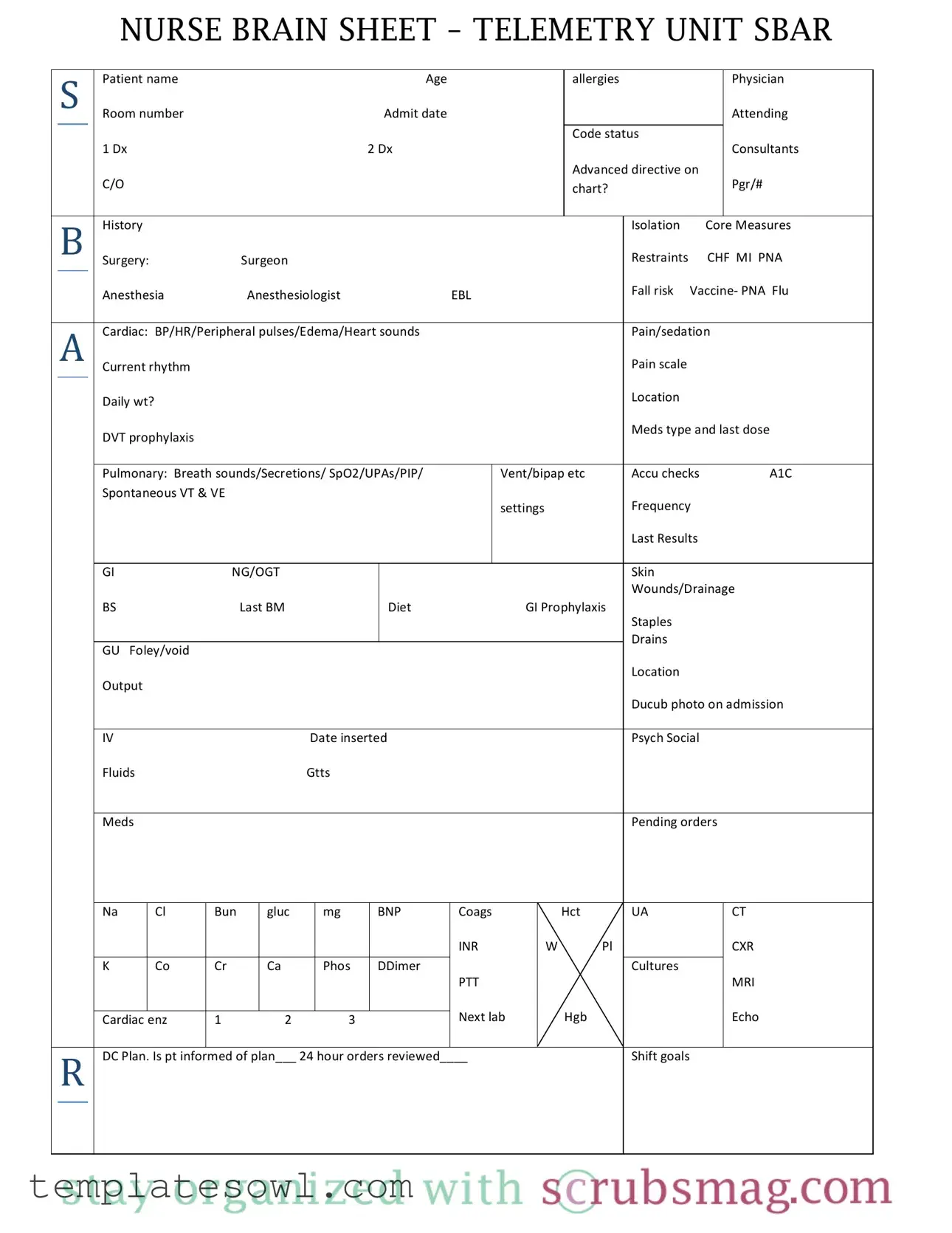
Fill Out Your Sheet Telemetry Form
The Sheet Telemetry form is a critical tool used in healthcare settings, especially in telemetry units where patient monitoring is essential. This form encompasses a wide array of patient-specific information, ensuring that healthcare providers can swiftly and efficiently respond to their patients' needs. Key sections include patient demographics, such as name, age, and physician details, along with vital clinical data including diagnosis codes and current medical conditions. The form emphasizes essential assessments, ranging from cardiac observations like blood pressure, heart rate, and rhythm, to pulmonary evaluations including breath sounds and oxygen saturation levels. Additionally, it tracks medication administration, dietary needs, and safety measures like fall risk and restraints. This comprehensive documentation aids in coordinating care among interdisciplinary teams, aligning treatment plans, and addressing patient concerns effectively. The organization of the form facilitates easy updates, ensuring that patient information remains accurate and relevant throughout their stay in the telemetry unit. By utilizing this form, healthcare providers are better equipped to deliver high-quality, patient-centered care.
Sheet Telemetry Example
NURSE BRAIN SHEET – TELEMETRY UNIT SBAR
|
S |
Patient name Age |
|
allergies |
|
Physician |
|||
|
|
|
|
Room number Admit date |
|
|
|
Attending |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Code status |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 Dx 2 Dx |
|
|
|
Consultants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advanced directive on |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C/O |
|
|
chart? |
|
Pgr/# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
History |
|
|
|
Isolation Core Measures |
|||
|
|
|
|
Surgery: Surgeon |
|
|
Restraints CHF MI PNA |
||
|
|
|
|
Anesthesia Anesthesiologist EBL |
|
|
Fall risk Vaccine‐ PNA Flu |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
A |
Cardiac: BP/HR/Peripheral pulses/Edema/Heart sounds |
|
|
Pain/sedation |
||||
|
|
|
|
Current rhythm |
|
|
|
Pain scale |
|
|
|
|
|
Daily wt? |
|
|
|
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DVT prophylaxis |
|
|
|
Meds type and last dose |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Pulmonary: Breath sounds/Secretions/ SpO2/UPAs/PIP/ |
Vent/bipap etc |
Accu checks A1C |
|||
|
|
|
|
Spontaneous VT & VE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
settings |
Frequency |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last Results |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GI NG/OGT |
|
|
|
Skin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wounds/Drainage |
|
|
|
|
|
BS Last BM |
Diet GI Prophylaxis |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Staples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drains |
|
|
|
|
|
GU Foley/void |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ducub photo on admission |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
IV Date inserted |
|
|
Psych Social |
||
|
|
|
|
Fluids Gtts |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meds |
|
|
|
Pending orders |
|
|
|
|
Na |
Cl |
Bun |
gluc |
mg |
BNP |
Coags |
|
UA |
CT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INR |
|
|
CXR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K |
Co |
Cr |
Ca |
Phos |
DDimer |
|
|
Cultures |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTT |
|
|
MRI |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Next lab |
|
|
Echo |
|||
Cardiac enz |
1 2 3 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
R DC Plan. Is pt informed of plan___ 24 hour orders reviewed____ |
|
Shift goals |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Nurse Brain Sheet for the Telemetry Unit serves as a comprehensive tool for nurses to document patient information, track vital signs, and ensure continuity of care. |
| Components | This form includes sections on patient demographics, medical history, assessment findings, and care plans, making it a versatile resource in a clinical setting. |
| Compliance | In states like California, the use of such forms aligns with legislative practices aimed at improving patient safety and documentation standards under the Nursing Practice Act. |
| Frequency of Use | Healthcare providers utilize the Sheet Telemetry form during each shift or after significant changes in a patient's condition, ensuring up-to-date and accurate records. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Sheet Telemetry
Completing the Sheet Telemetry form helps ensure all vital information about a patient is organized and clearly presented. This step-by-step guide will help you fill out the form accurately.
- Start with the Patient name field. Fill in the full name of the patient.
- Next, enter the Age of the patient.
- List any known allergies.
- Fill in the name of the attending Physician.
- Specify the Room number where the patient is located.
- Enter the Admit date.
- Indicate the Code status.
- Detail the 1st Diagnosis (Dx) and any additional diagnoses on subsequent lines.
- List any Consultants involved in the patient's care.
- Note if there is an Advanced directive present.
- Specify any concerns or complaints the patient has in the C/O section.
- Include the Pager number for the healthcare team.
- Indicate if the History chart is available.
- Mark if the patient is in Isolation.
- Fill in details regarding Core Measures such as surgery type and surgeon’s name.
- Document any Restraints being used.
- Add information on CHF, MI, and PNA if applicable.
- Specify Anesthesia details along with the Anesthesiologist’s name.
- Record the Estimated Blood Loss (EBL) during surgery.
- Note the patient’s Fall risk.
- Check for any administered Vaccines for PNA and Flu.
- In the Cardiac section, note BP/HR/Peripheral pulses/Edema/Heart sounds.
- Document Pain/sedation levels and the Current rhythm.
- Fill in the appropriate Pain scale.
- List the Daily wt? for the patient.
- Document the location and details of DVT prophylaxis.
- Record the type and last dose of Meds given.
- In the Pulmonary section, include details on breath sounds and any additional treatments.
- Complete the Accu checks and A1C results.
- Detail information about NG/OGT in the GI section.
- Note details about skin condition, wounds, and drainage.
- Record the last bowel movement in the Last BM section.
- Specify the patient’s diet and any GI prophylaxis.
- Document the condition of any staples or drains.
- For the GU section, indicate the status and output from Foley/void.
- Provide details about any IV lines and their insertion date.
- In the Psych/Social section, include relevant information.
- Record details about Fluids administered.
- List any Pending orders for lab results.
- Complete the sections for any necessary tests such as CT, MRI, Echo, and cardiac enzymes.
- Summarize the plan in the Plan section, ensuring the patient is informed.
- Verify if the 24-hour orders have been reviewed.
- Set clear Shift goals for the patient’s care.
What You Should Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the Sheet Telemetry form?
The Sheet Telemetry form is designed to provide healthcare professionals with a comprehensive overview of a patient's status in a telemetry unit. It fosters effective communication among caregivers and ensures that critical patient information is documented in one easily accessible location. This form includes vital details such as patient demographics, clinical history, vital signs, medications, and specific care protocols necessary for monitoring patients with cardiac conditions.
Who should complete the Sheet Telemetry form?
The Sheet Telemetry form should be completed by nursing staff, specifically those assigned to the telemetry unit. Nurses or other healthcare providers are responsible for documenting initial assessments upon patient admission and updating the form throughout the patient's stay. This ongoing documentation reflects changes in the patient’s condition and care plan, ensuring that all team members are informed and able to make timely decisions.
What key information is included in the Sheet Telemetry form?
The form includes several key sections: patient identification (name, age, physician, and room number), medical history (including diagnoses, allergies, and advanced directives), clinical assessments (such as vital signs, cardiac rhythm, and pain management), and laboratory test results. It also includes information regarding daily weight, medication administration, and any pending orders that need attention.
How often should the Sheet Telemetry form be updated?
The Sheet Telemetry form must be updated regularly to reflect the patient's current condition. Significant changes, such as modifications to medications, vital signs, or laboratory results, should be documented immediately. In addition, routine updates should occur at the beginning of each shift to review the patient's status and ensure that all healthcare team members are aware of the latest developments in the patient's care plan.
What is the significance of the SBAR communication model in the Sheet Telemetry form?
The SBAR model, which stands for Situation, Background, Assessment, and Recommendation, is a structured approach to communication that improves clarity and efficiency. Within the context of the Sheet Telemetry form, SBAR facilitates concise and effective information sharing among team members. This approach ensures that critical information is communicated quickly, improving patient safety and enabling timely interventions based on the presented patient data.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Sheet Telemetry form can be a daunting task, and mistakes can lead to confusion or miscommunication in patient care. One common error is not filling in the patient name section correctly. This is critical as it identifies the patient throughout the care process. Ensure the name is spelled accurately and matches the identification documents.
Another frequent mistake involves the age field. Omitting this information or entering an incorrect age can mislead healthcare professionals, affecting treatment plans and decisions. Double-check that the age is current and reflects the patient’s actual age on admission.
Allergies should not be overlooked. Leaving the allergies section blank can pose a serious risk to patient safety. It's essential to gather comprehensive allergy information from the patient or their chart to prevent administering any harmful medications.
Many individuals also fail to include the physician's name. This detail helps ensure that care is coordinated correctly. Documenting the attending physician's name accurately allows for effective communication and may affect treatment directions.
When it comes to medical history, the history section is sometimes filled in hastily. Insufficient details about prior medical conditions can hinder the healthcare team's understanding of the patient’s background, which is crucial for diagnosing and managing current issues. Provide as much relevant information as possible.
Another area where errors can occur is in the current rhythm and vital signs section. Recording incorrect values or neglecting to note abnormal findings can lead to inadequate monitoring of the patient’s condition. Be precise with these details to ensure proper assessment.
Mistakes also happen in the medications section. Entering the wrong type or dosage of medication can have severe consequences. Always confirm and include the last dose received, as well as any pending orders for medications.
Documentation of the IV insertion date is another area that warrants care. Forgetting to note when the IV was placed can complicate things later, especially if complications arise or if a change in care is necessary.
Finally, the DC Plan section is often rushed. It’s crucial to articulate the discharge planning clearly and confirm that the patient has been informed of their plan. This not only aids in continuity of care but also empowers the patient in managing their own health following discharge.
Documents used along the form
The Sheet Telemetry form is a critical tool in monitoring and managing patient care within a telemetry unit. It captures vital information, allowing caregivers to maintain clear communication and ensure patient safety. Several additional forms and documents complement this crucial record. Below is a list of those related documents, each serving a specific purpose in healthcare settings.
- Patient Admission Form: This form gathers essential information about the patient during their admission. It includes demographic details, medical history, and consent for treatment.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): This document tracks all medications administered to the patient. It ensures accurate dosing and timing, and helps avoid potential medication errors.
- Vital Signs Record: This form logs a patient's vital signs over time. It provides valuable data for tracking health status and identifying any physiological changes that may require intervention.
- Nursing Assessment Form: This document captures the initial assessment conducted by nursing staff. It includes a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's physical and emotional health upon admission.
- Discharge Summary: At the end of a patient's stay, this form outlines the patient's progress, final assessments, medications prescribed upon discharge, and follow-up care instructions.
- Incident Report Form: This form is completed when an unexpected event occurs that impacts patient safety, such as a fall or medication error. It documents the incident and is used for quality improvement purposes.
- Care Plan: A care plan is developed collaboratively by the healthcare team to outline specific goals and interventions for patient care. It is continually updated based on the patient’s status.
- Patient Transfer Form: This document facilitates the safe transfer of a patient from one unit or facility to another. It includes relevant details about the patient’s condition and care needs during the transfer process.
- Advance Directive Form: Patients may complete this form to outline their wishes regarding medical treatment in case they become unable to communicate their decisions. It provides important guidance for healthcare providers and family members.
Incorporating these documents into patient management helps streamline care processes and enhances communication among healthcare professionals. They support the delivery of comprehensive and coordinated care while placing a strong emphasis on patient safety and satisfaction.
Similar forms
The Sheet Telemetry form serves as a comprehensive tool for monitoring and documenting patient information in a telemetry unit. Here are six documents that are similar to this form, each playing a crucial role in patient care and information management:
- Nursing Assessment Form: Like the Sheet Telemetry form, the Nursing Assessment Form collects vital patient information upon admission. Both documents encompass aspects such as patient history, current medications, and physical assessments. They aim to provide a clear and organized view of a patient’s condition.
- Flow Sheet: Flow sheets are used to record ongoing assessments and data points during a patient's stay. Similar to the telemetry form, these documents emphasize tracking changes in vital signs, lab results, and other relevant information over time.
- SBAR Communication Tool: The SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) tool facilitates communication among healthcare team members. It complements the telemetry form by structuring key pieces of information, fostering clear and efficient discussions regarding patient care.
- Interdisciplinary Care Plan: This document outlines the collaborative plan of care for the patient. The Sheet Telemetry form contributes to this plan by detailing specific medical and nursing assessments, ensuring all team members are informed of essential updates.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): The MAR tracks all medications administered to patients. Like the telemetry form, it is vital for ensuring safety and efficacy in medication management by providing a comprehensive overview of medication types, dosages, and timing.
- Patient Discharge Summary: This summary provides essential information at a patient's discharge, including diagnosis, treatments received, and follow-up care. The telemetry form supports this document by documenting the patient’s journey and status throughout their hospital stay, ensuring continuity of care.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Sheet Telemetry form, there are key practices to follow. Keeping these in mind can enhance clarity and accuracy. Here are five essential dos and don'ts:
- Do fill in all relevant patient information completely.
- Do use clear and legible handwriting or type to ensure readability.
- Do double-check your entries for accuracy before submitting the form.
- Don't leave any mandatory fields blank, as this can lead to confusion.
- Don't use abbreviations that may not be universally understood by all healthcare providers.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The Sheet Telemetry form is only used for heart-related patients.
- Misconception 2: The form is only relevant during the initial admission process.
- Misconception 3: Completion of the form is the sole responsibility of the attending physician.
- Misconception 4: All information on the form is mandatory.
- Misconception 5: The Sheet Telemetry form is static and does not change.
- Misconception 6: Electronic versions of the form are more reliable than paper copies.
This form is designed for a variety of patients requiring telemetry monitoring, not just those with heart conditions. It includes sections for neurological, respiratory, and other medical concerns.
The Sheet Telemetry form is utilized throughout a patient's stay. It serves as a daily reference for monitoring and updating patient information, treatment plans, and care goals.
While physicians do play a key role, other healthcare professionals contribute to filling out the form. Nurses, therapists, and other team members actively provide information based on their interactions with the patient.
Although many sections require data, some areas can be filled out as needed. The primary goal is to capture essential patient information to facilitate effective care.
The form can evolve based on updated practices or specific unit needs. Regular reviews may lead to modifications that enhance its usability and relevance in patient care.
Both electronic and paper versions serve the same purpose. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the environment and the workflows of healthcare facilities.
Key takeaways
- Complete All Sections: Ensure that every field on the Sheet Telemetry form is filled out completely. Missing information can lead to misunderstandings regarding the patient's condition and treatment plan.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: When recording patient information, use straightforward language. This helps in maintaining clarity for all healthcare professionals who will review the form.
- Collaborate with Team Members: Utilize the SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) format to communicate effectively with colleagues. Share insights about the patient’s condition and treatment in a structured and organized manner.
- Document Changes Promptly: Any changes in the patient’s status should be immediately noted on the form. Timely documentation ensures that all team members are aware of any fluctuations in the patient’s health.
- Review Regularly: Routine check-ins and reviews of the Sheet Telemetry form throughout the shift can help catch missed details or changes in the patient's condition, thereby supporting better patient care.
- Employ a Standardized Approach: Consistency in filling out the form can minimize errors. Following a standardized procedure ensures that all necessary information is always captured, facilitating better communication across the care team.
Browse Other Templates
Employment Clearance Sample - Sign the clearance form to confirm your responsibilities have been met.
What Happens When You Report an Attorney to the Bar - The Client Security Fund may offer some reimbursement for losses due to attorney dishonesty.
Cvi Certificate of Veterinary Inspection - Veterinarians should be aware of the responsibilities related to this form.