the issue has been fully resolved.
Finally, not keeping a copy of the completed NCR form can be an oversight. Retaining a record is essential for future reference and for ensuring that all parties involved are aligned on actions taken and resolutions reached.
Documents used along the form
The Nonconformity Report (NCR) form serves as a crucial document for identifying and addressing issues within various organizational processes. Accompanying the NCR, additional forms and documents can help streamline the reporting and response process. Below is a description of these related documents.
- Edit Checklist: This document outlines the necessary revisions or modifications to address identified non-conformities. It serves as a simple guide for ensuring all required changes are accurately implemented.
- Change Request Form: Whenever a significant alteration is necessitated due to a non-conformity, this form facilitates formal requests for changes. It includes details about what changes are proposed, their rationale, and potential impacts.
- Root Cause Analysis Template: This template aids teams in investigating the underlying causes of a non-conformity. By providing a structured approach, it helps ensure that the analysis is comprehensive and meaningful.
- Corrective Action Plan: This document outlines the steps that will be taken to rectify the non-conformity. It provides a clear path toward compliance and includes responsibilities, timelines, and performance metrics.
- Verification Report: After corrective actions have been implemented, this report documents the verification process. It captures evidence that actions were taken and evaluates their effectiveness in resolving the identified issue.
- Closure Report: Finally, this report signifies the formal closing of the NCR. It summarizes the entire process, confirming that all actions have been completed and the non-conformity has been resolved.
Utilizing these complementary documents in conjunction with the Nonconformity Report form ensures a thorough and organized approach to addressing issues. This holistic strategy ultimately promotes continuous improvement and adherence to quality standards.
Similar forms
The Nonconformity Report (NCR) form serves an important role in quality management and compliance. It bears similarities to several other documents in its purpose, structure, and the information it conveys. Below is a list of six documents that share these characteristics with the NCR form:
- Corrective Action Plan (CAP): Like the NCR, the CAP outlines specific actions to address non-conformities. It includes root cause analysis and specifies how to prevent similar issues in the future.
- Audit Report: Audit reports summarize findings from assessments much like the NCR does. They document areas of concern and often recommend corrective actions to enhance compliance and performance.
- Incident Report: Similar to the NCR, an incident report records details of a specific issue or event. It provides information on what occurred, why it happened, and outlines steps taken to rectify the situation.
- Deviation Report: This document identifies instances where a process did not conform to established protocols, much like the NCR. It highlights the deviation and seeks to establish corrective measures.
- Quality Management Review: A quality management review examines overall processes and systems. It shares a common goal with the NCR of ensuring compliance and addressing any identified shortcomings in procedures.
- Action Item List: An action item list details tasks required to resolve issues, similar to the NCR’s proposed action plan. It helps teams track performance and ensure accountability for necessary changes.
In summary, the Nonconformity Report form is a crucial tool for detecting and correcting issues within processes. Its similarity to these other documents underscores its importance in maintaining quality and compliance standards.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Nonconformity Report form, there are several best practices and pitfalls to avoid. Here are four key dos and don’ts.
- Do provide a clear and detailed description of the non-conformity. This ensures that everyone understands the issue being addressed.
- Do include root cause analysis. Understanding why the non-conformity occurred is essential for effective corrective action.
- Don't rush through the completion dates. Timelines for corrective actions should be realistic and achievable to ensure compliance.
- Don't forget to have the auditee representative acknowledge the report. This acknowledgment is vital for accountability.
By following these guidelines, individuals can enhance the clarity and effectiveness of the Nonconformity Report form, ultimately improving the process of addressing non-conformities.
Misconceptions
Misconceptions about the Nonconformity Report form can lead to confusion. Here are seven common ones that people might have:
- It's only for major issues. Many think the form is only necessary for significant problems. In reality, it can be used for any nonconformity, regardless of size.
- Only auditors can fill it out. While auditors typically complete the form, anyone involved in the process can report nonconformities.
- Filling it out is a long process. Some believe that completing the report takes too much time. However, many sections require straightforward information that can be filled out quickly.
- It's just a formality. People sometimes see the report as a box to check. However, it's an important tool for identifying and fixing problems to improve processes.
- All nonconformities have the same action plan. A common misconception is that there's a one-size-fits-all solution. Each nonconformity requires a tailored action plan based on its specific root cause.
- Once completed, it's done for good. Some believe that once the form is submitted, the matter is finished. In truth, ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure the actions taken are effective.
- The auditor has the final say. While the auditor reviews the actions, collaboration between the auditor and the auditee is key in developing the action plan and ensuring it's accepted.
Understanding these misconceptions can help improve the use and effectiveness of the Nonconformity Report form.
Key takeaways
Using the Nonconformity Report (NCR) form effectively is crucial for addressing compliance issues. Here are key takeaways to keep in mind:
- Understand the Purpose: The NCR form is designed to identify and document instances of nonconformity within a process or system.
- Complete All Sections: Ensure every section of the form is filled out thoroughly, including details about the nonconformity, corrective actions, and verification processes.
- Be Specific: Provide clear and concise descriptions of the nonconformity. Vague descriptions can lead to confusion down the line.
- Involve the Right People: Ensure that both the auditor and the auditee are involved in the process, as their insights are essential for effective resolution.
- Investigate the Root Cause: Conduct a thorough root cause analysis. Understanding how and why the nonconformity occurred is crucial for preventing future issues.
- Set Realistic Deadlines: When outlining corrective actions, set achievable completion dates to encourage timely resolutions.
- Follow Up: After implementing corrective actions, ensure that the auditor verifies their effectiveness to close the NCR appropriately.
- Document Everything: Keep records of all communications and actions taken to provide a clear trail of the nonconformity handling process.
- Review Regularly: Periodically assess past NCRs to identify patterns. This helps in making informed improvements in processes to reduce future occurrences.
These takeaways can guide you through the completion and use of the Nonconformity Report form, helping ensure compliance and continuous improvement.
Browse Other Templates
Blue Cross Referral - Communicate clearly with both referring and referring to providers to avoid misunderstandings.
Virginia Sports Physical Form Pdf - Prior hospitalizations or surgeries may affect a student's ability to participate.
VA Education Program Change Request,Veterans Training Program Modification Form,Change of Educational Benefits Application,VA Program Transition Form,Request for Training Program Adjustment,Veteran's Educational Change Form,Application for Program Ch - If you're on active duty, consult an Education Service Officer about your program.
