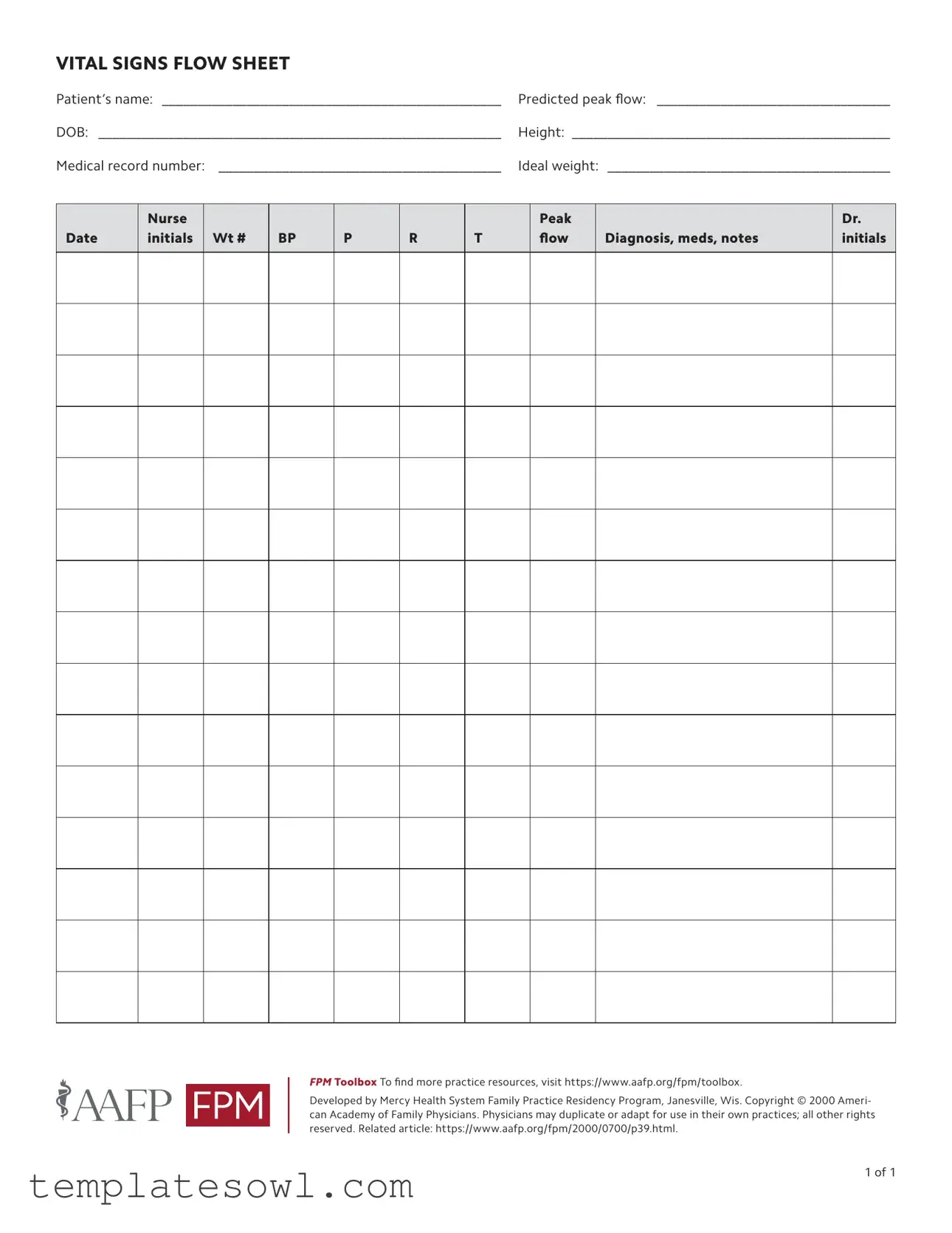
Fill Out Your Vital Signs Flow Sheet Form
In the world of healthcare, monitoring a patient’s vital signs is crucial for providing effective care and understanding their overall health status. The Vital Signs Flow Sheet serves as an essential tool in this process, allowing healthcare professionals to efficiently record and track important health metrics over time. This form collects fundamental patient information such as the patient's name, date of birth, height, and medical record number, which helps ensure accurate documentation. Along with basic identifiers, the form includes sections for recording weight, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, temperature, and predicted peak flow values. This ongoing log not only serves as a snapshot of a patient's current condition but also aids in diagnosing potential health issues and tracking the effectiveness of treatment plans. Physicians and nurses can make swift decisions based on the notes and medication listed, contributing to better patient outcomes. Developed by the Mercy Health System Family Practice Residency Program, this form reflects a commitment to patient care within an organized framework, enhancing healthcare delivery and facilitating communication among care teams.
Vital Signs Flow Sheet Example
VITAL SIGNS FLOW SHEET
Patient’s name: _________________________________________________ |
Predicted peak flow: __________________________________ |
DOB: __________________________________________________________ |
Height: _____________________________________________ |
Medical record number: _ ________________________________________ |
Ideal weight: _________________________________________ |
Date
Nurse initials
Wt #
BP
P
R
T
Peak flow
Diagnosis, meds, notes
Dr. initials
FPM Toolbox To find more practice resources, visit https://www.aafp.org/fpm/toolbox.
Developed by Mercy Health System Family Practice Residency Program, Janesville, Wis. Copyright © 2000 Ameri- can Academy of Family Physicians. Physicians may duplicate or adapt for use in their own practices; all other rights reserved. Related article: https://www.aafp.org/fpm/2000/0700/p39.html.
1 of 1
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Form Purpose | The Vital Signs Flow Sheet is designed to record a patient's vital signs and other relevant health metrics over time. |
| Patient Information | The form requires essential patient details, including name, date of birth, height, medical record number, and ideal weight. |
| Vital Signs Tracked | The flow sheet tracks weight, blood pressure (BP), pulse (P), respiration (R), temperature (T), and peak flow. |
| Documentation by Healthcare Provider | Nurse initials must be recorded alongside vital signs to ensure accountability and traceability. |
| Diagnosis and Notes Section | The form includes a space for documenting the diagnosis, prescribed medications, and any additional notes relevant to the patient’s care. |
| Signature Requirement | Doctor initials are required in the designated section to validate the recorded information and confirm treatment plans. |
| Copyright Information | The form is copyrighted by the American Academy of Family Physicians, allowing duplication and adaptation by physicians for their practices. |
| Practice Resources | A link to additional practice resources is provided: https://www.aafp.org/fpm/toolbox. |
| Related Article | A related article can be found at https://www.aafp.org/fpm/2000/0700/p39.html for further information on the use of the form. |
Guidelines on Utilizing Vital Signs Flow Sheet
To effectively fill out the Vital Signs Flow Sheet form, you'll need to provide specific information about the patient accurately. This will help healthcare professionals monitor health indicators and track changes over time.
- Start by entering the patient’s **name** in the designated field.
- Fill in the **predicted peak flow** value, which indicates the maximum speed at which a person can exhale.
- Input the patient’s **date of birth (DOB)** to confirm their age.
- Record the patient’s **height** in the space provided.
- Include the **medical record number** to easily reference the patient’s health history.
- Write down the patient’s **ideal weight** based on established medical guidelines.
- Enter the **date** you are filling out the form to maintain accurate records.
- Indicate your **initials** as the nurse filling out the form.
- Provide the **weight** of the patient at the time of assessment.
- Record the **blood pressure** (BP) reading in the appropriate sections.
- Document the **pulse** (P) rate to monitor heart activity.
- Enter the **respiratory rate** (R) to check breathing status.
- Note the **temperature** (T) for an indication of the patient's overall health.
- Fill in the **peak flow** reading based on the patient’s optimal airflow.
- Under **diagnosis, medications, and notes**, provide any relevant health information and medical history.
- Finally, record your **initials** as the doctor who reviews this form.
Once you have completed all sections of the form, ensure that the information is legible and accurate before submitting it into the patient’s medical record. This will help healthcare providers make informed decisions based on the patient’s vital signs and health status.
What You Should Know About This Form
1. What is a Vital Signs Flow Sheet?
A Vital Signs Flow Sheet is a structured document used by healthcare professionals to record and monitor a patient's vital signs over time. This includes important measurements such as weight, blood pressure, pulse, respiration rate, temperature, and peak flow. This tool aids in tracking a patient's health status and response to treatment.
2. How do you fill out the form correctly?
To fill out the Vital Signs Flow Sheet, start by entering the patient's name, date of birth, height, and medical record number at the top of the form. Each time vital signs are checked, record the values in the appropriate columns, along with the date and nurse's initials. The box for diagnosis, medications, and notes is for additional information relevant to the patient’s care, and you must ensure that a physician’s initials are included after entries are made.
3. Why is it important to monitor vital signs?
Monitoring vital signs is crucial because these measurements provide immediate insights into a patient's health. Changes in vital signs can indicate improvements or deteriorations in a patient's condition, allowing for timely interventions. Regular tracking helps healthcare providers make better-informed decisions regarding treatments and necessary follow-ups.
4. What does each column in the flow sheet represent?
Each column on the flow sheet represents different vital signs and related information. The 'Wt #' column stands for weight. 'BP' signifies blood pressure, while 'P' stands for pulse rate. 'R' denotes respiration rate, 'T' is temperature, and 'Peak flow' measures the maximum speed of expiration. The 'Diagnosis, meds, notes' column is for any relevant patient information or treatment plans, while the 'Dr. initials' column confirms a physician has reviewed the entries.
5. Can the Vital Signs Flow Sheet be reused?
Yes, the Vital Signs Flow Sheet can be duplicated or adapted for use in other practices by healthcare providers. However, specific rights are reserved, so it is crucial that only authorized personnel make copies or alterations to the form.
6. How often should the flow sheet be updated?
The flow sheet should be updated each time vital signs are taken. This could be during routine check-ups, hospital visits, or whenever a patient is assessed as part of their treatment plan. Consistent updates ensure an accurate history of the patient's health and treatment responses.
7. Where can I find additional resources related to the Vital Signs Flow Sheet?
Additional resources can be found in the FPM Toolbox on the American Academy of Family Physicians website. This site provides valuable practice resources that can assist healthcare professionals in better managing patient care and utilizing tools like the Vital Signs Flow Sheet effectively.
8. What happens if there is an error on the Vital Signs Flow Sheet?
If an error is identified on the flow sheet, it should be corrected immediately. Strikethrough the incorrect entry and write the correct information beside it. Initial the change to document accountability. This practice helps maintain the integrity of the patient’s medical records.
9. Is training required to use the Vital Signs Flow Sheet?
While formal training may not be mandatory, healthcare professionals should be familiar with how to accurately measure vital signs and complete the flow sheet. Understanding the form’s layout and purpose is essential for proper documentation and effective patient monitoring.
10. Can patients see their Vital Signs Flow Sheet?
Yes, patients have the right to access their medical records, including the Vital Signs Flow Sheet. Providing patients with their data fosters transparency in healthcare and encourages them to take an active role in their treatment and health management.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Vital Signs Flow Sheet form accurately is essential for providing quality patient care. However, there are common mistakes that individuals often make, which can have significant implications. One of the most frequently encountered errors occurs when the patient’s name is not filled in completely or correctly. It might seem minor, but any mismatch can lead to confusion and miscommunication regarding patient records and treatments.
Another mistake involves omitting critical information such as the date of birth or medical record number. These details are essential for tracking the patient's medical history and ensuring that the right measurements are associated with the correct individual. Leaving these fields blank can complicate the process of retrieving past treatments or medications.
Sometimes, practitioners forget to include vital signs like blood pressure or heart rate. Each measurement is important for understanding a patient's overall health status. If these details are not recorded, there may be gaps in the patient's health profile that could mislead medical decisions.
Additionally, it's crucial to ensure that the recorded values are accurate. For example, when documenting the weight, blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and temperature, errors can easily occur if the measurements are taken hurriedly or carelessly. Always double-check numbers to confirm they reflect reality.
Another common oversight is neglecting to include the nurse's or doctor's initials next to their respective entries. Initials help identify who took the measurements and who is responsible for the information recorded. This is vital for accountability and fosters better communication among healthcare professionals.
Finally, misunderstanding the significance of the peak flow measurement leads to errors in documenting this important metric. Properly recorded peak flow values help in assessing a patient's respiratory status, particularly for those with asthma. Skipping this measurement or failing to interpret it correctly can overlook critical signs that require attention.
Documents used along the form
In a healthcare setting, the Vital Signs Flow Sheet is essential for tracking a patient's vital statistics. However, several other forms and documents complement this flow sheet, contributing to comprehensive patient care and management. Below is a list of common forms often used alongside the Vital Signs Flow Sheet.
- Patient Intake Form: This document gathers important information about the patient's medical history, current medications, allergies, and lifestyle habits. It ensures that healthcare providers have a comprehensive understanding of the patient's health at the outset.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): This form tracks the medications prescribed to a patient, including dosages and administration times. It helps prevent medication errors and ensures that patients receive the correct treatments.
- Progress Notes: Healthcare providers use progress notes to document a patient's ongoing condition and treatment plan. These notes provide a chronological record of the patient's health, enabling any medical professional to understand the patient's journey.
- Discharge Summary: Created when a patient is discharged from a facility, this document summarizes the patient's treatment during hospitalization, including key findings and follow-up care instructions. It is crucial for continuity of care.
- Consent for Treatment Form: This form ensures that a patient or their guardian provides informed consent for specific medical procedures or treatments. It protects both the patient and the provider by confirming that the patient understands the risks and benefits involved.
- Advance Directive: An advance directive outlines a patient's wishes regarding medical treatment in the event they become unable to communicate. This document is vital for guiding healthcare decisions aligned with the patient’s values.
- Referral Form: This form is used to refer a patient to a specialist for further evaluation or treatment. It typically contains pertinent information about the patient's condition and any necessary supporting documents.
- Lab Results Report: This document provides the results of laboratory tests performed on the patient. Lab results are crucial for diagnosis and treatment planning, ensuring that healthcare providers can make informed decisions based on data.
These forms and documents collectively enhance patient care, ensuring thorough documentation, informed decision-making, and smooth communication among healthcare providers. Each plays a specific role in promoting effective treatment and ensuring that patient needs are met holistically.
Similar forms
The Vital Signs Flow Sheet captures a range of essential patient data. Its design and purpose are similar to the following documents:
- Patient Assessment Form: This form collects comprehensive patient information, including medical history and physical examination results. Like the Vital Signs Flow Sheet, it also provides a framework for recording ongoing observations.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): The MAR tracks the administration of medications to patients. Both documents serve as key tools for monitoring and ensuring patient safety during treatment.
- Daily Nursing Progress Notes: Nurses document their daily observations and care provided in these notes. Similar to the Vital Signs Flow Sheet, this document tracks patient status over time.
- Clinical Pathway Document: This outlines the expected course of treatment for specific conditions. The flow sheet aligns with it by recording vital signs that inform the clinical pathway's effectiveness.
- Patient Care Plan: This plan details the strategies for addressing a patient's health needs. Both documents share the goal of ensuring comprehensive care through consistent monitoring.
- Discharge Summary: The discharge summary summarizes the patient's hospital stay, including vital signs and treatment responses. This is similar to the flow sheet’s role in tracking pertinent data during care.
- Encounter Form: This document records services provided during a patient visit. Both the encounter form and the flow sheet help ensure continuity of care by maintaining clear records of patient interactions.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Vital Signs Flow Sheet form, there are important guidelines to follow. Here’s a helpful list of things you should and shouldn’t do:
- Do write legibly to ensure all information is easily readable.
- Do fill in all required fields, including patient's name and medical record number.
- Do double-check your entries for accuracy before submitting.
- Do use appropriate units for measurements, such as pounds for weight and mmHg for blood pressure.
- Do include observations and notes that may assist in patient care.
- Don't leave any blanks unless specifically instructed.
- Don't use abbreviations that may be confusing to others.
- Don't alter the form in any way that changes the intended format.
- Don't forget to sign and date the form to validate the information provided.
Misconceptions
Many people have misunderstandings about the Vital Signs Flow Sheet form. Here are eight common misconceptions:
- It's Only for Certain Patients: Some think this form is only necessary for specific conditions. In reality, it’s useful for monitoring any patient's vital signs over time.
- One Size Fits All: People often believe one form fits every situation. Each patient requires individual attention, so the flow sheet can be customized to track specific needs.
- It's Only Used in Hospitals: Many assume it's only relevant in hospital settings. However, this form is valuable in various healthcare environments, including clinics and private practices.
- It's Just a Checklist: Some view it merely as a checklist. In fact, it serves as a comprehensive tool for recording and assessing patient data to inform care decisions.
- Only Nurses Use It: There’s a belief that only nurses complete this form. Physicians and other healthcare professionals often reference and utilize it, too.
- Once Completed, It’s No Longer Relevant: People may think the information loses its value after being filled out. This form is meant for ongoing tracking, helping to identify trends over time.
- It’s Just about Numbers: Some believe it only involves capturing numerical data. The flow sheet also includes space for notes and observations, which are critical for patient context.
- Data Doesn’t Need to Be Updated: A common myth is that once the sheet is filled, it doesn’t require changes. Regular updates are essential to reflect the patient's current status accurately.
Understanding these misconceptions can lead to better use of the Vital Signs Flow Sheet and ultimately improve patient care.
Key takeaways
Utilizing the Vital Signs Flow Sheet form effectively can enhance patient monitoring and improve healthcare delivery. Here are some key takeaways to consider:
- The form requires essential patient information, including name, date of birth, and height. Accurate input is crucial.
- It is important to record the patient’s weight and vital signs regularly in the designated columns. This tracking allows for better evaluation of the patient's health over time.
- Ensure that the predicted peak flow and ideal weight sections are filled out. These metrics can provide insights into respiratory health and overall nutrition status.
- Each entry should be initialed by the nurse and the attending physician for accountability and clarity. This habit promotes accurate communication within the healthcare team.
- Any relevant diagnosis, medications, and notes should be documented in the form. This inclusion helps in maintaining a comprehensive patient history.
- Resources for further practice and utilization of the form are available at the FPM Toolbox online. This can assist in improving the use of the Vital Signs Flow Sheet within the practice.
Browse Other Templates
Forever 21 - Ensure your application represents your best professional self.
Lincoln Financial Distribution Request Form Pdf - If you're unsure about your distribution reason, consult the Lincoln website.
Tractor Inspection Checklist - The role of the inspector is vital to the safety and preparedness of the tractor for use.