Fill Out Your Psychiatric Progress Note Form
The Psychiatric Progress Note form serves as an essential tool in the mental health field, specifically designed to facilitate comprehensive documentation by qualified professionals, such as psychiatrists or advanced practice nurses with prescribing privileges. This form allows practitioners to track a patient’s progress, ensuring that crucial information is recorded accurately and consistently. Key sections of the form include identifying information, which captures personal details such as the patient's name, date of birth, and gender—crucial for proper identification and reference. The form also requires documentation of interim history and mental status evaluations, enabling the provider to assess changes in the patient's condition since the last visit. Additionally, it addresses medications, including whether they are being taken as prescribed, any side effects, and potential allergic reactions. In a broader context, the form encompasses therapeutic interventions and the patient's response to these treatments, aiding in the continuous adjustment of care strategies. The inclusion of laboratory test results and vital signs further enriches the patient record, contributing to a holistic understanding of the individual's health status. As such, the Psychiatric Progress Note is not just a record; it is a pivotal component of the clinical process that promotes informed decision-making and enhances the quality of care delivered to those in need.
Psychiatric Progress Note Example

M S D P S T A N D A R D I Z E D D O C U M E N T A T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
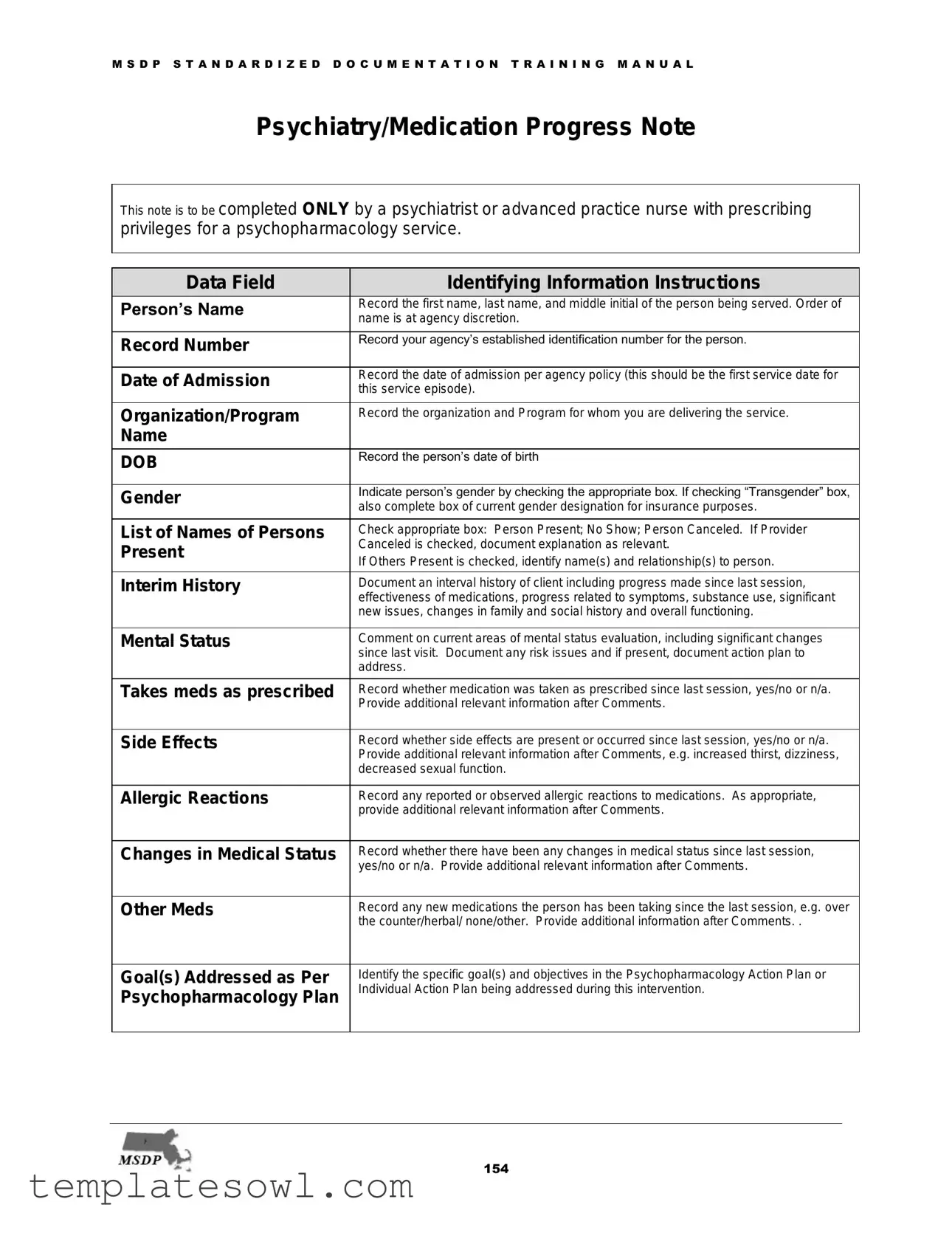
Psychiatry/Medication Progress Note
This note is to be completed ONLY by a psychiatrist or advanced practice nurse with prescribing privileges for a psychopharmacology service.
Data Field |
|
|
Identifying Information Instructions |
|
Person’s Name |
|
|
Record the first name, last name, and middle initial of the person being served. Order of |
|
|
|
name is at agency discretion. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Record Number |
|
|
Record your agency’s established identification number for the person. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date of Admission |
|
|
Record the date of admission per agency policy (this should be the first service date for |
|
|
|
this service episode). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Organization/Program |
|
|
Record the organization and Program for whom you are delivering the service. |
|
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOB |
|
|
Record the person’s date of birth |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gender |
|
|
Indicate person’s gender by checking the appropriate box. If checking “Transgender” box, |
|
|
|
also complete box of current gender designation for insurance purposes. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
List of Names of Persons |
|
|
Check appropriate box: Person Present; No Show; Person Canceled. If Provider |
|
Present |
|
|
Canceled is checked, document explanation as relevant. |
|
|
|
If Others Present is checked, identify name(s) and relationship(s) to person. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interim History |
|
|
Document an interval history of client including progress made since last session, |
|
|
|
|
effectiveness of medications, progress related to symptoms, substance use, significant |
|
|
|
|
new issues, changes in family and social history and overall functioning. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mental Status |
|
|
Comment on current areas of mental status evaluation, including significant changes |
|
|
|
|
since last visit. Document any risk issues and if present, document action plan to |
|
|
|
|
address. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Takes meds as prescribed |
|
|
Record whether medication was taken as prescribed since last session, yes/no or n/a. |
|
|
|
|
Provide additional relevant information after Comments. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Side Effects |
|
|
Record whether side effects are present or occurred since last session, yes/no or n/a. |
|
|
|
|
Provide additional relevant information after Comments, e.g. increased thirst, dizziness, |
|
|
|
|
decreased sexual function. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allergic Reactions |
|
|
Record any reported or observed allergic reactions to medications. As appropriate, |
|
|
|
|
provide additional relevant information after Comments. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in Medical Status |
|
|
Record whether there have been any changes in medical status since last session, |
|
|
|
|
yes/no or n/a. Provide additional relevant information after Comments. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Meds |
|
|
Record any new medications the person has been taking since the last session, e.g. over |
|
|
|
|
the counter/herbal/ none/other. Provide additional information after Comments. . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goal(s) Addressed as Per |
|
|
Identify the specific goal(s) and objectives in the Psychopharmacology Action Plan or |
|
Psychopharmacology Plan |
|
|
Individual Action Plan being addressed during this intervention. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
154

M S D P S T A N D A R D I Z E D D O C U M E N T A T I O N T R A I N I N G M A N U A L
Therapeutic Interventions |
|
|
Check one or more of the types of interventions delivered in the session: |
Delivered in Session |
|
|
Psychotherapy, Counseling/Coaching, Collaborative Medication Management, |
|
|
Collaborative Medication Education/Symptom/Illness Management, Injections, Physical |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assessment, Coordination of Care. For additional interventions utilized check other. |
|
|
|
Describe the content of the interventions. If any |
|
|
|
psychotic is prescribed it is suggested that the |
|
|
|
carefully documented. |
|
|
|
|
Response to Intervention |
|
|
Document person’s response to intervention(s) delivered in the session and person’s |
Delivered in Session and |
|
|
progress towards goals and objectives. If no progress is made over time, this section |
|
|
should also address changes in strategy to produce positive change in the person. |
|
Progress Toward Goals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and Objectives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lab Tests Ordered |
|
|
Summarize key laboratory test results received and reviewed. Check appropriate box to |
|
|
|
indicate whether key laboratory test results were ordered or, reviewed (with person). If |
|
|
|
lab results were not received, describe action to be taken to obtain results. |
|
|
|
|
AIMS Findings |
|
|
If AIMS (Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale) test was administered, document |
|
|
findings. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Height/Weight/BMI |
|
|
Record information pertaining to person’s height, weight, body mass index, blood |
Blood Pressure/VS |
|
|
pressure, and vital signs as relevant. Document if there has been communication |
|
|
between the prescriber and the PCP. Provide additional relevant information as |
|
|
|
|
appropriate. |
|
|
|
|
Diagnosis |
|
|
Document whether the person’s diagnosis has changed or not. If diagnosis has |
|
|
|
changed, check yes and proceed to Comprehensive Assessment Update form. |
Data Field |
|
|
Medication Orders Today |
None Prescribed |
|
|
Check box if no medications are prescribed today. If so, proceed to Next Appointment |
|
|
|
data field. |
Rationale for Changes in |
|
|
Document rationale for any medication changes. For each medication prescribed, |
Medications |
|
|
indicate if the medication is renewed(renew) /changed, newly prescribed (new) or |
|
|
discontinued (D/C). Write the name of the medication (med), dosage (dose), frequency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(frequency), # of Days, quantity (qty), and number of refills (refills) prescribed. |
|
|
|
For each new medication prescribed, the person should be given information about |
|
|
|
medication risks and benefits. Check the appropriate box indicating whether person has |
|
|
|
given “informed consent”, i.e. demonstrated an understanding of medication’s risks and |
|
|
|
benefits. Documentation of “Informed Consent” is mandatory. If the person does not |
|
|
|
demonstrate an understanding of the risks and benefits, then the prescriber should |
|
|
|
indicate in the Instructions /Comments Section what steps should be taken. |
|
|
|
This section should not be a substitute for a complete listing of medications. |
|
|
|
|
Instructions/Comments, as |
|
|
Document any additional relevant instructions or |
applicable: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Next Appointment |
|
|
Document time frame when the person should return to see the prescriber. |
|
|
|
|
MD/DO/APN (Print Name) |
|
|
Legibly print the MD/DO/APN’s name. |
|
|
|
|
MD/DO/APN Signature & |
|
|
Legibly record provider’s signature, credentials and date. |
Credentials |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supervisor - Print |
|
|
If required, legibly print name of supervisor, credentials and date. |
Name/Credential (If |
|
|
|
needed) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supervisor - Signature (If |
|
|
If required, legible record Supervisor Signature. |
needed) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
155
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Psychiatric Progress Note is essential for documenting psychiatric evaluations and medication management exclusively by authorized professionals. |
| Eligibility | This note must be completed only by psychiatrists or advanced practice nurses who possess prescribing privileges. |
| Identifying Information | Records must include the person's name, record number, date of admission, and the organization or program responsible for the service. |
| Mental Status Evaluation | The note requires a comprehensive assessment of the person's current mental status and any significant changes since the last session. |
| Medication Management | It’s crucial to document whether medications were taken as prescribed and whether any side effects or allergic reactions occurred. |
| Changes in Medical Status | Clinicians must note any changes in the person's medical condition and provide relevant updates on their treatment plan. |
| Goals Updated | The form should reflect the specific goals and objectives being addressed during the session in relation to the treatment plan. |
| Informed Consent | Documentation of informed consent is mandatory for any new medications prescribed, ensuring the person understands the associated risks and benefits. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Psychiatric Progress Note
Completing the Psychiatric Progress Note form involves careful attention to detail as it aims to capture essential information regarding a patient’s mental health care. The next steps will guide you through the process of filling out each section accurately, ensuring that valuable insights into the patient's progress and treatment are recorded appropriately.
- Identifying Information:
- Enter the patient’s full name including first name, last name, and middle initial.
- Record the agency-specific identification number for the patient.
- Document the date of admission, which should align with agency policy.
- Name the organization and program providing the service.
- Fill in the patient’s date of birth.
- Select the patient’s gender, checking the relevant box. If “Transgender” is selected, provide the current gender designation.
- Indicate the status of the patient’s attendance by checking the appropriate box: Present, No Show, or Canceled. If canceled, explain the reason if necessary, and note any other persons present with their relation to the patient.
- Interim History:
- Summarize the patient's progress, medication effectiveness, symptom changes, and any substance use since the last session.
- Include details on any new significant issues or changes in the patient's social or family history.
- Assess and document the overall functioning of the patient.
- Mental Status:
- Evaluate and comment on the patient's current mental status, noting any significant changes since the last visit.
- Address any risk issues and outline an action plan if necessary.
- Medications:
- Record whether medications were taken as prescribed since the last session.
- Note any side effects experienced, along with relevant details.
- Document any allergic reactions to medications.
- Indicate any changes in medical status or additional medications taken.
- Goals:
- Identify specific goals from the Psychopharmacology Action Plan being addressed during this session.
- Therapeutic Interventions:
- Check off the types of interventions delivered, which may include psychotherapy, medication management, or coordination of care.
- If applicable, describe any off-label use of medications or combinations of medications prescribed.
- Response to Intervention:
- Summarize the patient's response to interventions conducted and their progress toward the established goals.
- If no progress has been made, suggest adjustments to the treatment strategy.
- Lab Tests:
- Document key lab test results and indicate whether they were ordered or reviewed with the patient.
- If results were not received, outline the next steps to obtain them.
- AIMS Findings:
- Report findings if the AIMS test was administered.
- Vital Signs:
- Record relevant measurements such as height, weight, BMI, and blood pressure.
- Note any communication between the prescriber and the patient’s primary care provider.
- Diagnosis:
- Indicate if there has been any change in the patient's diagnosis; if so, proceed to the update form.
- Medication Orders:
- Check if no medications have been prescribed today. If so, move to the next appointment section.
- Document the rationale for any medication adjustments and the specifics for each medication prescribed.
- Provide information about medication risks and benefits, along with notes on informed consent.
- Instructions/Comments:
- Include any additional relevant instructions or psycho-educational information for the patient.
- Next Appointment:
- Specify when the patient should return for their next visit.
- Provider Information:
- Print the name of the MD/DO/APN legibly, along with their signature and credentials.
- If required, also print and sign the name of the supervisor.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Psychiatric Progress Note form?
The Psychiatric Progress Note form is a structured way for healthcare providers to document important information about a patient's mental health treatment. It is specifically designed for use by psychiatrists or advanced practice nurses with prescribing rights for psychopharmacology services. This note helps ensure continuity of care, tracks medication effectiveness, and captures any changes in the patient's condition.
Who is qualified to complete the Psychiatric Progress Note?
This form should be completed only by licensed psychiatrists or advanced practice nurses who have prescribing privileges for psychopharmacology. The responsibility lies with these professionals to maintain accurate and comprehensive records for each patient interaction.
What information is required in the Identifying Information section?
In this section, you need to enter the patient's name, record number, date of admission, organization/program, date of birth, and gender. It's also important to indicate whether the patient was present, canceled, or a no-show during the visit.
How should interim history be documented?
The interim history section should detail the patient’s progress since the last session. Include information about medication effectiveness, any changes in symptoms, substance use, new issues, and improvements or declines in the patient's overall functioning.
What should be included in the Medication Orders section?
In this section, document any new medications prescribed, specifying if they are renewed, changed, or discontinued. Include details like the name, dosage, frequency, quantity, and the number of refills. Additionally, confirm that informed consent was given by the patient, indicating they understand the risks and benefits associated with each medication.
What is the role of the Goal(s) Addressed section?
This section identifies the specific treatment goals from the Psychopharmacology Action Plan that are being targeted during the session. It's crucial for tracking the effectiveness of the treatment plan and ensuring that the patient's needs are being met continuously.
Why is documenting the Response to Intervention important?
Documenting the patient's response to interventions helps provider teams assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies. It also guides future care plans. If a patient shows no progress, the note should reflect adjustments in strategies to foster improvement.
What should be done if a patient's diagnosis changes?
If there has been a change in the patient's diagnosis, it is essential to document this in the relevant section and complete a Comprehensive Assessment Update form. This step ensures that all parties involved in the patient's care are aware of the change and can adjust treatment accordingly.
Common mistakes
When filling out the Psychiatric Progress Note form, individuals often make mistakes that can disrupt the continuity of care and lead to confusion in future sessions. One common error is failing to provide complete and accurate identifying information. It is crucial to include the person's full name, record number, and date of admission correctly. Without precise details, tracking the individual's progress becomes difficult, potentially complicating their treatment plan.
Another mistake is neglecting to adequately document the interim history. This section is essential for understanding a client's progress since the last session. Failing to note changes in symptoms, medication effectiveness, or any new issues can hinder the psychiatrist's ability to make informed decisions. Instead of a brief summary, a more thorough description will help ensure that all relevant factors are taken into account during treatment.
People sometimes overlook the importance of clearly detailing therapeutic interventions. Simply checking boxes without explanation can result in a lack of understanding of what actually occurred during the session. It’s beneficial to describe the content of interventions, noting what techniques were used and how the client responded. This documentation can provide a richer context for any future interactions, ensuring that everyone involved in the individual’s care is on the same page.
Lastly, many forget to emphasize the necessity of informed consent. When prescribing medications, it is vital to ensure that the individual fully understands the associated risks and benefits. The lack of clear documentation regarding informed consent can lead to misunderstandings about the treatment process. By meticulously noting whether the person comprehended the information provided, healthcare providers can help safeguard against future issues and promote a more collaborative therapeutic environment.
Documents used along the form
The Psychiatric Progress Note form serves as a critical documentation tool in the mental health field, but it often accompanies several other documents to provide a complete picture of a patient's care. Below is a list of some commonly used forms that complement the Progress Note. Each of these plays an important role in ensuring comprehensive and effective treatment.
- Comprehensive Assessment Update Form: This document is used to capture any changes in a patient's diagnosis or treatment plan. It includes detailed information regarding the patient's clinical condition and the rationale for any modifications made to the initial assessment.
- Psychopharmacology Action Plan: This plan outlines specific treatment goals and objectives related to medication management. It serves as a roadmap for both the patient and provider, detailing what the treatment aims to achieve over a designated period.
- Individual Action Plan: Similar to the Psychopharmacology Action Plan, this document emphasizes individualized goals for the patient. It promotes engagement in the treatment process by aligning mental health objectives with the patient’s personal aspirations.
- Lab Test Order Form: When laboratory tests are needed to monitor a patient's health status or medication effects, this form is utilized. It tracks test requests, results, and any necessary follow-up actions based on those results.
- AIMS Findings Form: For patients undergoing medication management, particularly with antipsychotics, this form documents the results of the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale. It assesses and records symptoms related to involuntary movements, which could indicate side effects from medications.
- Therapeutic Intervention Documentation: This form details the types of interventions provided during a session, such as psychotherapy or medication education. It ensures that all therapeutic actions are recorded to evaluate their effectiveness over time.
- Medication Order Form: This form documents any prescribed medications, including dosage and administration guidelines. It also records important consent information, ensuring that patients are informed about their treatment regimens.
- Next Appointment Reminder: This document specifies the recommended follow-up date and time for the next patient visit, facilitating continuity of care and ensuring that the patient remains engaged in their treatment plan.
Together, these documents provide a holistic view of a patient's treatment journey. They enhance communication among healthcare providers while ensuring that each patient receives tailored care based on their individual needs and symptoms.
Similar forms
- Clinical Assessment Form: This document captures detailed information about a client’s mental and physical health. Similar to the Psychiatric Progress Note, it emphasizes the client's history, presenting issues, and overall status. Both forms aim to document the client's progress and any changes in their treatment plan.
- Medication Reassessment Note: This note is often completed during follow-up appointments. Like the Psychiatric Progress Note, it documents the effectiveness of medications and any side effects experienced since the last visit. It highlights the importance of ongoing evaluation of treatment efficacy.
- Therapeutic Session Note: This document records interventions provided during a therapy session. It shares similarities with the Psychiatric Progress Note in detailing the types of therapies used and the client’s response to those interventions. Both notes aim to assess progress toward therapeutic goals.
- Intake Assessment Form: Taken at the beginning of treatment, this form gathers comprehensive background information. While the Psychiatric Progress Note focuses more on ongoing treatment and progress, both documents serve the purpose of informing treatment strategy based on the individual’s needs and history.
- Discharge Summary: This summary is completed at the end of treatment. Like the Psychiatric Progress Note, it highlights treatment outcomes, goals achieved, and any ongoing recommendations. Both documents aim to provide a clear picture of the client’s journey through the mental health care system.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing the Psychiatric Progress Note form, it is essential to follow proper guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Below are four dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
- Do: Record the person's full name, including the first name, last name, and middle initial as required in the Identifying Information section.
- Do: Document any interim history regarding the client's progress and mental status clearly and concisely.
- Don't: Skip any of the mandatory fields, such as the date of admission or medication orders, as this can lead to incomplete documentation.
- Don't: Use vague language or abbreviations that may not be understood by others reviewing the document.
Misconceptions
1. Anyone can fill out the Psychiatric Progress Note form. This is incorrect. Only a psychiatrist or an advanced practice nurse with prescribing privileges is authorized to complete this form. Completing it without the proper qualifications can lead to incorrect documentation and potential issues with patient care.
2. The progress note is simply a checkbox exercise. Many believe it's just about checking boxes; however, each section requires thoughtful consideration and reflection on the patient's progress, mental status, and treatment response. Detailed narrative enhances understanding and continuity of care.
3. It isn’t necessary to document if medications are taken as prescribed. In fact, this documentation is crucial. It helps in assessing the effectiveness of the treatment plan and ensuring adherence to prescribed therapies.
4. Only major changes in diagnosis need to be noted. This is a misconception. Any changes, no matter how minor, should be documented to maintain accurate medical history and ensure comprehensive care. Accurate records help all providers involved in a patient's care.
5. AIMS findings are optional to document. On the contrary, documenting AIMS findings is essential if the test has been administered. These findings are key to monitoring potential side effects and ensuring appropriate adjustments in treatment.
6. The next appointment date does not require a specific time frame. This is misleading. It is important to document a clear timeframe for the patient's next appointment to maintain continuity in treatment and monitor progress effectively.
7. Instructions and comments can be vague. Clarity is critical. This section should provide clear and specific information regarding any additional instructions or recommendations for the patient. Ambiguity can lead to misunderstandings and insufficient care.
8. Once signed, the progress note cannot be amended. This is inaccurate. While documentation should be thorough and accurate from the start, any amendments should be carefully noted. Corrections and additional notes can be made as necessary to capture the true context of the patient’s care.
Key takeaways
When filling out the Psychiatric Progress Note form, keep the following key takeaways in mind:
- Accurate Patient Identification: Clearly record the patient's full name, record number, date of birth, and gender. This ensures that the right person is receiving the documented services.
- Comprehensive Interim History: Provide a detailed interval history of the client’s progress, including any changes in symptoms, medication effectiveness, or significant new issues since the last session.
- Document Mental Status Evaluation: Pay attention to the mental status during the visit. Note any significant changes, risks, and necessary action plans to address identified issues.
- Medications and Side Effects: Record all medications taken and any side effects experienced. A clear account of allergies and other medications will also help in providing comprehensive care.
- Informed Consent is Mandatory: Ensure the patient understands the risks and benefits of any prescribed medication. Document their consent thoroughly; if consent is not obtained, clarify the next steps in the comments section.
Completing this form accurately and thoroughly is critical to delivering effective and safe psychiatric care.
Browse Other Templates
Rental Charge Documentation Form - Completing this form is a critical step in maintaining good standing with HUD.
G325 - It is important to specify if there is no spouse or former spouse when completing the G-325.
Service About Self - Regularly volunteers at shelters, providing essential services to the homeless.