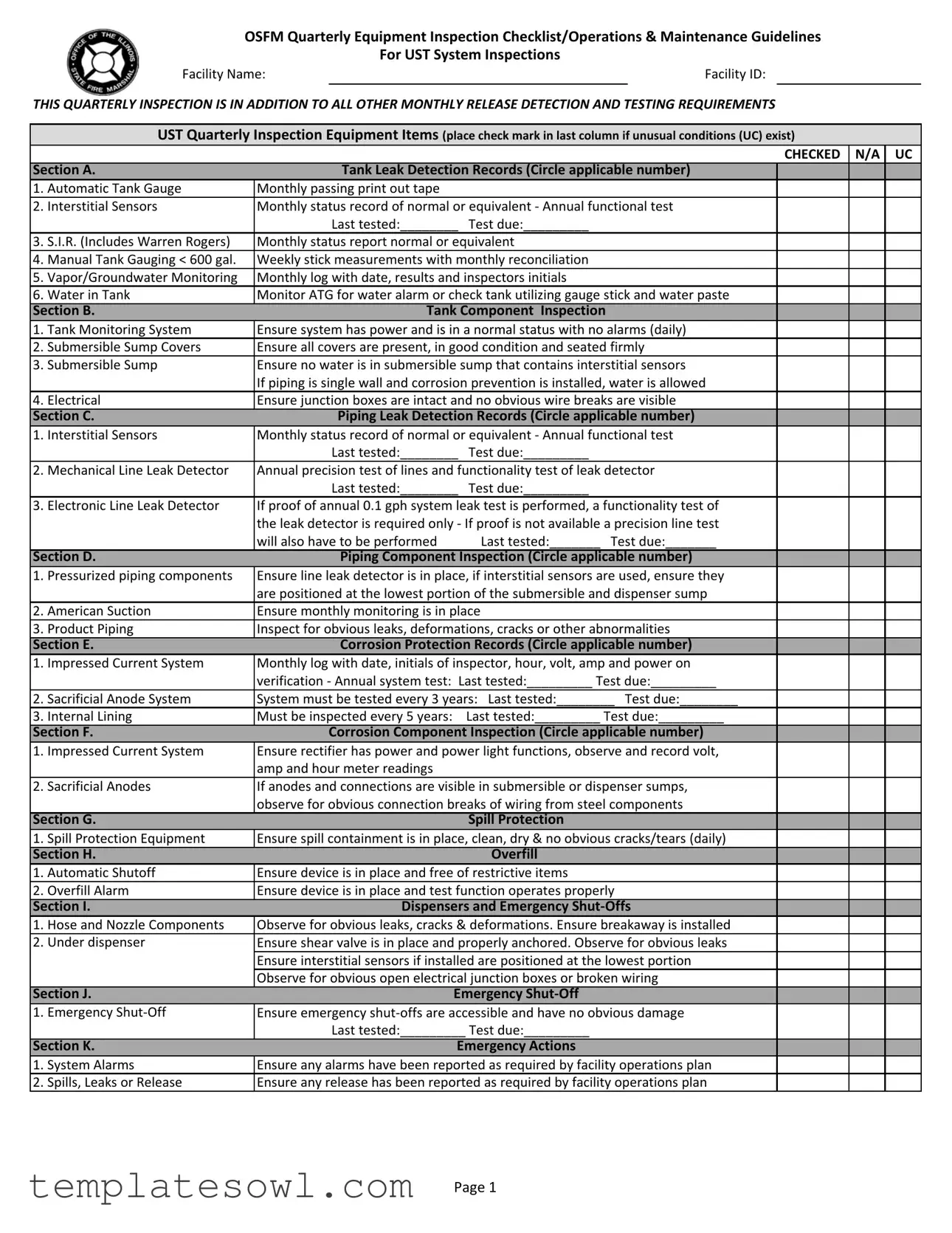
Fill Out Your Quarterly Inspection Report Form
The Quarterly Inspection Report form plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and compliance of underground storage tank (UST) systems. It is designed to conduct thorough reviews of various equipment and components, including tank leak detection records, tank component inspections, piping leak detection, and corrosion protection. Each section has specific tasks, ranging from checking automatic tank gauge printouts to verifying the condition of submersible sump covers. Facility operators must document any unusual conditions found during the inspection and note the status of equipment in categories related to spill protection, overfill systems, and emergency shut-offs. Each line item requires careful attention and must be checked off accordingly, highlighting areas that need immediate attention or further monitoring. Alongside these inspections, the form verifies that all monthly record-keeping requirements have been met and mandates the personal involvement of certified operators, reinforcing the commitment to environmental safety and regulatory compliance. This comprehensive approach not only aids in detecting potential issues but also provides a blueprint for maintaining operational integrity in UST management.
Quarterly Inspection Report Example

OSFM Quarterly Equipment Inspection Checklist/Operations & Maintenance Guidelines
|
|
|
For UST System Inspections |
|||||
|
Facility Name: |
|
|
Facility ID: |
|
|||
THIS QUARTERLY INSPECTION IS IN ADDITION TO ALL OTHER MONTHLY RELEASE DETECTION AND TESTING REQUIREMENTS |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UST Quarterly Inspection Equipment Items (place check mark in last column if unusual conditions (UC) exist) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
CHECKED |
N/A |
UC |
Section A. |
|
Tank Leak Detection Records (Circle applicable number) |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Automatic Tank Gauge |
Monthly passing print out tape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Interstitial Sensors |
Monthly status record of normal or equivalent - Annual functional test |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Last tested:________ |
Test due:_________ |
|
|
|
|
3. |
S.I.R. (Includes Warren Rogers) |
Monthly status report normal or equivalent |
|
|
|
|||
4. |
Manual Tank Gauging < 600 gal. |
Weekly stick measurements with monthly reconciliation |
|
|
|
|||
5. |
Vapor/Groundwater Monitoring |
Monthly log with date, results and inspectors initials |
|
|
|
|||
6. |
Water in Tank |
Monitor ATG for water alarm or check tank utilizing gauge stick and water paste |
|
|
|
|||
Section B. |
|
Tank Component Inspection |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Tank Monitoring System |
Ensure system has power and is in a normal status with no alarms (daily) |
|
|
|
|||
2. |
Submersible Sump Covers |
Ensure all covers are present, in good condition and seated firmly |
|
|
|
|||
3. |
Submersible Sump |
Ensure no water is in submersible sump that contains interstitial sensors |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
If piping is single wall and corrosion prevention is installed, water is allowed |
|
|
|
|||
4. |
Electrical |
Ensure junction boxes are intact and no obvious wire breaks are visible |
|
|
|
|||
Section C. |
|
Piping Leak Detection Records (Circle applicable number) |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Interstitial Sensors |
Monthly status record of normal or equivalent - Annual functional test |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Last tested:________ |
Test due:_________ |
|
|
|
|
2. |
Mechanical Line Leak Detector |
Annual precision test of lines and functionality test of leak detector |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Last tested:________ |
Test due:_________ |
|
|
|
|
3. |
Electronic Line Leak Detector |
If proof of annual 0.1 gph system leak test is performed, a functionality test of |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
the leak detector is required only - If proof is not available a precision line test |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
will also have to be performed |
Last tested:_______ Test due:_______ |
|
|
|
||
Section D. |
|
Piping Component Inspection (Circle applicable number) |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Pressurized piping components |
Ensure line leak detector is in place, if interstitial sensors are used, ensure they |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
are positioned at the lowest portion of the submersible and dispenser sump |
|
|
|
|||
2. |
American Suction |
Ensure monthly monitoring is in place |
|
|
|
|||
3. |
Product Piping |
Inspect for obvious leaks, deformations, cracks or other abnormalities |
|
|
|
|||
Section E. |
|
Corrosion Protection Records (Circle applicable number) |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Impressed Current System |
Monthly log with date, initials of inspector, hour, volt, amp and power on |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
verification - Annual system test: Last tested:_________ Test due:_________ |
|
|
|
|||
2. |
Sacrificial Anode System |
System must be tested every 3 years: Last tested:________ Test due:________ |
|
|
|
|||
3. |
Internal Lining |
Must be inspected every 5 years: |
Last tested:_________ Test due:_________ |
|
|
|
||
Section F. |
Corrosion Component Inspection (Circle applicable number) |
|
|
|
||||
1. |
Impressed Current System |
Ensure rectifier has power and power light functions, observe and record volt, |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
amp and hour meter readings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Sacrificial Anodes |
If anodes and connections are visible in submersible or dispenser sumps, |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
observe for obvious connection breaks of wiring from steel components |
|
|
|
|||
Section G. |
|
|
Spill Protection |
|
|
|
||
1. |
Spill Protection Equipment |
Ensure spill containment is in place, clean, dry & no obvious cracks/tears (daily) |
|
|
|
|||
Section H. |
|
|
Overfill |
|
|
|
||
1. |
Automatic Shutoff |
Ensure device is in place and free of restrictive items |
|
|
|
|||
2. |
Overfill Alarm |
Ensure device is in place and test function operates properly |
|
|
|
|||
Section I. |
|
Dispensers and Emergency |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Hose and Nozzle Components |
Observe for obvious leaks, cracks & deformations. Ensure breakaway is installed |
|
|
|
|||
2. |
Under dispenser |
Ensure shear valve is in place and properly anchored. Observe for obvious leaks |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Ensure interstitial sensors if installed are positioned at the lowest portion |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Observe for obvious open electrical junction boxes or broken wiring |
|
|
|
|||
Section J. |
|
Emergency |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
Emergency |
Ensure emergency |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Last tested:_________ Test due:_________ |
|
|
|
||
Section K. |
|
Emergency Actions |
|
|
|
|||
1. |
System Alarms |
Ensure any alarms have been reported as required by facility operations plan |
|
|
|
|||
2. |
Spills, Leaks or Release |
Ensure any release has been reported as required by facility operations plan |
|
|
|
|||
Page 1

Remarks needed if unusual conditions exists (also incude the date owner was notified and actions taken):
Verify that each monthly recordkeeping requirement on the 1st page has been accomplished by initialing in the blanks below. (Initial
all that are applicable)
Tank Leak Detection/Interstitial Monitoring
Jan |
Feb |
March |
April |
May |
|
June |
July |
|
Aug |
|
Sept |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Line Interstitial Monitoring/Automatic Line Leak Detectors |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Jan |
Feb |
March |
April |
May |
|
June |
July |
|
Aug |
|
Sept |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Impressed Current System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Jan |
Feb |
March |
April |
May |
|
June |
July |
|
Aug |
|
Sept |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, and Annual Inspection Items (indicate how often):
Daily:
Monthly:
Quarterly:
Annually: Submit annual Financial Responsibility Report from www.sfm.illinois.gov at Applications & Forms.
Identify the manner in which facility owners/operators will properly dispose of regulated substances spilled at the facility:
A/B Operators must conduct the quarterly inspections personally. Sign & date the form when inspection is done.
If using this form as part of your Operations & Maintenance Plan, attach the list of your class A/B & C Operators & your facility's Emergency Response Procedures form. The facility Owner must sign the O&M Plan with the A/B Operator, but only the A/B Operator is required to sign the Quarterly Inspection report.
Printed Name of A/B Operator |
|
Signature of A/B Operator |
|
Date of Inspection |
(Quarterly Equipment Inspection Checklist |
Page 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of the Report | The Quarterly Inspection Report is designed to enhance the safety and compliance of underground storage tank (UST) systems through systematic inspection and documentation. |
| Mandated Inspections | According to state regulations, facilities must conduct a quarterly inspection in addition to all monthly release detection and testing requirements. |
| Record Keeping | Operators must maintain records of equipment inspection results, ensuring accurate logs for monitoring leak detection systems and corrosion protection methods. |
| Owner’s Responsibilities | The facility owner is required to sign the Operations & Maintenance Plan, while only the A/B Operator must sign the Quarterly Inspection Report. |
| Governing Laws | This form is governed by laws established under the Illinois Environmental Protection Act pertaining to UST safety and compliance. |
| Inspection Frequency | Inspections must occur quarterly, but daily and monthly checks are also necessary to ensure ongoing compliance and safety. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Quarterly Inspection Report
Completing the Quarterly Inspection Report form is an essential process that contributes to the oversight of equipment and systems in your facility. This guide outlines what to do step by step, ensuring accuracy and adherence to requirements.
- Facility Information: Begin by filling in the Facility Name and Facility ID at the top of the form.
- Inspection Checklist: Progress through each section of the checklist, marking off items that have been thoroughly inspected. Place a checkmark in the last column if unusual conditions exist for any item.
- Tank Leak Detection Records: Circle the applicable numbers related to your tank leak detection methods, ensuring you document the date of last testing and next due date where requested.
- Tank Component Inspection: Inspect components such as the tank monitoring system and submersible sump. Record findings as necessary.
- Piping Leak Detection Records: Circle the applicable numbers for interstitial sensors and line leak detectors. Document testing dates.
- Piping Component Inspection: Inspect pressurized piping components and product piping for any visible issues.
- Corrosion Protection Records: Complete this section by circling applicable testing frequencies and documenting the last tested date.
- Spill Protection: Confirm that spill protection equipment is in place and functioning properly.
- Overfill Controls: Check automatic shutoff devices and overfill alarms; ensure they operate correctly.
- Dispensers and Emergency Shut-Offs: Inspect all components for leaks and proper installations.
- Emergency Shut-Off: Ensure emergency shut-offs are accessible and operational.
- Emergency Actions: Confirm alarms are reported as specified in the facility's operations plan.
- Remarks Section: Write any necessary remarks if unusual conditions are found, including the date the owner was notified.
- Initials for Recordkeeping: Verify monthly recordkeeping by initialing next to each month listed under the relevant categories.
- Submission Information: Note how often additional inspection items occur (daily, monthly, quarterly, annually).
- Operator Signatures: Have the A/B Operator print their name, sign, and date the form when the inspection is complete.
Once the form is filled out, it should be submitted as part of your operational and maintenance documentation. It is important to maintain a copy for your records, as periodic inspections will contribute to ongoing compliance with regulations. Ensure the timely completion of any required follow-up actions noted during the inspection.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Quarterly Inspection Report form?
The Quarterly Inspection Report form is designed to ensure that underground storage tank (UST) systems are operating safely and in compliance with regulatory standards. It provides a structured way for facility owners and operators to verify that all necessary inspections and tests have been conducted, as well as to identify any unusual conditions that may require immediate attention.
Who is responsible for completing the inspection?
According to the guidelines, the A/B Operators must conduct the quarterly inspections personally. Their involvement is crucial, as they possess the necessary knowledge and training to identify potential problems and ensure comprehensive compliance with state regulations.
What specific items are included in the inspection checklist?
The inspection checklist is divided into several sections, each targeting critical elements of UST systems. These include tank leak detection records, tank component inspections, piping leak detection records, corrosion protection records, spill protection, overfill equipment, dispensers, emergency shut-off mechanisms, and actions taken during emergencies. Each section is designed to thoroughly evaluate the condition and functionality of the equipment involved.
How do I deal with unusual conditions found during the inspection?
If you encounter any unusual conditions during the inspection, it is essential to note these in the remarks section of the form. Ensure you specify what the condition is, the date the owner was notified, and the actions that were taken to address it. Clear documentation will aid in tracking and resolving issues effectively.
Is there a required timeline for submitting the inspection report?
The completed Quarterly Inspection Report should be signed and dated by the A/B Operator. Although the form itself does not specify an immediate submission deadline, keeping thorough records and submitting them alongside your annual reports as per compliance requirements is essential. This documentation serves as a critical part of your facility's overall operations and maintenance plan.
What to do if testing shows a failure in any equipment?
In the event that testing reveals a failure in any equipment, immediate corrective actions must be taken. This may involve repairs or replacements to ensure the UST system is functioning correctly. Furthermore, all findings should be documented in the inspection report, along with details of the actions taken, and communicated with appropriate personnel as part of compliance procedures.
Can the Quarterly Inspection Report form be used for other purposes?
This form can indeed be part of a broader Operations & Maintenance Plan. If you choose to use the Quarterly Inspection Report as part of such a plan, remember to attach the list of your class A/B & C Operators and your facility's Emergency Response Procedures. The thorough integration of these components enhances overall safety and compliance preparedness.
What should be done if I do not have a certified A/B Operator?
If a facility does not have a certified A/B Operator, it cannot carry out the quarterly inspections until one is obtained. Certification for these operators is mandatory, as they are tasked with vital responsibilities concerning the safety and regulatory compliance of the UST systems.
What records must I maintain beyond the Quarterly Inspection Report?
In addition to the Quarterly Inspection Report, you are responsible for maintaining records of all monthly release detection and testing requirements, daily inspections of spill protection equipment, and any other required inspections. These records should be kept systematically to ensure that they are readily accessible for review during inspections by regulatory agencies.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Quarterly Inspection Report form can seem straightforward, but there are common pitfalls that people often encounter. Avoiding these mistakes not only ensures compliance but also promotes safety and efficiency in facility management.
One common mistake is not checking the latest dates for tests and inspections. Relevant sections require you to fill in the last tested date and the next test due. Forgetting to update this information can lead to confusion or, worse, compliance issues. Remember, accurate dates keep you on track with necessary evaluations.
Another frequent error involves overlooking signature requirements. The A/B Operator must sign this form when the inspection is completed. Without a signature, the document doesn't have the validity it needs. Some might assume it's optional, but skipping this step can lead to unnecessary complications.
Many people fail to initial the monthly records on the first page. This section helps verify that all monthly monitoring has been completed. By neglecting to provide initials, you might fail to show due diligence in recordkeeping, which could impact future inspections.
Another mistake lies in improperly documenting unusual conditions. If any unusual conditions exist during the inspection, detailed remarks are necessary. Providing insufficient details or vague remarks could lead to questions down the line regarding how the situation was handled.
Additionally, some folks forget to thoroughly inspect spill protection equipment. This inspection must be conducted daily, and confirming that it’s clean, dry, and free from cracks is crucial. Incomplete checks can pose serious safety risks, and overlooking these simple tasks can have detrimental effects.
One aspect that gets overlooked is the importance of regular communication with the facility operations plan. Any alarms or spills must be reported as specified. Failing to communicate this information can lead to dire consequences in emergency situations. Always ensure proper channels of communication are maintained.
People often make the mistake of misunderstanding the frequency of inspections. Daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual requirements are clearly outlined, but some may misinterpret these guidelines. Observing the inspection frequency correctly ensures that the facility operates within safety regulations and company policy.
Another common error is not updating the emergency procedures. When attaching the Emergency Response Procedures form, it’s vital to ensure that the information is current and applicable. Relying on outdated procedures can be detrimental in moments that require immediate action.
Lastly, failing to observe mutual conditions among the inspection components can lead to oversight. Each section of the report contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of operations. Ensure each aspect is examined comprehensively for any anomalies. A well-rounded inspection leads to better facility management.
Avoiding these nine mistakes will streamline your inspection process, enhance safety, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Remember, a thorough and accurate Quarterly Inspection Report is a key component in maintaining a safe facility.
Documents used along the form
The Quarterly Inspection Report form serves as a crucial document for ensuring the safety and regulatory compliance of underground storage tank (UST) systems. Alongside this comprehensive inspection report, there are several other forms and documents that assist facilities in maintaining proper operations and adhering to safety standards. Each of these documents plays a vital role in the overall management of the UST system. Here are some key documents often used in conjunction with the Quarterly Inspection Report form:
- Monthly Release Detection Report: This report tracks the monthly findings related to leak detection methods and helps in verifying compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Annual Financial Responsibility Report: Required by state law, this document demonstrates that the facility has the financial means to cover potential liability resulting from leaks or spills.
- Operations and Maintenance Plan: This plan outlines the procedures for safely operating and maintaining the UST system, ensuring routine inspections and corrective actions are documented and followed.
- Leak Detection Method Establishment Forms: Facilities may use these forms to define which leak detection methods are being implemented and to confirm their effectiveness through documented testing.
- Corrective Action Plan: In the case of any leaks or other hazardous incidents, this plan provides a structured approach for responding and mitigating potential damage.
- Emergency Response Procedures: This document details the steps to take in an emergency, ensuring that all staff are prepared to act swiftly and effectively if accidents occur.
- Staff Training Records: Proper documentation of staff training ensures that all personnel are certified and knowledgeable about the operation and safety protocols of the UST system.
- Storage Tank Registration Documents: Used for keeping track of each tank’s registration status, these documents help ensure compliance with both state and federal regulations.
- Inspection Checklists for Monthly and Annual Reviews: These checklists supplement the Quarterly Inspection Report, ensuring all required inspections are completed on time and properly documented.
Together, these forms and documents create a comprehensive framework for monitoring and maintaining UST systems. Adopting and adhering to rigorous inspection and reporting practices not only protects the facility but also helps safeguard the environment and public health.
Similar forms
-
Monthly Inspection Report: Similar to the Quarterly Inspection Report, the Monthly Inspection Report tracks routine inspections and maintenance actions. It focuses on a shorter period and often includes specific tasks completed within that month.
-
Annual Inspection Report: This document summarizes findings from an annual review and is typically more comprehensive. It often includes a broader range of assessment criteria compared to the Quarterly Inspection Report.
-
Leak Detection Report: This report specifically addresses the results and conditions related to leak detection systems. It emphasizes functionality and any issues that were identified during the inspection period.
-
Safety Compliance Checklist: This document is used to ensure that all safety regulations and standards are met. It parallels the Quarterly Inspection Report in process but focuses more on compliance with safety laws and protocols.
-
Maintenance Log: Similar to the Quarterly Inspection Report in its purpose of tracking equipment status, the Maintenance Log records all maintenance activities performed on the equipment over time.
-
Emergency Response Plan: While not purely inspection-focused, this document covers procedures to follow in case of incidents. It complements the Quarterly Inspection Report by addressing preparedness for emergencies and ensuring proper response measures are in place.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Quarterly Inspection Report form, certain practices can improve accuracy and compliance. Here are some guidelines:
- Do ensure all fields are completed as required, including facility name and ID.
- Do double-check measurements and data entries for correctness before submission.
- Do report any unusual conditions noted during the inspection accurately, including dates and actions taken.
- Do make sure the A/B Operator's signature is obtained at the end of the form.
- Don't leave any applicable sections blank; this can lead to compliance issues.
- Don't overlook the monthly recordkeeping; all required initials must be documented.
- Don't submit the form without conducting a thorough review of all entries.
- Don't ignore instructions related to attached documentation, such as the Emergency Response Procedures form.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The Quarterly Inspection Report is the only inspection required.
- Misconception 2: Only certified inspectors can fill out the form.
- Misconception 3: The report serves as a standalone document.
- Misconception 4: Inspections are only necessary if there is a known issue.
- Misconception 5: Documentation is optional.
- Misconception 6: The form can be filed without a signature.
- Misconception 7: All items on the checklist require action.
Many people believe that the Quarterly Inspection Report replaces all other inspection requirements. In reality, this report is in addition to monthly release detection and testing that must also be performed.
Some individuals assume that only certified inspectors are allowed to complete the report. However, facility A/B operators are responsible for personally conducting the inspections and signing the report.
It is a common misunderstanding that the Quarterly Inspection Report can function independently. The form must be viewed in conjunction with the Operations & Maintenance Plan for best practices and compliance oversight.
Some facility owners believe that inspections are only required when problems are apparent. Regular inspections are essential to prevent issues and ensure compliance with safety regulations, regardless of visible conditions.
A misconception exists that maintaining documentation of inspections is optional. Accurate recordkeeping is crucial and is mandated to track compliance and for future reference during audits.
There is an assumption that the form can be submitted without proper signatures. The A/B operator must sign the report to validate the inspection, thus ensuring accountability.
Some users believe every item on the checklist necessitates action or that it signals a problem. The checklist includes "N/A" options, allowing for flexibility based on the specific circumstances of the facility.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the Quarterly Inspection Report (QIR) form is a crucial task for facility owners and operators to ensure compliance and maintain safety standards. Here are the key takeaways to consider:
- Personal Conduct of Inspections: Only class A/B operators are authorized to perform the inspections, which adds a level of accountability.
- Comprehensive Recordkeeping: It’s essential to circle applicable numbers for various inspection components, ensuring nothing is overlooked during the review process.
- Addressing Unusual Conditions: If any unusual conditions exist, it is critical to check the corresponding box and provide detailed remarks about the situation, including the date of notification and actions taken.
- Monthly Verification: Each monthly recordkeeping requirement must be verified by initialing in the designated blanks. This measure strengthens compliance with safety protocols.
- Documentation and Signature Requirements: The A/B operator must sign and date the form upon completion of the inspection. This signature serves as a confirmation of accountability and thoroughness.
- Emergency Response Considerations: Ensure that the Emergency Response Procedures form is attached for comprehensive emergency management. This assists in a swift response should any incidents occur.
- Avoiding Legal Issues: Keep the Quarterly Inspection Report on file to demonstrate compliance and due diligence. This documentation is essential in case of inspections by authorities.
- Regular Maintenance Routines: Daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual inspection items should be clearly indicated. Regular maintenance helps to mitigate risks of leaks and spills.
- Financial Responsibility Report: The annual Financial Responsibility Report must be submitted, emphasizing the importance of financial accountability in environmental risk management.
By adhering to these guidelines, facilities can better ensure compliance while prioritizing safety and environmental protection. Properly filling out this report is not just a regulatory requirement but also a best practice for operational excellence.
Browse Other Templates
If I Get Fired From My Job Can I Collect Unemployment - Claimants must list names and contact details of individuals they communicated with at potential employers.
Transunion Dispute Not Working - Document more queries on a separate paper if needed.